
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
No product will be formed in the reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the dark no bromine free radical will be generated, therefore, no free radical reaction will occur. Carbon tetrachloride does not facilitate the production of positively charged
No reaction takes place between ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
(b)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with
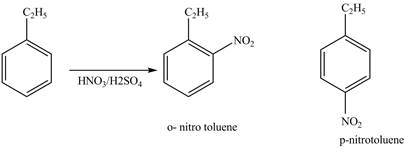
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. The nitronium ion
The corresponding
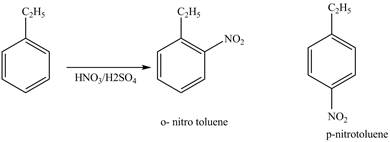
Figure 1
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with
(c)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
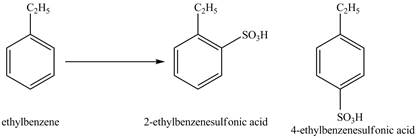
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid, the
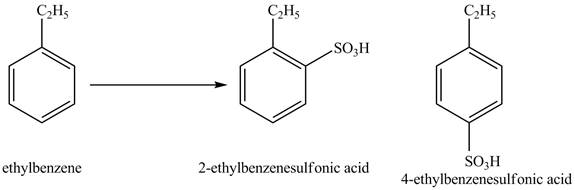
Figure 2
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
(d)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
Concept introduction:
Friedel Craft acylation is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the synthesis of the monoacylated product takes place from the reaction between aromatic rings and acyl chlorides.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction of ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
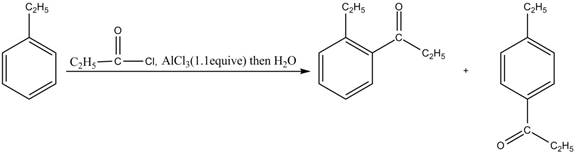
Explanation of Solution
Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminum chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution. Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. The acyl group attacks either ortho or para position of ethylbenzene to form the product. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
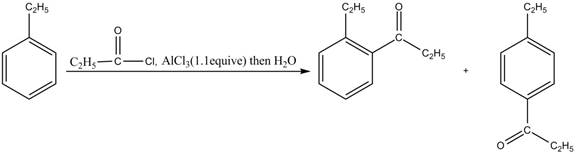
Figure 3
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
(e)
Interpretation:
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
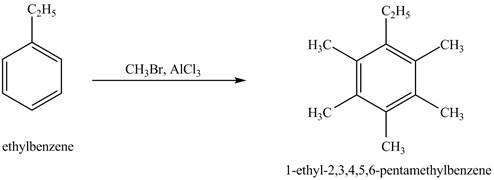
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the presence of
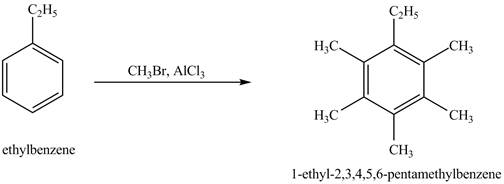
Figure 4
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
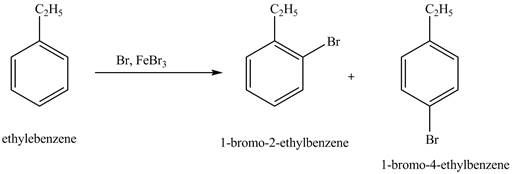
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In this reaction, positively charged
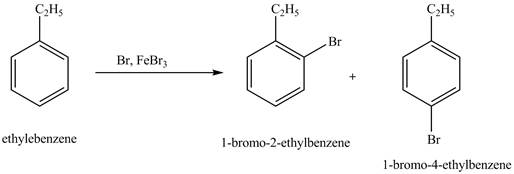
Figure 5
The products for the exothermic reaction ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Design experiments in UV-Vis to figure the optimal mole ratio of copper (1:1, 2:1, 3:1 and etc)versus ethambutol using all necessary chemicals including dihydrochloride and copper nitrate hemipentahydrate and sodium hydroxide. Show how UV-Vis absorbance and maximum wavelength would change in responsearrow_forwardCorrect each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the condensed structure it would have if it were dissolv a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO—CH,—C—CH,—OH X 5 2 2 2 HO–CH,—CH,—C—CH,—OH Explanation Check Center Accessi ©2025 on 5 Carrow_forwardMake the calculations to prepare 2M H2SO4, from concentrated H2SO4 (98%; density: 1.84 g/mL).arrow_forward
- H CH3 CH3 b) Write the products of your compound and the following reagents. If the reaction would not work for your compound, write "no reaction" and explain the problem. NaCN H* H₂NNHCH5 H* -à NaBH -à CH2MgBr Cro₁₂ --à H3O+ -à c) Would your compound give a positive Tollen's test? Why or why not?arrow_forwardHomework 4 Chem 204 Dr. Hellwig Consider this compound, which will be referred to as "your compound". a) Name your compound according to the IUPAC system. Include stereochemistry (E/Z/R/S) H CH3 CH3arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- 21.50 Determine the combinations of haloalkane(s) and alkoxide(s) that could be used to synthesize the following ethers through Williamson ether synthesis. (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) H₂COarrow_forward1. Arrange the following in order of increasing bond energy (lowest bond energy first, highest bond energy last). Provide your rationale. C=C, C-F, C=C, C-N, C-C List the bond order for each example.arrow_forwardWhat is the major enolate formed when treated with LDA? And why that one?arrow_forward
- 4. Calculate the total number of sigma bonds and total number of pi bonds in each of the following compounds. a. HH :D: +1 I H-N-C-C-O-H I H b. HH H Н :N=C-C-C=C-CEC-H :0: total o H-C-H H-C = `C-H I H. 11 H-C = C= CH H total o total π total π 1 Harrow_forwardIn the following reaction, what quantity in moles of CH₃OH are required to give off 4111 kJ of heat? 2 CH₃OH (l) + 3 O₂ (g) → 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O(g) ∆H° = -1280. kJarrow_forwardIndicate the processes in the dismutation of Cu2O.arrow_forward
