
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 79P
Figure 15-54 shows the kinetic energy K of a simple pendulum versus its angle
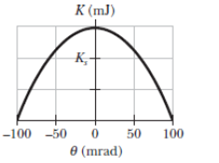
Figure 15-54 Problem 79.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
If a 1/2 inch diameter drill bit spins at 3000 rotations per minute, how fast is the outer edge moving as it contacts a piece of metal while drilling a machine part?
Need help with the third question (C)A gymnast weighing 68 kg attempts a handstand using only one arm. He plants his hand at an angl reesulting in the reaction force shown.
Q: What is the direction of the force on the current carrying conductor in the
magnetic field in each of the cases 1 to 8 shown below?
(1)
B
B
B into page
X X X
x
X X X X
(2)
B
11 -10°
B
x I
B
I out of page
(3)
I into page
(4)
B out of page
out of page
I
N
N
S
x X X X
I
X
X X X
I
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
S
Chapter 15 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 15 - Which of the following describe for the SHM of...Ch. 15 - The velocity vt of a particle undergoing SHM is...Ch. 15 - The acceleration at of a particle undergoing SHM...Ch. 15 - Which of the following relationships between the...Ch. 15 - You are to complete Fig. 15-22a so that it is a...Ch. 15 - You are to complete Fig. 15-23a so that it is a...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-24 shows the xt curves for three...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-25 shows plots of the kinetic energy K...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-26 shows three physical pendulums...Ch. 15 - You are to build the oscillation transfer device...
Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-28, a springblock system is put into...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-29 gives, for three situations, the...Ch. 15 - An object undergoing simple harmonic motion takes...Ch. 15 - A 0.12 kg body undergoes simple harmonic motion of...Ch. 15 - What is the maximum acceleration of a platform...Ch. 15 - An automobile can be considered to be mounted on...Ch. 15 - SSM In an electric shaver, the blade moves back...Ch. 15 - A particle with a mass of 1.00 1020 kg is...Ch. 15 - SSM A loudspeaker produces a musical sound by...Ch. 15 - What is the phase constant for the harmonic...Ch. 15 - The position function x = 6.0 m cos3 rad/st /3...Ch. 15 - An oscillating blockspring system takes 0.75 s to...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-31, two identical springs of spring...Ch. 15 - What is the phase constant for the harmonic...Ch. 15 - SSM An oscillator consists of a block of mass...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of a block...Ch. 15 - SSM Two particles oscillate in simple harmonic...Ch. 15 - Two particles execute simple harmonic motion of...Ch. 15 - ILW An oscillator consists of a block attached to...Ch. 15 - GO At a certain harbor, the tides cause the ocean...Ch. 15 - A block rides on a piston a squat cylindrical...Ch. 15 - GO Figure 15-33a is a partial graph of the...Ch. 15 - ILW In Fig. 15-31, two springs are attached to a...Ch. 15 - GO Figure 15-34 shows block 1 of mass 0.200 kg...Ch. 15 - SSM WWW A block is on a horizontal surface a shake...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-35, two springs are joined and...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-36, a block weighing 14.0 N, which...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-37, two blocks m = 1.8 kg and M = 10...Ch. 15 - SSM When the displacement in SHM is one-half the...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-38 gives the one-dimensional potential...Ch. 15 - SSM Find the mechanical energy of a blockspring...Ch. 15 - An oscillating blockspring system has a mechanical...Ch. 15 - ILW A 5.00 kg object on a horizontal frictionless...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-39 shows the kinetic energy K of a...Ch. 15 - GO A block of mass M = 5.4 kg, at rest on a...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-41, block 2 of mass 2.0 kg...Ch. 15 - A 10 g particle undergoes SHM with an amplitude of...Ch. 15 - If the phase angle for a blockspring system in SHM...Ch. 15 - GO A massless spring hangs from the ceiling with a...Ch. 15 - A 95 kg solid sphere with a 15 cm radius is...Ch. 15 - SSM WWW The balance wheel of an old-fashioned...Ch. 15 - ILW A physical pendulum consists of a meter stick...Ch. 15 - SSM In Fig. 15-42, the pendulum consists of a...Ch. 15 - Suppose that a simple pendulum consists of a small...Ch. 15 - a If the physical pendulum of Fig. 15-13 and the...Ch. 15 - A physical pendulum consists of two meter-long...Ch. 15 - A performer seated on a trapeze is swinging back...Ch. 15 - A physical pendulum has a center of oscillation at...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-44, a physical pendulum consists of a...Ch. 15 - GO A rectangular block, with face lengths a = 35...Ch. 15 - GO The angle of the pendulum of Fig. 15-11b is...Ch. 15 - Prob. 50PCh. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-46, a stick of length L = 1.85 m...Ch. 15 - GO The 3.00 kg cube in Fig. 15-47 has edge lengths...Ch. 15 - SSM ILW In the overhead view of Fig. 15-48, a long...Ch. 15 - Prob. 54PCh. 15 - GO A pendulum is formed by pivoting a long thin...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-50: a 2.50 kg disk of diameter D = 42.0...Ch. 15 - The amplitude of a lightly damped oscillator...Ch. 15 - For the damped oscillator system shown in Fig....Ch. 15 - SSM WWW For the damped oscillator system shown in...Ch. 15 - The suspension system of a 2000 kg automobile sags...Ch. 15 - For Eq. 15-45, suppose the amplitude xm is given...Ch. 15 - Hanging from a horizontal beam are nine simple...Ch. 15 - A. 1000 kg car carrying four 82 kg people travels...Ch. 15 - Although California is known for earthquakes, is...Ch. 15 - A loudspeaker diaphragm is oscillating in simple...Ch. 15 - A uniform spring with k = 8600 N/m is cut into...Ch. 15 - GO In Fig. 15-51, three 10, 000 kg ore cars are...Ch. 15 - A 2.00 kg block hangs from a spring. A 300 g body...Ch. 15 - SSM In the engine of a locomotive, a cylindrical...Ch. 15 - GO A wheel is free to rotate about its fixed axle....Ch. 15 - A 50.0 g stone is attached to the bottom of a...Ch. 15 - A uniform circular disk: whose radius R is 12.6 cm...Ch. 15 - SSM A vertical spring stretches 9.6 cm when a 1.3...Ch. 15 - A massless spring with spring constant 19 N/m...Ch. 15 - A 4.00 kg block is suspended from a spring with k...Ch. 15 - A 55.0 g block oscillates in SHM on the end of a...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-53 gives the position of a 20 g block...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-53 gives the position xt of a block...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-54 shows the kinetic energy K of a...Ch. 15 - A block is in SHM on the end of a spring, with...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of a 0.50 kg...Ch. 15 - A simple pendulum of length 20 cm and mass 5.0 g...Ch. 15 - The scale of a spring balance that reads from 0 to...Ch. 15 - A 0.10 kg block oscillates back and forth along a...Ch. 15 - The end point of a spring oscillates with a period...Ch. 15 - The tip of one prong of a tuning fork undergoes...Ch. 15 - Prob. 87PCh. 15 - A block weighing 20 N oscillates at one end of a...Ch. 15 - A 3.0 kg particle is in simple harmonic motion in...Ch. 15 - A particle executes linear SHM with frequency 0.25...Ch. 15 - SSM What is the frequency of a simple pendulum 2.0...Ch. 15 - A grandfather clock has a pendulum that consists...Ch. 15 - A 4.00 kg block hangs from a spring, extending it...Ch. 15 - What is the phase constant for SMH with at given...Ch. 15 - An engineer has an odd-shaped 10 kg object and...Ch. 15 - A spider can tell when its web has captured, say,...Ch. 15 - A torsion pendulum consists of a metal disk with a...Ch. 15 - When a 20 N can is hung from the bottom of a...Ch. 15 - For a simple pendulum, find the angular amplitude...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-59, a solid cylinder attached to a...Ch. 15 - SSM A 1.2 kg block sliding on a horizontal...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of an 0.80...Ch. 15 - A block sliding on a horizontal frictionless...Ch. 15 - A damped harmonic oscillator consists of a block m...Ch. 15 - A block weighing 10.0 N is attached to the lower...Ch. 15 - A simple harmonic oscillator consists of a block...Ch. 15 - The vibration frequencies of atoms in solids at...Ch. 15 - Figure 15-61 shows that if we hang a block on the...Ch. 15 - The physical pendulum in Fig. 15-62 has two...Ch. 15 - A common device for entertaining a toddler is a...Ch. 15 - A 2.0 kg block executes SHM while attached to a...Ch. 15 - In Fig. 15-64, a 2500 kg demolition ball swings...Ch. 15 - The center of oscillation of a physical pendulum...Ch. 15 - A hypothetical large slingshot is stretched 2.30 m...Ch. 15 - What is the length of a simple pendulum whose full...Ch. 15 - A 2.0 kg block is attached to the end of a spring...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
16.
a. Calculate the standard free energy change as a pair of electrons is transferred from succinate to mole...
