
Concept explainers
In order to determine the mass moment of inertia of a flywheel of radius 600 mm, a 12-kg block is attached to a wire that is wrapped around the flywheel. The block is released and is observed to fall 3 m in 4.6 s. To eliminate bearing friction from the computation, a second block of mass 24 kg is used and is observed to fall 3 m in 3.1 s. Assuming that the moment of the couple due to friction remains constant, determine the mass moment of inertia of the flywheel.
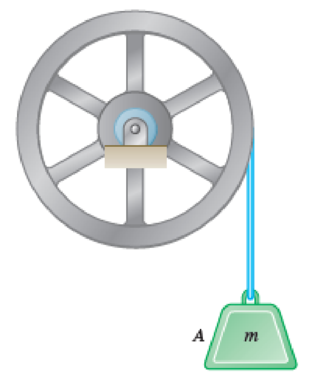
Fig. P16.32 and P16.33
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals and Applications
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
- A disk with radius R and mass m begins from rest and then moves without slipping while being pulled horizontall by a force P acting at its center axle. Show that the velocity of the wheel after T seconds is v= 2PT/3m. (Hint: use both linear and angular-impulse principles.) m REG P ¹The radius of gyration has units of length and is related to the inertia by k = IG/m. It corresponds to the distance at which a mass equivalent to the mass of the rigid body would produce the same inertia as the actual rigid body. Recall that the inertia of a particle of mass m at a distance r from an axis of ortation is mr². Rather that using r the convention is to define the radus of gyration with the symbol k.arrow_forwardA disk with mass m and radius R is released from rest at a height h and rolls without slipping down a ramp. What is the velocity of the center of the disk when it reaches the bottom of the slope? (Hint Use the work-energy principle. At each instant the disk rotates around the contact point C, thus the inertia used for rotatonal kinetic energy should be computed around point C not point G.) m C harrow_forwardThe space capsule has no angular velocity when the jet at A is activated for 1 s in a direction parallel to the axis. Knowing that the capsule has a mass of 1000 kg, that its radii of gyration are Kz=Ky =1.00m and Kz=1.25m A produces a thrust of 50 N, determine the axis of precession and the rates of precession and spin after the jet has stopped.arrow_forward
- 3arrow_forwardProblem 2: The drum shown weighs 80lb and has a mass moment of inertia about O of 0.8 lb.ft?. Starting from rest, the cable wrapped around the drum is subjected to a vertical force P which resulted in a constant angular acceleration of 20 rad/s². Determine magnitude of P and the reaction at the support pin at O. Neglect the mass of the cable 0.5 fiarrow_forwardPractice Problem In the mechanism shown, link 3 has a mass of 5 kg, and polar mass moment of inertia of 0.02 kg.m2 about its center of mass (G3). Sliding block 2 is moving upward. 250 Determine the instantaneous force F required to produce this motion assuming that the slider blocks are massless. 09 = BD=25 cm BG3=10 cm, ac,=8 m/s2, a3=35 rad/s? cwarrow_forward
- A 5-kg homogeneous disk with a radius of 0.2 m is connected to a spring (k=50 N/m) as shown. At the instant shown (position 1), the spring is undeformed. The disk is released from rest and rolls without slipping to position 2, which is 0.1 m down the 25-degree incline. A clockwise constant 2 N-m couple is applied to the disk as it rolls down the inclined surface. Note: I disk = mR²2 2 N-m 0.2 5-kg 25° k = 50 N/m 10000000 1. Which of the following forces does negative work on the system? Friction between the disk and the inclined surface + x Mark 0.00 out of 20.00 2. Which of the following best approximates the magnitude of the work done by the spring? 0.250 J + ✓ 3. Which of the following best approximates the work done by the 2 N-m couple? -1.000 J + ✓ 4. Which of the following gives the correct expression of the kinetic energy of the system at position 2 in terms of the disk's angular velocity, w₂? 0.15 w2*2 + 4.53 rad/s + x 5. Which of the following best approximates the magnitude…arrow_forwardThe 30-kg reel is mounted on a 20 kg cart. The reel is free to rotate about the axle O. The radius of gyration, kO, about the mass center, O, is 250 mm and a cable is wrapped around the inner hub of the wheel. The mass of the wheels on the cart and the mass of the cable may be neglected. The system is at rest when a force, P, of 50 N is applied to the end of the cable. a) Determine the velocity of the cart after 4 seconds m/s b) determine the angular velocity of the reel, in rad/s. [Correct answers are a) 4.0 m/s b) 16 rad/sarrow_forwardPlease show all steps.arrow_forward
- Each arm of a Proell governor is 240 mm long and each rotating ball has a mass of 3 kg. The central load acting on the sleeve is 30 kg. The pivots of all the arms are 30 mm from the axis of rotation. The vertical height of the governor is 190 mm. The extension links of the lower arms are vertical height of the governor speed is 180 r.p.m when the sleeve is in the mid-position. Determine the lengths of the extension links and the tension in the upper arms.arrow_forwardA uniform hemisphere of mass m = 5 kg. and radius r = 0.5m. is released from rest on a horizontal surface in the position when OG is horizontal as shown in the figure below. The mass centre G of the hemisphere is at a distance (3/8)r from point O and its mass moment of inertia about O is ( ) 2 1 0 = 2/ 5 mr . If the friction between the hemisphere and the horizontal surface is sufficient to prevent slipping, (3/8)r Hand draw the free body, kinematic and kinetic diagrams for the hemisphere (shown above) showing all the forces and moments acting on it at the initiation of its motionarrow_forwardA bowler sends his ball down the lane with a forward velocity of 10 ft/s and backspin of 12 rad/s. His ball weighs 16 lbs and has a diameter of 10 in. Knowing that a bowling ball has more weight concentrated towards the center, we will estimate the mass moment of inertia as: I = mr². Starting from t, at the moment the ball hits the alley, and knowing the coefficient of friction is 0.10, determine: (a) The time t, when the ball starts to roll forward without sliding (b) The speed of the ball at this time (c) The distance the ball has traveled at this time 00 Voarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





