
(a)
Interpretation:
Draw the structural formula the compound formed by the reaction of given compound with sodium borohydride.
Concept Introduction:
Answer to Problem 57P
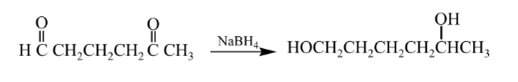
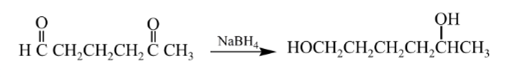
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Therefore, the product formed will be as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
Draw the structural formula the compound formed by the reaction of given compound with sodium borohydride.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Answer to Problem 57P
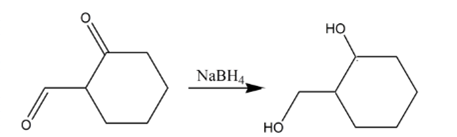
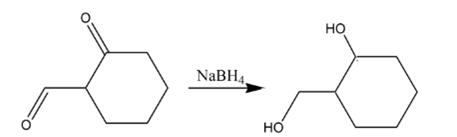
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Therefore, the product formed will be as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
Draw the structural formula the compound formed by the reaction of given compound with sodium borohydride.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Answer to Problem 57P
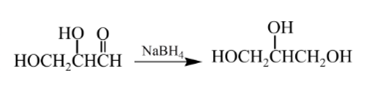
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Therefore, the product formed will be as follows:
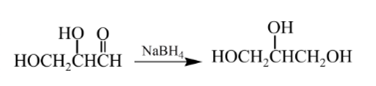
(d)
Interpretation:
Draw the structural formula the compound formed by the reaction of given compound with sodium borohydride.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Answer to Problem 57P
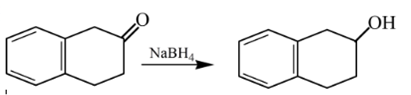
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Therefore, the product formed will be as follows:
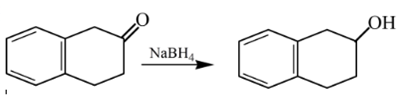
(e)
Interpretation:
Draw the structural formula the compound formed by the reaction of given compound with sodium borohydride.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Answer to Problem 57P
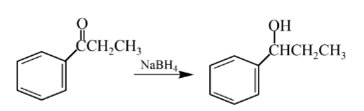
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Therefore, the product formed will be as follows:
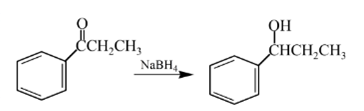
(f)
Interpretation:
Draw the structural formula the compound formed by the reaction of given compound with sodium borohydride.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Answer to Problem 57P
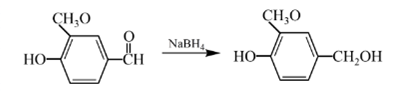
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced in secondary alcohols. The most commonly used reagent for reduction of aldehydes and ketone is sodium borohydride
Therefore, the product formed will be as follows:
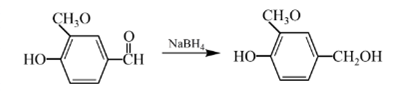
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Hi, I need your help i dont know which one to draw please. I’ve attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forwardDraw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forward
- Indicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forward
- Name an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forwardGiven the hydrazones indicated, draw the structures of the enamines that can be formed. Indicate the most stable enamine (explain). C6H5 C6H5 H C6H5 Harrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,


