
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of reaction products when ethyl pentanoate undergoes ester hydrolysis under acidic conditions has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Breaking of the carbon‑oxygen single bond present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part” is one of the important reactions of ester. This process of breaking the bond between the carbon‑oxygen is known as ester hydrolysis or saponification. The condition prevails in the reaction determines it as ester hydrolysis of saponification.
Ester hydrolysis takes place in ester when it is treated with strong acid or enzymes as catalyst. Reverse of esterification reaction is the ester hydrolysis.
Saponification is the reaction that ester undergoes when a strong base is used to give the product as
(a)
Answer to Problem 16.130EP
The IUPAC names of the products obtained are,
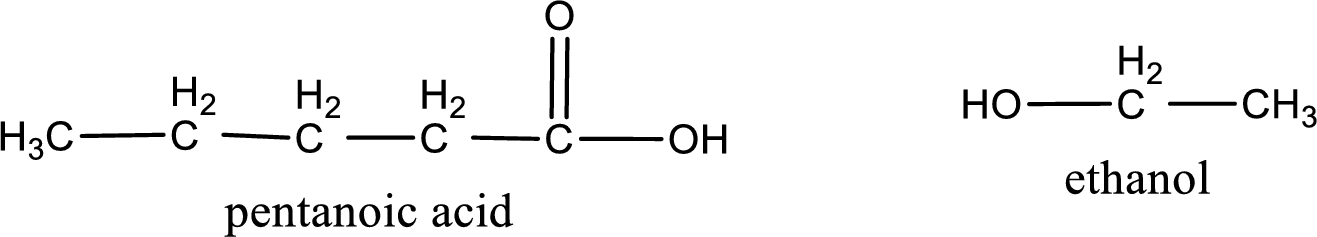
Explanation of Solution
Given name of ester is ethyl pentanoate. The structure of ethyl pentanoate can be given as,
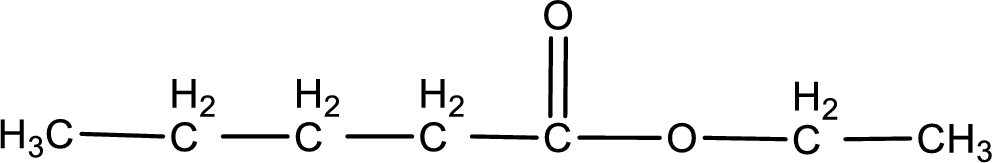
Under acidic conditions, esters undergo hydrolysis resulting in breakage of the carbon‑oxygen single bond that is present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part”. The product that is obtained on ester hydrolysis in acidic conditions is carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The complete reaction and the structure of the product obtained can be written as shown below,
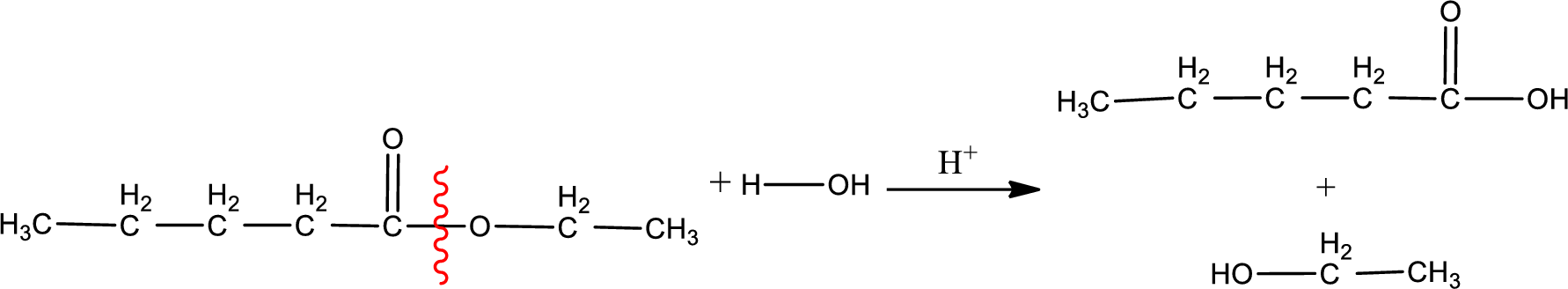
The IUPAC names of the product obtained can be given using
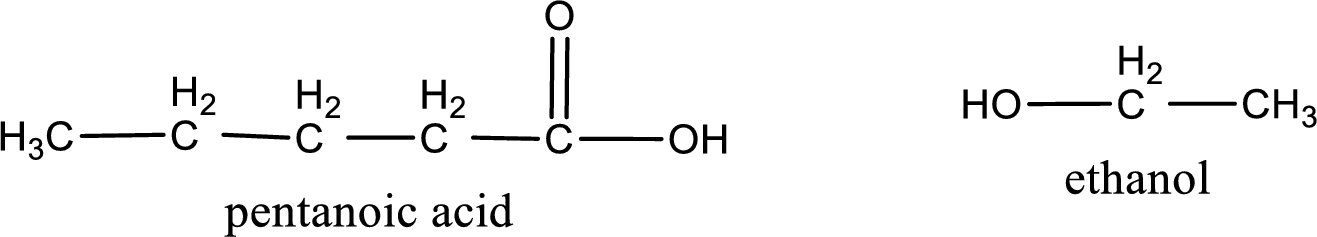
IUPAC names of the products obtained when ethyl pentanoate undergoes hydrolysis under acidic condition are written.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of reaction products when ethyl methanoate undergoes ester hydrolysis under acidic conditions has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Breaking of the carbon‑oxygen single bond present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part” is one of the important reactions of ester. This process of breaking the bond between the carbon‑oxygen is known as ester hydrolysis or saponification. The condition prevails in the reaction determines it as ester hydrolysis of saponification.
Ester hydrolysis takes place in ester when it is treated with strong acid or enzymes as catalyst. Reverse of esterification reaction is the ester hydrolysis.
Saponification is the reaction that ester undergoes when a strong base is used to give the product as carboxylic acid salt and alcohol.
(b)
Answer to Problem 16.130EP
The structural formula and IUPAC names of the products obtained are,
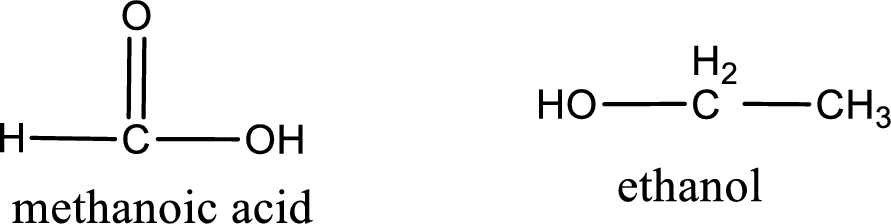
Explanation of Solution
Given name of ester is ethyl methanoate. The structure of ethyl methanoate can be given as,
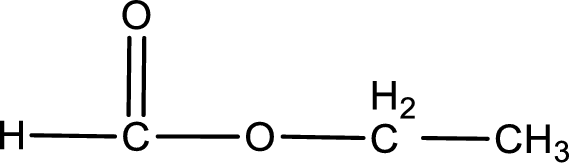
Under acidic conditions, esters undergo hydrolysis resulting in breakage of the carbon‑oxygen single bond that is present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part”. The product that is obtained on ester hydrolysis in acidic conditions is carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The complete reaction and the structure of the product obtained can be written as shown below,
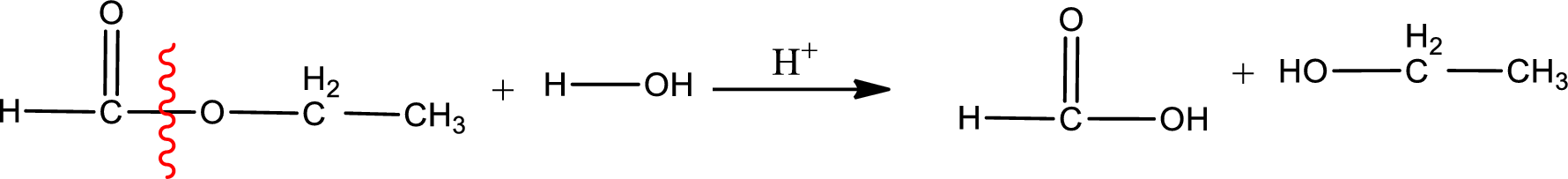
The IUPAC names of the product obtained can be given using IUPAC nomenclature of naming the compounds. The IUPAC names and the structure of the product obtained are,

IUPAC names of the products obtained when ethyl methanoate undergoes hydrolysis under acidic condition are written.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of reaction products when isopropyl pentanoate undergoes ester hydrolysis under acidic conditions has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Breaking of the carbon‑oxygen single bond present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part” is one of the important reactions of ester. This process of breaking the bond between the carbon‑oxygen is known as ester hydrolysis or saponification. The condition prevails in the reaction determines it as ester hydrolysis of saponification.
Ester hydrolysis takes place in ester when it is treated with strong acid or enzymes as catalyst. Reverse of esterification reaction is the ester hydrolysis.
Saponification is the reaction that ester undergoes when a strong base is used to give the product as carboxylic acid salt and alcohol.
(c)
Answer to Problem 16.130EP
The structural formula and IUPAC names of the products obtained are,
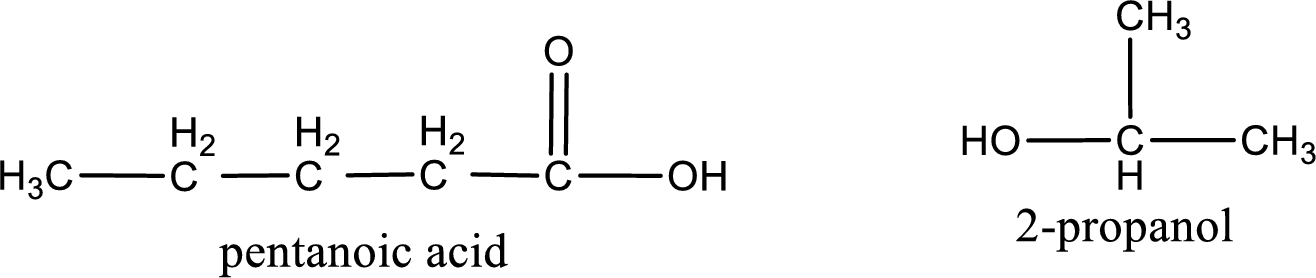
Explanation of Solution
Given name of ester is isopropyl pentanoate. The structure of isopropyl pentanoate can be given as,
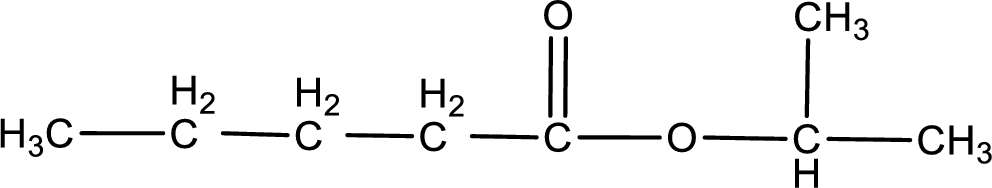
Under acidic conditions, esters undergo hydrolysis resulting in breakage of the carbon‑oxygen single bond that is present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part”. The product that is obtained on ester hydrolysis in acidic conditions is carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The complete reaction and the structure of the product obtained can be written as shown below,
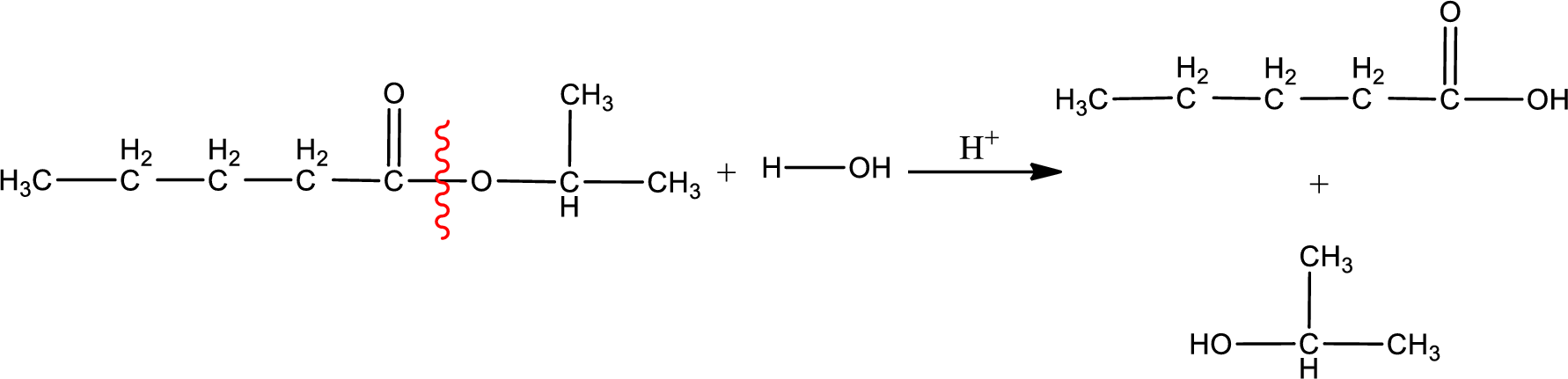
The IUPAC names of the product obtained can be given using IUPAC nomenclature of naming the compounds. The IUPAC names and the structure of the product obtained are,
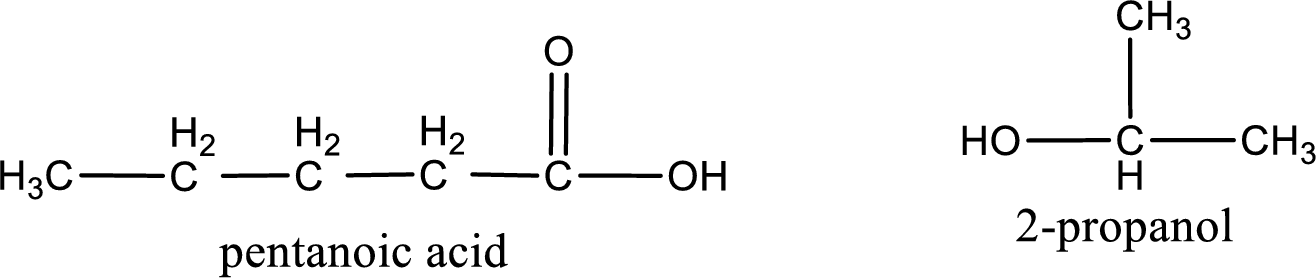
IUPAC names of the products obtained when isopropyl pentanoate undergoes hydrolysis under acidic condition are written.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of reaction products when isopropyl methanoate undergoes ester hydrolysis under acidic conditions has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Breaking of the carbon‑oxygen single bond present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part” is one of the important reactions of ester. This process of breaking the bond between the carbon‑oxygen is known as ester hydrolysis or saponification. The condition prevails in the reaction determines it as ester hydrolysis of saponification.
Ester hydrolysis takes place in ester when it is treated with strong acid or enzymes as catalyst. Reverse of esterification reaction is the ester hydrolysis.
Saponification is the reaction that ester undergoes when a strong base is used to give the product as carboxylic acid salt and alcohol.
(d)
Answer to Problem 16.130EP
The structural formula and IUPAC names of the products obtained are,

Explanation of Solution
Given name of ester is isopropyl methanoate. The structure of isopropyl methanoate can be given as,
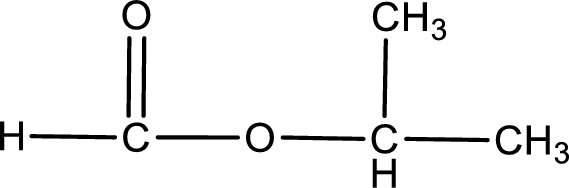
Under acidic conditions, esters undergo hydrolysis resulting in breakage of the carbon‑oxygen single bond that is present between the “acid part” and “alcohol part”. The product that is obtained on ester hydrolysis in acidic conditions is carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The complete reaction and the structure of the product obtained can be written as shown below,
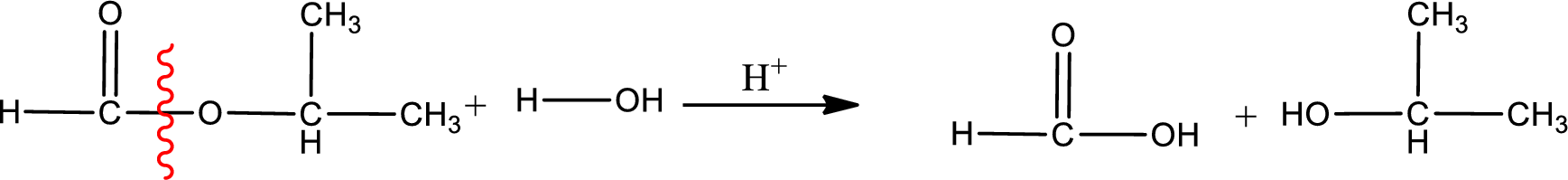
The IUPAC names of the product obtained can be given using IUPAC nomenclature of naming the compounds. The IUPAC names and the structure of the product obtained are,

IUPAC names of the products obtained when isopropyl methanoate undergoes hydrolysis under acidic condition are written.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry, Hybrid (with Owlv2 Quick Prep For General Chemistry Printed Access Card)
- Why are normal electrode potentials also called relative electrode potentials?arrow_forwardEasily differentiate between electrochemical potential and Galvani potential.arrow_forwardConstruct a molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide. Identify the relevant point group,include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Make sure toaccount for the difference in electronegativity between C and O. Hint: CO is substantiallyisoelectronic to N2. (PLEASE DRAW THE ENTIRE MO DIAGRAM!!!)arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





