
Concept explainers
17-30 Answer true or false.
(a) The reduction of an
(b) The reduction of a
(c) The oxidation of an aldehyde gives a
(d) The oxidation of a primary alcohol gives a ketone.
(e) Tollens’ reagent can be used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone.
(f) Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, reduces an aldehyde to a primary alcohol.
(g) The addition of one molecule of alcohol to the carbonyl group of a ketone gives a hemiacetal.
(h) The reaction of an aldehyde with two molecules of alcohol gives an acetal, plus a molecule
of water.
(j) The formation of hemiacetals and acetals is reversible.
(j) The cyclic hemiacetal formed from 4-hydroxy-pentanal has two stereocenters and can exist as
a mixture of 22 = 4 stereoisomers.
(a)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reduction of an aldehyde always gives an alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction is the addition of a hydrogen atom to a compound.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In aldehydes, the functional group is
Oxidation of aldehydes forms primary alcohol. For example, reduction of pentanal gives 1-pentanol.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reduction of ketones always gives a secondary alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Reduction is the addition of a hydrogen atom to a compound.
Answer to Problem 22P
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Reduction of ketones, hydrogen is added to the carbonyl carbon and gives secondary alcohol.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The oxidation of aldehydes gives a carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Oxidation is the process in which oxygen is added to the molecule.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation of aldehydes, oxygen is added to the carbonyl group and form carboxylic acid.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The oxidation of primary alcohol gives ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Oxidation is the process in which oxygen is added to the molecule.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation of primary alcohol first converted into aldehyde and followed by carboxylic acids.
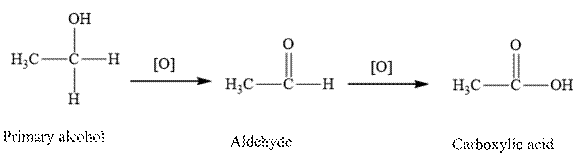
Therefore, the given statement is false.
(e)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
Tollen’s reagent can be used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Tollen’s reagent is a mild oxidizing agent.
Tollen’s reagent is reacts with the aldehyde group of a compound. The carbonyl group acts as a reducing agent and reduces the silver ion of the Tollen’s regent to silver metal.
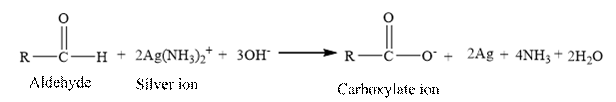
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes undergo oxidation easily, even with mild oxidizing agents and give carboxylic acid.
Ketone does not undergo oxidation with mild oxidizing agent due to selectivity of aldehyde and ketone for oxidation is used to differentiate an aldehyde and a ketone. Therefore, aldehyde and ketones are distinguished by using Tollen’s regent.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(f)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
Sodium borohydride,
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. The aldehydes undergoes a reduction reaction where in the addition of hydrogen occurs at the double bond between the oxygen and the carbon of the carbonyl group present in the aldehyde.
Answer to Problem 22P
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
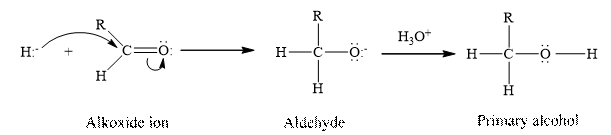
(g)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The addition of one molecule of alcohol to the carbonyl group of a ketone gives a hemiacetal.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In Hemiacetal, carbon is added to hydroxyl group and alkoxy group.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
When a molecule of alcohol is added to a ketone, the hydrogen of the alcohol is added o the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group, while the alkoxy group of the alcohol is added to the carbon of the carbonyl group. Hence ketone forms hemiacetal when the reacts with one molecule of alcohol.
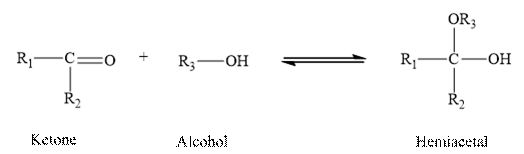
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reaction of an aldehyde with two molecules of alcohol gives an acetal, plus a molecule of water.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In acetal, carbon is bonded to two alkoxy groups.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Two molecules of an alcohol are added to an aldehyde to form hemiacetal. And it is unstable and it reacts with another molecule of an alcohol in the presence of an acid forms acetal and water.
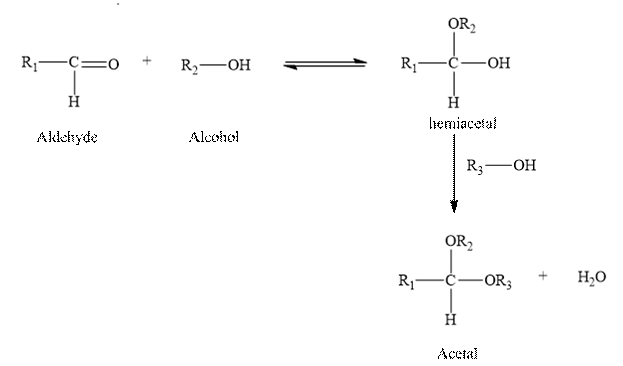
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The formation of hemiacetals and acetal is reversible.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In Hemiacetal, carbon is added to hydroxyl group and alkoxy group. In acetal, carbon is added to a two alkoxy groups.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
By using large excess of alcohol hemiacetals and acetals are reversible by the removal of water molecules. To shift the equilibrium towards the left side by the hydrolysis of the acetal to the aldehyde or ketone and alcohol.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The cyclic hemiacetal formed from 4-hydroxypentanal has two stereocentres and can exists as a mixture of
Concept Introduction:
A stereocentre is a carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it. The stereocentres of molecule can be calculated by using
n= stereocentre.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The cyclic hemiacetal; obtained from 4-hydroxypentanal has two stereocenters.
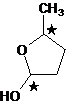
4- hydroxypentanal has two stereocenters, therefore it have 4 stereoisomers.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- AN IR spectrum, a 13 CMR spectrum, and a 1 HMR spectrum were obtained for an unknown structure with a molecular formula of C9H10. Draw the structure of this compound.arrow_forwardAN IR spectrum, a 13 CMR spectrum, and a 1 HMR spectrum were obtained for an unknown structure with a molecular formula of C9H10. Draw the structure of this compound.arrow_forward(a) What is the hybridization of the carbon in the methyl cation (CH3*) and in the methyl anion (CH3¯)? (b) What is the approximate H-C-H bond angle in the methyl cation and in the methyl anion?arrow_forward
- Q8: Draw the resonance structures for the following molecule. Show the curved arrows (how you derive each resonance structure). Circle the major resonance contributor.arrow_forwardQ4: Draw the Lewis structures for the cyanate ion (OCN) and the fulminate ion (CNO). Draw all possible resonance structures for each. Determine which form for each is the major resonance contributor.arrow_forwardIn the following molecule, indicate the hybridization and shape of the indicated atoms. CH3 N CH3 HÖ: H3C CI: ::arrow_forward
- Q3: Draw the Lewis structures for nitromethane (CH3NO2) and methyl nitrite (CH3ONO). Draw at least two resonance forms for each. Determine which form for each is the major resonance contributor.arrow_forwardQ1: Draw a valid Lewis structures for the following molecules. Include appropriate charges and lone pair electrons. If there is more than one Lewis structure available, draw the best structure. NH3 Sulfate Boron tetrahydride. C3H8 (linear isomer) OCN NO3 CH3CN SO2Cl2 CH3OH2*arrow_forwardQ2: Draw all applicable resonance forms for the acetate ion CH3COO. Clearly show all lone pairs, charges, and arrow formalism.arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward9. The following reaction, which proceeds via the SN1/E1 mechanisms, gives three alkene products (A, B, C) as well as an ether (D). (a) Show how each product arises mechanistically. (b) For the alkenes, determine the major product and justify your answer. (c) What clues in the reaction as shown suggest that this reaction does not go by the SN2/E2 mechanism route? (CH3)2CH-CH-CH3 CH3OH 1 Bl CH3OH ⑧· (CH3)2 CH-CH=CH2 heat H ⑥③ (CH3)2 C = C = CH3 © СнЗ-С-Снаснз сна (CH 3 ) 2 C H G H CH 3 оснзarrow_forwardPlease Don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





