
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260663778
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.1, Problem 16.19P
The control rod AC is guided by two pins that slide freely in parallel curved slots of radius 200 mm. The rod has a mass of l0 kg, and its mass center is located at point G. Knowing that for the position shown the vertical component of the velocity of C is 1.25 m/s upward and the vertical component of the acceleration of C is 5 m/s2 upward, determine the magnitude of the force P.
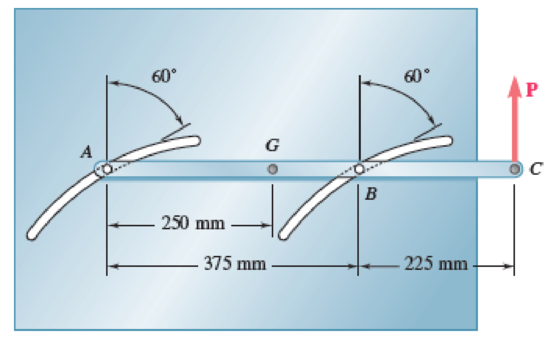
Fig. P16.19
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An elastic bar of the length L and cross section area A is rigidly attached
to the ceiling of a room, and it supports a mass M. Due to the
acceleration of gravity g the rod deforms vertically. The deformation of
the rod is measured by the vertical displacement u(x) governed by the
following equations:
dx
(σ(x)) + b(x) = 0
PDE
σ(x) = Edx
du
Hooke's law
(1)
b(x) = gp=
body force per unit volume
where E is the constant Young's modulus, p is the density, and σ(x) the
axial stress in the rod.
g
* I u(x)
L
2
متوسعة الفرج بو عمامة المستوى رم
الواجب المنزلي رقم
04
تمرین الوان
حسب يتمعن العبارات الأتية :
A= (+2)+(-45) B=(+13)-
C = (+17)-(+13)-(-20)+(-19
D= [(-15)-(+15)]-[(+20) +
هست قیم مدرج مبدؤه النقطة
ة الطول
:tcm
A(-2,5): B(+ 2,5) ≤ C (+5)
المسافتين : BAD
ين الثاني
لمستوي مبدؤه 8 وحدته
Please do not rely too much on AI, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer!!!!! You can borrow ideas from AI, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! ( If you write by hand or don't use AI, I'll give you a big thumbs up )
Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!
Chapter 16 Solutions
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two solid cylinders, A and B, have the same mass m...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.1FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.2FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.3FBPCh. 16.1 - The 400-lb crate shown is lowered by means of two...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - A loading car is at rest on a track forming an...
Ch. 16.1 - A 2100-lb rear-wheel-drive tractor carries a 900...Ch. 16.1 - A uniform rod BC of mass 4 kg is connected to a...Ch. 16.1 - A 2000-kg truck is being used to lift a 400-kg...Ch. 16.1 - The support bracket shown is used to transport a...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.8PCh. 16.1 - A 20-kg cabinet is mounted on casters that allow...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.9, assuming that the casters are...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.11PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.12PCh. 16.1 - The retractable shelf shown is supported by two...Ch. 16.1 - Bars AB and BE, each with a mass of 4 kg, are...Ch. 16.1 - At the instant shown, the tensions in the vertical...Ch. 16.1 - Three bars, each of mass 3 kg, are welded together...Ch. 16.1 - Members ACE and DCB are each 600 mm long and are...Ch. 16.1 - A prototype rotating bicycle rack is designed to...Ch. 16.1 - The control rod AC is guided by two pins that...Ch. 16.1 - The coefficients of friction between the 30-lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.21PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.22PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in translation, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - For a rigid body in centroidal rotation, show that...Ch. 16.1 - It takes 10 min for a 2.4-Mg flywheel to coast to...Ch. 16.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 16.1 - The 10-in.-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 10-in.-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 100-mm-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 180-mm-radius disk is at rest when it is...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.30, assuming that the direction of...Ch. 16.1 - In order to determine the mass moment of inertia...Ch. 16.1 - The flywheel shown has a radius of 20 in., a...Ch. 16.1 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a mass moment...Ch. 16.1 - Two disks A and B, of mass mA = 2 kg and mB = 4...Ch. 16.1 - Two disks A and B, of mass mA = 2 kg and mB = 4...Ch. 16.1 - Gear A weighs 1 lb and has a radius of gyration of...Ch. 16.1 - The 25-lb double pulley shown is at rest and in...Ch. 16.1 - A belt of negligible mass passes between cylinders...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.40PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass of 6 kg and an initial angular...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.42PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass mA = 4 kg, a radius rA = 300 mm,...Ch. 16.1 - Disk B is at rest when it is brought into contact...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.45PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.46PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in plane motion, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - A uniform slender rod AB rests on a frictionless...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.49PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.50PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.51PCh. 16.1 - A 250-lb satellite has a radius of gyration of 24...Ch. 16.1 - A rectangular plate of mass 5 kg is suspended from...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.54PCh. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - The 12-lb uniform disk shown has a radius of r =...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.58PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.59PCh. 16.1 - 16.60 and 16.61The 400-lb crate shown is lowered...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.61PCh. 16.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W = 14 lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.63PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.64PCh. 16.1 - A uniform slender bar AB with a mass m is...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.66PCh. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.69, assuming that the sphere is...Ch. 16.1 - A bowler projects an 8-in.-diameter ball weighing...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.72PCh. 16.1 - A uniform sphere of radius r and mass m is placed...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m has a linear...Ch. 16.2 - A cord is attached to a spool when a force P is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.6CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5FBPCh. 16.2 - Two identical 4-lb slender rods AB and BC are...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7FBPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.8FBPCh. 16.2 - Show that the couple I of Fig. 16.15 can be...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender rod of length L = 900 mm and...Ch. 16.2 - A crate of mass 80 kg is held in the position...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender rod of length L = 36 in. and...Ch. 16.2 - In Prob. 16.78, determine (a) the distance h for...Ch. 16.2 - An athlete performs a leg extension on a machine...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.81PCh. 16.2 - A turbine disk weighing 50 lb rotates at a...Ch. 16.2 - The 80-lb tailgate of a car is supported by the...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform rod of length L and mass m is supported...Ch. 16.2 - Three stage lights are mounted on a pipe fixture...Ch. 16.2 - An adapted launcher uses a torsional spring about...Ch. 16.2 - A 4-kg slender rod is welded to the edge of a 3-kg...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.88PCh. 16.2 - The object ABC consists of two slender rods welded...Ch. 16.2 - A 3.5-kg slender rod AB and a 2-kg slender rod BC...Ch. 16.2 - A 9-kg uniform disk is attached to the 5-kg...Ch. 16.2 - Derive the equation MC=IC for the rolling disk of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.93PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.94PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.95PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.96PCh. 16.2 - A 40-kg flywheel of radius R = 0.5 m is rigidly...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.98PCh. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101A drum of 80-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101A drum of 80-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101A drum of 80-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - Gear C has a mass of 5 kg and a centroidal radius...Ch. 16.2 - Two uniform disks A and B, each with a mass of 2...Ch. 16.2 - A single-axis personal transport device starts...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - The center of gravity G of a 1.5-kg unbalanced...Ch. 16.2 - A small clamp of mass mB is attached at B to a...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.115PCh. 16.2 - A 4-lb bar is attached to a 10-lb uniform cylinder...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform rod AB with a mass m and a length of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.118PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.119PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.120PCh. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 8-kg uniform rod AB is attached to a...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform rod ABD is attached to the crank...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The test rig shown was developed to perform...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.127 for = 90. 16.127The test rig...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform slender bar BD is attached to bar...Ch. 16.2 - The motion of the uniform slender rod of length L...Ch. 16.2 - At the instant shown, the 20-ft-long, uniform...Ch. 16.2 - A driver starts his car with the door on the...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.133PCh. 16.2 - The hatchback of a car is positioned as shown to...Ch. 16.2 - The 6-kg rod BC connects a 10-kg disk centered at...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.136PCh. 16.2 - In the engine system shown, l = 250 mm and b = 100...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.137 when = 90. 16.137In the engine...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two disks, each with a mass m and a radius r, are...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender bar AB of mass m is suspended as...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform rod AB, of mass 15 kg and length 1 m, is...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform slender 2-kg bar BD is attached to the...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.147PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.148PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.149PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.150PCh. 16.2 - (a) Determine the magnitude and the location of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.152PCh. 16 - A cyclist is riding a bicycle at a speed of 20 mph...Ch. 16 - The forklift truck shown weighs 3200 lb and is...Ch. 16 - The total mass of the Baja car and driver,...Ch. 16 - Identical cylinders of mass m and radius r are...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.157RPCh. 16 - The uniform rod AB of weight W is released from...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.159RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.160RPCh. 16 - A cylinder with a circular hole is rolling without...Ch. 16 - Two 3-kg uniform bars are connected to form the...Ch. 16 - A crate of mass 80 kg is held in the position...Ch. 16 - The Geneva mechanism shown is used to provide an...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Look at the following description of a problem domain:
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A thin uniform rod of mass m and length 2r rests in a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius r. A moment M = mgr horizontal plane. is applied to the rod. Assume that the bowl is fixed and its rim is in the HINT: It will help you to find the length l of that portion of the rod that remains outside the bowl. M 2r Ꮎ a) How many degrees of freedom does this system have? b) Write an equation for the virtual work in terms of the angle 0 and the motion of the center of mass (TF) c) Derive an equation for the variation in the position of the center of mass (i.e., Sŕƒ) a. HINT: Use the center of the bowl as the coordinate system origin for the problem. d) In the case of no applied moment (i.e., M = 0), derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation e) In the case of an applied moment (i.e., M: = mgr 4 -) derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation. f) Can the angle 0 and…arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forward= The frame shown is fitted with three 50 cm diameter frictionless pulleys. A force of F = 630 N is applied to the rope at an angle ◊ 43°. Member ABCD is attached to the wall by a fixed support at A. Find the forces indicated below. Note: The rope is tangent to the pully (D) and not secured at the 3 o'clock position. a b •C *су G E e d BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 81 cm b 50 cm с 59 cm d 155 cm For all answers, take x as positive to the right and positive upward. At point A, the fixed support exerts a force of: A = + ĴN and a reaction couple of: →> ΜΑ Member CG is in Select an answer magnitude У as k N-m. and carries a force of N.arrow_forward
- The lower jaw AB [Purple 1] and the upper jaw-handle AD [Yellow 2] exert vertical clamping forces on the object at R. The hand squeezes the upper jaw-handle AD [2] and the lower handle BC [Orane 4] with forces F. (Member CD [Red 3] acts as if it is pinned at D, but, in a real vise-grips, its position is actually adjustable.) The clamping force, R, depends on the geometry and on the squeezing force F applied to the handles. Determine the proportionality between the clamping force, R, and the squeezing force F for the dimensions given. d3 d4 R 1 B d1 2 d2 D... d5 F 4 F Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value d1 65 mm d2 156 mm d3 50 mm 45 d4 d5 113 mm 30 mm R = Farrow_forwardA triangular distributed load of max intensity w =460 N/m acts on beam AB. The beam is supported by a pin at A and member CD, which is connected by pins at C and D respectively. Determine the reaction forces at A and C. Enter your answers in Cartesian components. Assume the masses of both beam AB and member CD are negligible. cc 040 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl W A C D -a- B Ул -b- x Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value α 5.4 m b 8.64 m C 3.24 m The reaction at A is A = i+ ĴN. λ = i+ Ĵ N. The reaction at C is C =arrow_forward56 Clamps like the one shown are commonly used in woodworking applications. This clamp has the dimensions given in the table below the figure, and its jaws are mm thick (in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the picture). a.) The screws of the clamp are adjusted so that there is a uniform pressure of P = 150 kPa being applied to the workpieces by the jaws. Determine the force carried in each screw. Hint: the uniform pressure can be modeled in 2-D as a uniform distributed load with intensity w = Pt (units of N/m) acting over the length of contact between the jaw and the workpiece. b.) Determine the minimum vertical force (parallel to the jaws) required to pull either one of the workpieces out of the clamp jaws. Use a coefficient of static friction between all contacting surfaces of μs = 0.56 and the same clamping pressure given for part (a). 2013 Michael Swanbom A B C a Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale.…arrow_forward
- Determine the force in each member of the space truss given F=5 kN. Use positive to indicate tension and negative to indicate compression. F E Z -2 m. B 3 m C 5 m 3 m A -4 m. AB = KN FAC = FAD = KN KN KN FBC = KN FBD FBE = = KN Farrow_forwardA short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method. (Answer: (a) 45.7C, (b)45.3C, (c)87.2 kJ)arrow_forwardA short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License