
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation : To classify the given saccharide as mono, di, tri or polysaccharide.
Concept Introduction : Carbohydrates are composed of certain monomer units called as monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy
(a)
Answer to Problem 75UTC
Melezitose is a tri-saccharide as it is composed of three monosaccharide units.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
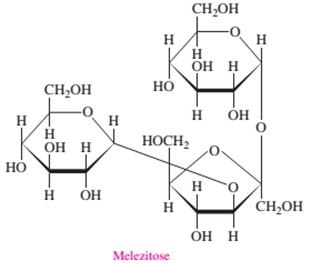
In the given structure of molecule there are three sugar molecules bonded with each other. Hence there are three monosaccharide units bonded to each other by two glycosidic linkages that make it a tri-saccharide molecule.
(b)
Interpretation : To identify the keto and aldohexose present in melezitose.
Concept Introduction : Carbohydrates are composed of certain monomer units called as monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehyde and ketones which are bonded with each other to form polysaccharides.
(b)
Answer to Problem 75UTC
Melezitose is composed of two aldohexose (glucose) and one ketohexose (fructose) units.
Explanation of Solution
In the given structure of molecule there are three sugar molecules; out of which two are pyranose rings with total 6 C atoms hence they should be aldohexose monosaccharides whereas one is furanose ring bonded with two −CH2OH groups at both terminals that proves it as a ketohexose. Hence Melezitose is composed of two aldohexose and one ketohexose units.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Basic Chemistry
- Please help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forward
- Draw the productsarrow_forwardDraw the correct productsarrow_forwardE Organic Chemistry Maxwell Draw the correct products, in either order, for the ozonolysis reaction: 1) O3, CH2Cl2, -78 °C Product 1 + Product 2 2) Zn, HOAc Draw product 1. Select Draw Templates More C H O presented by M Draw product 2. Erase Select Draw Templates M / # # carrow_forward
- ✓ edict the products of this organic reaction: ---- ။ A CH3–C−NH–CH2–C−CH3 + KOH ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. C 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibiliarrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: A HO-C-CH3 + CH3NH2 P+ H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. marrow_forwardH 1) OsO4, pyridine 2) Na2SO3 or NaHSO3 in H₂O 2 productsarrow_forward
- ● Biological Macromolecules Naming and drawing cyclic monosaccharides Your answer is incorrect. • Row 1: Your answer is incorrect. Row 3: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 4: Your answer is incorrect. Try again... 0/5 Give the complete common name, including anomer and stereochemistry labels, of the following molecules. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS resource. CH2OH OH OH H H I H OH OH H] H CH2OH H OH ẞ-L-sorbose HOCH2 OH OH H HOCH2 H OH OH H OH H H CH2OH OH H H OH H I- H OH H OH Explanation Recheck W E R % 25 α B Y X & 5 D F G H McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Pr Parrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? + R -A HO IN + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forwardStuc X ctclix ALE X A ALE אן A ALEX Lab (195 X Nut x M Inb x NU X NUT X Unt x + → C www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQ1g8NUi-mObKa_ZLx2twjEhK7mVG6PulJI006NcKTV37JxMpZuyrVCdQolLAKqp_7U3r1GUD3... New Chrome available: Naomi Question 26 of 39 (4 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited Give the IUPAC name. 2,3-dimethylhexane Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of a constitutional isomer of the alkane above that contains a different number of carbons in its longest chain. Skip Part Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 3 Finance headline Q Search mwa Harvard Intensifi... X Save For Later 00 dlo HB Submit Assignment 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility a 9:11 PM 4/22/2025arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



