
Concept explainers
The method in which the distance measurement of star is similar to human binocular vision.
Explanation of Solution
Consider an object at point A. Observe it from points B and C some distance apart. The position of Object at A appears different from two points.
This apparent change in position of the object due to change in point of the observer is called parallax. The parallax is also the angle opposite to baseline that lines AC and BC make with the line AD. Binocular vision is the method of measuring distance by naked eye.
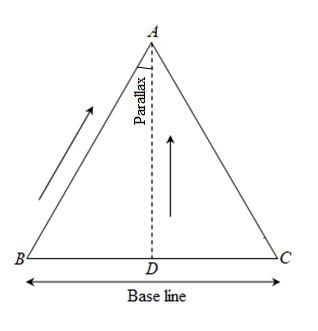
To measure the distance of any astronomical object requires a very large baseline and highly precise angular measurements. Due to revolution of Earth around Sun, the direction of a nearby stars changes from Earth.Nearby stars appear to move back and forth relative to more distant stars and the motion knownas stellar parallax.
Relation between a star’s distance and its parallax:
Here,
The parallax of a star is half of the angle through which star shift.The larger the parallax p, the smaller is the distance d to the star.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Universe: Stars And Galaxies
- A man slides two boxes up a slope. The two boxes A and B have a mass of 75 kg and 50 kg, respectively. (a) Draw the free body diagram (FBD) of the two crates. (b) Determine the tension in the cable that the man must exert to cause imminent movement from rest of the two boxes. Static friction coefficient USA = 0.25 HSB = 0.35 Kinetic friction coefficient HkA = 0.20 HkB = 0.25 M₁ = 75 kg MB = 50 kg P 35° Figure 3 B 200arrow_forwardA golf ball is struck with a velocity of 20 m/s at point A as shown below (Figure 4). (a) Determine the distance "d" and the time of flight from A to B; (b) Determine the magnitude and the direction of the speed at which the ball strikes the ground at B. 10° V₁ = 20m/s 35º Figure 4 d Barrow_forwardThe rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forward
- A particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be (F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the y and z component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardneed answer asap please thank youarrow_forward3. a. Determine the potential difference between points A and B. b. Why does point A have a higher potential energy? Q = +1.0 C 3.2 cm 4.8 cm Aarrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning