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Name three shoreline features that are produced, in part, by longshore transport. ______________________ ______...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
WHAT IF? Suppose two plant populations exchange pollen and seeds. In one population, individuals of genotype AA...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Endospore formation is called (a) _____. It is initiated by (b) _____. Formation of a new cell from an endospor...
Microbiology: An Introduction
How does an obligate aerobe differ from a facultative aerobe?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q: What is the direction of the magnetic field at point A, due to the current I in a wire, in each of the cases 1 to 6 shown below? Note: point A is in the plane of the page. ▪A I I ▪A (1) (2) ▪A • I (out of page) (3) ▪A I x I (into page) ▪A ▪A I (4) (5) (6)arrow_forwardA tennis ball is thrown into the air with initial speed vo=46 m/s and angle (theta) 38 degrees from the ground. Find the distance it travels (x) when it hits the ground.arrow_forwardProblem 04.08 (17 points). Answer the following questions related to the figure below. ථි R₁ www R₂ E R₁ www ли R₁ A Use Kirchhoff's laws to calculate the currents through each battery and resistor in terms of R1, R2, E1, & E2. B Given that all the resistances and EMFs have positive values, if E₁ > E2 and R₁ > R2, which direction is the current flowing through E₁? Through R₂? C If E1 E2 and R₁ > R2, which direction is the current flowing through E₁? Through R2?arrow_forward
- A 105- and a 45.0-Q resistor are connected in parallel. When this combination is connected across a battery, the current delivered by the battery is 0.268 A. When the 45.0-resistor is disconnected, the current from the battery drops to 0.0840 A. Determine (a) the emf and (b) the internal resistance of the battery. 10 R2 R₁ ww R₁ Emf 14 Emf Final circuit Initial circuitarrow_forwardA ball is shot at an angle of 60° with the ground. What should be the initial velocity of the ball so that it will go inside the ring 8 meters away and 3 meters high. Suppose that you want the ball to be scored exactly at the buzzer, determine the required time to throw and shoot the ball. Full solution and figure if there is.arrow_forwardCorrect answer please. I will upvote.arrow_forward
- Define operational amplifierarrow_forwardA bungee jumper plans to bungee jump from a bridge 64.0 m above the ground. He plans to use a uniform elastic cord, tied to a harness around his body, to stop his fall at a point 6.00 m above the water. Model his body as a particle and the cord as having negligible mass and obeying Hooke's law. In a preliminary test he finds that when hanging at rest from a 5.00 m length of the cord, his body weight stretches it by 1.55 m. He will drop from rest at the point where the top end of a longer section of the cord is attached to the bridge. (a) What length of cord should he use? Use subscripts 1 and 2 respectively to represent the 5.00 m test length and the actual jump length. Use Hooke's law F = KAL and the fact that the change in length AL for a given force is proportional the length L (AL = CL), to determine the force constant for the test case and for the jump case. Use conservation of mechanical energy to determine the length of the rope. m (b) What maximum acceleration will he…arrow_forward9 V 300 Ω www 100 Ω 200 Ω www 400 Ω 500 Ω www 600 Ω ww 700 Ω Figure 1: Circuit symbols for a variety of useful circuit elements Problem 04.07 (17 points). Answer the following questions related to the figure below. A What is the equivalent resistance of the network of resistors in the circuit below? B If the battery has an EMF of 9V and is considered as an ideal batter (internal resistance is zero), how much current flows through it in this circuit? C If the 9V EMF battery has an internal resistance of 2 2, would this current be larger or smaller? By how much? D In the ideal battery case, calculate the current through and the voltage across each resistor in the circuit.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardIf the block does reach point B, how far up the curved portion of the track does it reach, and if it does not, how far short of point B does the block come to a stop? (Enter your answer in m.)arrow_forwardTruck suspensions often have "helper springs" that engage at high loads. One such arrangement is a leaf spring with a helper coil spring mounted on the axle, as shown in the figure below. When the main leaf spring is compressed by distance yo, the helper spring engages and then helps to support any additional load. Suppose the leaf spring constant is 5.05 × 105 N/m, the helper spring constant is 3.50 × 105 N/m, and y = 0.500 m. Truck body yo Main leaf spring -"Helper" spring Axle (a) What is the compression of the leaf spring for a load of 6.00 × 105 N? Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m (b) How much work is done in compressing the springs? ☑ Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY