
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 94P
What is the phase constant for SMH with a(t) given in Fig. 15-57 if the position function x(t) has the form x = xm cos(
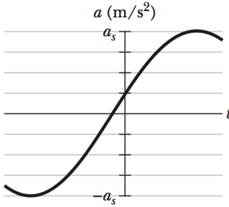
Figure 15-57 Problem 94.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Two moles of carbon monoxide (CO) start at a pressure of 1.4 atm and a volume of 35 liters. The gas is then
compressed adiabatically to 1/3 this volume. Assume that the gas may be treated as ideal.
Part A
What is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ
AU =
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Does the internal energy increase or decrease?
internal energy increases
internal energy decreases
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
?
J
Does the temperature of the gas increase or decrease during this process?
temperature of the gas increases
temperature of the gas decreases
Submit
Request Answer
Your answer is partially correct.
Two small objects, A and B, are fixed in place and separated by 2.98 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a charge of
+0.776 μC, and object B has a charge of -0.776 μC. How many electrons must be removed from A and put
onto B to make the electrostatic force that acts on each object an attractive force whose magnitude is 12.4 N?
e (mea
is the
es a co
le E o
ussian
Number
Tevtheel
ed Media
!
Units
No units →
answe
Tr2E
4
Problem 4) A particle is being pushed up a smooth slot by a rod. At the instant when 0 = rad,
the angular speed of the arm is ė = 1 rad/sec, and the angular acceleration is = 2 rad/sec².
What is the net force acting on the 1 kg particle at this instant? Express your answer as a vector
in cylindrical coordinates. Hint: You can express the radial coordinate as a function of the angle
by observing a right triangle. (20 pts)
Ꮎ
2 m
Figure 3: Particle pushed by rod along vertical path.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 15 - Which of the following describe for the SHM of...Ch. 15 - The velocity vt of a particle undergoing SHM is...Ch. 15 - The acceleration at of a particle undergoing SHM...Ch. 15 - Which of the following relationships between the...Ch. 15 - You are to complete Fig. 15-22a so that it is a...Ch. 15 - You are to complete Fig. 15-23a so that it is a...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-24 shows the xt curves for three...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-25 shows plots of the kinetic energy K...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-26 shows three physical pendulums...Ch. 15 - You are to build the oscillation transfer device...
Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-28, a springblock system is put into...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-29 gives, for three situations, the...Ch. 15 - An object undergoing simple harmonic motion takes...Ch. 15 - A 0.12 kg body undergoes simple harmonic motion of...Ch. 15 - What is the maximum acceleration of a platform...Ch. 15 - An automobile can be considered to be mounted on...Ch. 15 - SSM In an electric shaver, the blade moves back...Ch. 15 - A particle with a mass of 1.00 1020 kg is...Ch. 15 - SSM A loudspeaker produces a musical sound by...Ch. 15 - What is the phase constant for the harmonic...Ch. 15 - The position function x = 6.0 m cos3 rad/st /3...Ch. 15 - An oscillating blockspring system takes 0.75 s to...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-31, two identical springs of spring...Ch. 15 - What is the phase constant for the harmonic...Ch. 15 - SSM An oscillator consists of a block of mass...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of a block...Ch. 15 - SSM Two particles oscillate in simple harmonic...Ch. 15 - Two particles execute simple harmonic motion of...Ch. 15 - ILW An oscillator consists of a block attached to...Ch. 15 - GO At a certain harbor, the tides cause the ocean...Ch. 15 - A block rides on a piston a squat cylindrical...Ch. 15 - GO Figure 15-33a is a partial graph of the...Ch. 15 - ILW In Fig. 15-31, two springs are attached to a...Ch. 15 - GO Figure 15-34 shows block 1 of mass 0.200 kg...Ch. 15 - SSM WWW A block is on a horizontal surface a shake...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-35, two springs are joined and...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-36, a block weighing 14.0 N, which...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-37, two blocks m = 1.8 kg and M = 10...Ch. 15 - SSM When the displacement in SHM is one-half the...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-38 gives the one-dimensional potential...Ch. 15 - SSM Find the mechanical energy of a blockspring...Ch. 15 - An oscillating blockspring system has a mechanical...Ch. 15 - ILW A 5.00 kg object on a horizontal frictionless...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-39 shows the kinetic energy K of a...Ch. 15 - GO A block of mass M = 5.4 kg, at rest on a...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-41, block 2 of mass 2.0 kg...Ch. 15 - A 10 g particle undergoes SHM with an amplitude of...Ch. 15 - If the phase angle for a blockspring system in SHM...Ch. 15 - GO A massless spring hangs from the ceiling with a...Ch. 15 - A 95 kg solid sphere with a 15 cm radius is...Ch. 15 - SSM WWW The balance wheel of an old-fashioned...Ch. 15 - ILW A physical pendulum consists of a meter stick...Ch. 15 - SSM In Fig. 15-42, the pendulum consists of a...Ch. 15 - Suppose that a simple pendulum consists of a small...Ch. 15 - a If the physical pendulum of Fig. 15-13 and the...Ch. 15 - A physical pendulum consists of two meter-long...Ch. 15 - A performer seated on a trapeze is swinging back...Ch. 15 - A physical pendulum has a center of oscillation at...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-44, a physical pendulum consists of a...Ch. 15 - GO A rectangular block, with face lengths a = 35...Ch. 15 - GO The angle of the pendulum of Fig. 15-11b is...Ch. 15 - Prob. 50PCh. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-46, a stick of length L = 1.85 m...Ch. 15 - GO The 3.00 kg cube in Fig. 15-47 has edge lengths...Ch. 15 - SSM ILW In the overhead view of Fig. 15-48, a long...Ch. 15 - Prob. 54PCh. 15 - GO A pendulum is formed by pivoting a long thin...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-50: a 2.50 kg disk of diameter D = 42.0...Ch. 15 - The amplitude of a lightly damped oscillator...Ch. 15 - For the damped oscillator system shown in Fig....Ch. 15 - SSM WWW For the damped oscillator system shown in...Ch. 15 - The suspension system of a 2000 kg automobile sags...Ch. 15 - For Eq. 15-45, suppose the amplitude xm is given...Ch. 15 - Hanging from a horizontal beam are nine simple...Ch. 15 - A. 1000 kg car carrying four 82 kg people travels...Ch. 15 - Although California is known for earthquakes, is...Ch. 15 - A loudspeaker diaphragm is oscillating in simple...Ch. 15 - A uniform spring with k = 8600 N/m is cut into...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-51, three 10, 000 kg ore cars are...Ch. 15 - A 2.00 kg block hangs from a spring. A 300 g body...Ch. 15 - SSM In the engine of a locomotive, a cylindrical...Ch. 15 - GO A wheel is free to rotate about its fixed axle....Ch. 15 - A 50.0 g stone is attached to the bottom of a...Ch. 15 - A uniform circular disk: whose radius R is 12.6 cm...Ch. 15 - SSM A vertical spring stretches 9.6 cm when a 1.3...Ch. 15 - A massless spring with spring constant 19 N/m...Ch. 15 - A 4.00 kg block is suspended from a spring with k...Ch. 15 - A 55.0 g block oscillates in SHM on the end of a...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-53 gives the position of a 20 g block...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-53 gives the position xt of a block...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-54 shows the kinetic energy K of a...Ch. 15 - A block is in SHM on the end of a spring, with...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of a 0.50 kg...Ch. 15 - A simple pendulum of length 20 cm and mass 5.0 g...Ch. 15 - The scale of a spring balance that reads from 0 to...Ch. 15 - A 0.10 kg block oscillates back and forth along a...Ch. 15 - The end point of a spring oscillates with a period...Ch. 15 - The tip of one prong of a tuning fork undergoes...Ch. 15 - Prob. 87PCh. 15 - A block weighing 20 N oscillates at one end of a...Ch. 15 - A 3.0 kg particle is in simple harmonic motion in...Ch. 15 - A particle executes linear SHM with frequency 0.25...Ch. 15 - SSM What is the frequency of a simple pendulum 2.0...Ch. 15 - A grandfather clock has a pendulum that consists...Ch. 15 - A 4.00 kg block hangs from a spring, extending it...Ch. 15 - What is the phase constant for SMH with at given...Ch. 15 - An engineer has an odd-shaped 10 kg object and...Ch. 15 - A spider can tell when its web has captured, say,...Ch. 15 - A torsion pendulum consists of a metal disk with a...Ch. 15 - When a 20 N can is hung from the bottom of a...Ch. 15 - For a simple pendulum, find the angular amplitude...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-59, a solid cylinder attached to a...Ch. 15 - SSM A 1.2 kg block sliding on a horizontal...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of an 0.80...Ch. 15 - A block sliding on a horizontal frictionless...Ch. 15 - A damped harmonic oscillator consists of a block m...Ch. 15 - A block weighing 10.0 N is attached to the lower...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of a block...Ch. 15 - The vibration frequencies of atoms in solids at...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-61 shows that if we hang a block on the...Ch. 15 - The physical pendulum in Fig. 15-62 has two...Ch. 15 - A common device for entertaining a toddler is a...Ch. 15 - A 2.0 kg block executes SHM while attached to a...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-64, a 2500 kg demolition ball swings...Ch. 15 - The center of oscillation of a physical pendulum...Ch. 15 - A hypothetical large slingshot is stretched 2.30 m...Ch. 15 - What is the length of a simple pendulum whose full...Ch. 15 - A 2.0 kg block is attached to the end of a spring...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
45. The tabulated data were collected for this reaction:
[NO2](M) [F2](M) Initial Rate (M/s)
0.100 0.100...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
10. The dorsal pigment pattern of frogs can be either “leopard” (white pigment between dark spots) or “mottled”...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
A large brewery has a pipe of cross-sectional area 0.2m2 flowing carbon dioxide at 1000kPa,0C with a volume-flo...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
2. The structural and function unit of life is (a) a cell, (b) an organ, (c) the organism, (d) a molecule.
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy & Physiology) Standalone Book
Body, Heal Thyself The precision of mitotic cell division is essential for repairing damaged tissues like those...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4 Problem 4) A particle is being pushed up a smooth slot by a rod. At the instant when 0 = rad, the angular speed of the arm is ė = 1 rad/sec, and the angular acceleration is = 2 rad/sec². What is the net force acting on the 1 kg particle at this instant? Express your answer as a vector in cylindrical coordinates. Hint: You can express the radial coordinate as a function of the angle by observing a right triangle. (20 pts) Ꮎ 2 m Figure 3: Particle pushed by rod along vertical path.arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly. Thank you!!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. Calculate. Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the steps and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise. Answer all parts and show all work please.arrow_forwardA player kicks a football at the start of the game. After a 4 second flight, the ball touches the ground 50 m from the kicking tee. Assume air resistance is negligible and the take-off and landing height are the same (i.e., time to peak = time to fall = ½ total flight time). Calculate: Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What Are Sound Wave Properties? | Physics in Motion; Author: GPB Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GW6_U553sK8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY