
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321948908
Author: Mark F. Sanders, John L. Bowman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 19, Problem 17P
Consider this human pedigree for a vision defect.
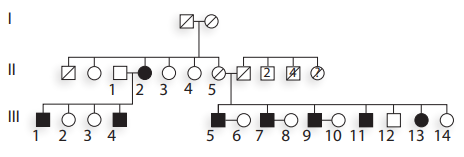
What is the most probable mode of inheritance of the disease? Identify any discrepancies between the pedigree and your proposed mode of transmission, and provide possible explanations for these exceptions.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Consider a Droscophilia fly with a genotype of Nn XqYY. The dominant allele of the sex-linked gene specifies a black body and the recessive a white body. The recessive autosomal allele specifies hairy bristles while the dominant allele specifies smooth bristles.
i)What is the ploidy of this fly?
ii) What would the sex of this fly be?
iii)What would the phenotype of this fly be with respect to these two loci?
Compare and contrast the molecular and phenotypic features of Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes.
Over a thousand different alleles at the CFTR locus have been discovered that can cause cystic fibrosis. What difficulties might the presence of so many different alleles at this locus create for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic fibrosis?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
Ch. 19 - 17.1 Reciprocal crosses of experimental animals or...Ch. 19 - 17.2 How are some of the characteristics of the...Ch. 19 - 17.3 The human mitochondrial genome encodes...Ch. 19 - What is the evidence that transfer of DNA from the...Ch. 19 - Draw a graph depicting the relative amounts of...Ch. 19 - Prob. 6PCh. 19 - 17.7 What is the evidence that the ancient...Ch. 19 - 17.8 Outline the steps required for a gene...Ch. 19 - 17.9 Consider the phylogenetic tree presented in...Ch. 19 - Most large protein complexes in mitochondria and...
Ch. 19 - What insights have analyses of human mitochondrial...Ch. 19 - You are a genetic counselor, and several members...Ch. 19 - A mutation in Arabidopsis immutans results in the...Ch. 19 - What type or types of inheritance are consistent...Ch. 19 - You have isolated (1) a streptomycin-resistant...Ch. 19 - You have isolated two petite mutants, pet1 and...Ch. 19 - 17.15 Consider this human pedigree for a vision...Ch. 19 - A 50- year - old man has been diagnosed with MELAS...Ch. 19 - 17.17 The first person in a family to exhibit...Ch. 19 - Prob. 20PCh. 19 - Prob. 21PCh. 19 - 17.19 What is the most likely mode of inheritance...Ch. 19 - 17.20 In , the Russian Tsar Nicholaswas deposed,...Ch. 19 - 17.21 The dodo bird (Raphus cucullatus) lived on...Ch. 19 - Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) in plants has...Ch. 19 - 17.23 Wolves and coyotes can interbreed in...Ch. 19 - Prob. 27PCh. 19 - Prob. 28P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- We often speak of diseases such as phenylketonuria (PKU) andachondroplasia as having a genetic basis. Explain whether the followingstatements are accurate with regard to the genetic basis ofany human disease (not just PKU and achondroplasia).A. An individual must inherit two copies of a mutant allele to havedisease symptoms.B. A genetic predisposition means that an individual has inheritedone or more alleles that make it more likely that she or he willdevelop disease symptoms than other individuals in a populationwill.C. A genetic predisposition to develop a disease may be passedfrom parents to offspring.D. The genetic basis for a disease is always more important thanthe environment.arrow_forwardNiemann Pick Type C disease is a recessive disorder that causes the accumulation of cholesterol and other lipids in lysosomes, ultimately affecting both the liver and the nervous system. Below are the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring of a family with a history of Niemann Pick. 7 NN ( all normal phenotype) 3 Nn (all normal phenotype) 4 nn (1 early onset dementia, 1 mid-life onset dementia, 2 late-onset dementia). From this information, Niemann-Pick disease is an example of: A) variable expressivity B) incomplete dominance C) incomplete penetrance D) variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance E) multiple allelesarrow_forwardRegarding albinism, discuss some social and environmental implications of the genetic disorder.arrow_forward
- Determine what is the most likely mode of inheritance of this disease (whether it is inherited as the result of an X-linked dominant or X-linked recessive trait). Use "A" for the allele associated with the dominant phenotype, and lowercase "a"" for the allele associated with the recessive phenotype. Write the most probable genotype for each individual based on the mode of inheritance you have determined. Show how all the partners are crossed and the expected offspring produced (You may use Punnett Square). OT I OT do IIarrow_forwardA man and a woman have a child with cystic fibrosis. Neither parent has cystic fibrosis. How could this happen? a) Both parents carry the cystic fibrosis allele, and each passed that allele to their child. b) The child had a spontaneous mutation on both copies of their CFTR alleles, leading to cystic fibrosis. c) One parent gave the child two copies of the cystic fibrosis CFTR allele. c) One parent gave the child a wild type CFTR allele, and the other parent gave them a cystic fibrosis CFTR gene.arrow_forwardWhile sitting at home during Movement Control Order (MCO) because of pandemic covid19, observe two different traits of a couple in your family (eg. your mom & dad or your sister & her husband or your brother & his wife, etc). Draw a genetic cross that involves cross of the parents with the chosen 2 pairs of their contracting traits. Imagine that the cross obeys the Mendelian Laws, show the cross and gametes production for each generation (P, F1 and F2). By Using a Punnet square as symbolic representation of the results for the cross, determine the phenotypes, genotypes, phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio of F2 generation in the family.arrow_forward
- Please find an Image/Graphic to represent sickle cell disease: Use at least two different images to help the audience understand the cause and/or inheritance pattern of the disorder you chose. Include a brief 1-2 sentence caption below each image that gives a description of the image and explains its relevance to your chosen disorder. The two images should NOT convey the same exact information. Ideas of images to use include: karyotypes, pedigrees, DNA sequences, etc. Please note: the images should be specific to your chosen disorder. The 2 required images must be related to cause and/or inheritance pattern. Images of an individual with the disorder will not count toward your 2 required images as they do not contribute to the audience's understanding of cause and/or inheritance pattern.arrow_forwardPKU is an inherited disease caused by a recessive allele. If a woman and her husband, who are both carriers (heterozygotes) for the disorder, have three children, what is the probability of each of the following? a) All three children are of normal phenotype. b) All three children have the disease. c) Any 2 of the three children have the normal phenotype.arrow_forwardFor the following question, please explain in as much detail as possible. Below is a human pedigree and corresponding RFLP data. Explain the type of transmission for the type of albinism depicted in this family. What does the pedigree tell you about the individual labeled Y's genotype? There are two genes known to cause this type of albinism found in this family: OCA1 and OCA2. If we know 1 (albino great grandmother) had mutation in OCA1 which gene would you hypothesize is mutated in individual Y's genome? Explain your reasoning. generations Key: D ở abino Ped. III2 II13 IV1 IV 2 IV3 IV4 IV5 IV6 III13 III14 IV 15 IV16 IV17 ID (P) (Q) (X) (Y) Band size 20kb 15kb X 12kb 10kb X X 8kb X X X 5kb X X X X X X X X 3kb 2kbarrow_forward
- The karyotypes shown here depict chromosomal abnormalities. Name the syndromes and if they are male or female?arrow_forwardGiven the karyotype shown at right, is this a male or a female? Normal or abnormal? What would the phenotype of this individual be?arrow_forwarda) explain why a diagnosis of ASD is not possible in young babies. b) Given the current understanding of the concordance of ASD, if one of the children detected in these data was an identical twin, how certain is that the other twin would also meet the diagnostic criteria for ASD?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY