
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 8FP
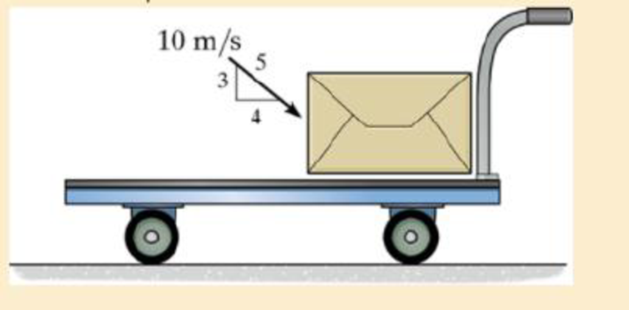
The cart and package have a mass of 20 kg and 5 kg, respectively. If the cart has a smooth surface and it is initially at rest, while the velocity of the package is as shown, determine the final common velocity of the cart and package after the impact.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 3.
1.5 m
B
PROBLEM 16.121
End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the inclined surface, while end B is
attached to a collar of negligible mass which can slide along the vertical rod
shown. Knowing that the rod is released from rest when = 35° and neglecting the
effect of friction, determine immediately after release (a) the angular acceleration
of the rod, (b) the reaction at B.
25°
Problem 1. End A of the uniform 5-kg bar is pinned freely to the collar, which has an acceleration
a = 4 m/s² along the fixed horizontal shaft. If the bar has a clockwise angular velocity @ = 2 rad/s
as it swings past the vertical, determine the components of the force on the bar at A for this instant.
Answers: Ax = 5 N, Ay = 57.1 N
L
X
AO
0.8 m
@
a
=
MMB 241- Tutorial 1.pdf
1/3
80%
+ +
MMB 241 - Dynamics of Particles
Tutorial 1
Topic: Kinematics of Particles:- Displacement, velocity and acceleration of particles.
QUESTIONS
1. If v = (4t+5) m/s, where t is in seconds, determine a when t = 2 s.
2. If s = (2t³) m, where t is in seconds, determine v when t = 2 s.
3. If a = 2 m/s², determine v at s = 4 m if v = 3 m/s at s = 0.
4. If a = 4 m/s², determines when t = 3 s if v = 2 m/s and s = 2 m when t=0.
5. A particle moves along a straight line such that its position is defined by s = (t² - 6t + 5) m.
Determine the average velocity, the average speed, and the acceleration of the particle
when t = 6 s.
6. A particle is moving with a velocity of vo when s=0 and t=0. If it is subjected to a
deceleration of a = -kv³ where k is a constant, determine its velocity and position as
functions of time.
7. A particle travels along a straight-line path such that in 4s it moves from an initial position
SA = -8 m to a position SB = +3 m. Then in…
Chapter 15 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 15 - The 0.5kg ball strikes the rough ground and...Ch. 15 - Prob. 2FPCh. 15 - Prob. 3FPCh. 15 - The wheels of the 1.5-Mg car generate the traction...Ch. 15 - Prob. 5FPCh. 15 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 3PCh. 15 - Each of the cables can sustain a maximum tension...Ch. 15 - Crates A and B weigh 100 lb and 50 lb,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 8P
Ch. 15 - Prob. 9PCh. 15 - During operation the jack hammer strikes the...Ch. 15 - For a short period of time, the frictional driving...Ch. 15 - The 2.5-Mg van is traveling with a speed of 100...Ch. 15 - Prob. 14PCh. 15 - The towing force acting on the 400-kg safe varies...Ch. 15 - Prob. 18PCh. 15 - Prob. 19PCh. 15 - If it takes 35 s for the 50-Mg tugboat to increase...Ch. 15 - Prob. 23PCh. 15 - The balloon has a total mass of 400 kg including...Ch. 15 - Prob. 26PCh. 15 - Prob. 30PCh. 15 - Prob. 7FPCh. 15 - The cart and package have a mass of 20 kg and 5...Ch. 15 - The 5-kg block A has an initial speed of 5 m/s as...Ch. 15 - Prob. 10FPCh. 15 - Prob. 11FPCh. 15 - The cannon and support without a projectile have a...Ch. 15 - The 5-Mg bus B is traveling to the right at 20...Ch. 15 - Prob. 36PCh. 15 - A railroad car having a mass of 15 Mg is coasting...Ch. 15 - A ballistic pendulum consists of a 4-kg wooden...Ch. 15 - Prob. 39PCh. 15 - Prob. 43PCh. 15 - Prob. 44PCh. 15 - Prob. 45PCh. 15 - The 30-Mg freight car A and 15-Mg freight car B...Ch. 15 - Blocks A and B have masses of 40 kg and 60 kg,...Ch. 15 - Block A has a mass of 5 kg and is placed on the...Ch. 15 - Solve Prob. 15-53 if the coefficient of kinetic...Ch. 15 - Prob. 56PCh. 15 - Prob. 13FPCh. 15 - Prob. 14FPCh. 15 - The 30-lb package A has a speed of 5 ft/s when it...Ch. 15 - The ball strikes the smooth wall with a velocity...Ch. 15 - Prob. 17FPCh. 15 - Prob. 18FPCh. 15 - Prob. 58PCh. 15 - Prob. 59PCh. 15 - Prob. 61PCh. 15 - Prob. 62PCh. 15 - Prob. 63PCh. 15 - Prob. 64PCh. 15 - A 1-lb ball A is traveling horizontally at 20 ft/s...Ch. 15 - Prob. 69PCh. 15 - Prob. 73PCh. 15 - Two smooth disks A and B each have a mass of 0.5...Ch. 15 - Prob. 75PCh. 15 - The cue ball A is given an initial velocity (vA)1...Ch. 15 - Prob. 78PCh. 15 - Prob. 79PCh. 15 - A ball of negligible size and mass m is given a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 81PCh. 15 - The 20-lb box slides on the surface for which k =...Ch. 15 - Prob. 84PCh. 15 - Prob. 85PCh. 15 - Prob. 90PCh. 15 - Prob. 92PCh. 15 - Disks A and B have a mass of 15 kg and 10 kg,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 19FPCh. 15 - Prob. 20FPCh. 15 - Initially the 5-kg block is moving with a constant...Ch. 15 - Prob. 22FPCh. 15 - Prob. 23FPCh. 15 - Prob. 24FPCh. 15 - Determine the angular momentum HO of the 6-lb...Ch. 15 - Determine the angular momentum HP of the 6-lb...Ch. 15 - Prob. 96PCh. 15 - Determine the angular momentum Hp, of each of the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 98PCh. 15 - Determine the angular momentum Hp of the 3-kg...Ch. 15 - The 800-lb roller-coaster car starts from rest on...Ch. 15 - The 800-lb roller-coaster car starts from rest on...Ch. 15 - If the rod of negligible mass is subjected to a...Ch. 15 - The amusement park ride consists of a 200-kg car...Ch. 15 - An earth satellite of mass 700 kg is launched into...Ch. 15 - Prob. 115PCh. 15 - Prob. 116PCh. 15 - Prob. 119PCh. 15 - The gauge pressure of water at A is 150.5 kPa....Ch. 15 - Prob. 121PCh. 15 - The fountain shoots water in the direction shown....Ch. 15 - A plow located on the front of a locomotive scoops...Ch. 15 - Prob. 124PCh. 15 - Water is discharged from a nozzle with a velocity...Ch. 15 - Prob. 127PCh. 15 - Prob. 128PCh. 15 - Sand drops onto the 2-Mg empty rail car at 50 kg/s...Ch. 15 - Prob. 133PCh. 15 - A rocket has an empty weight of 500 lb and carries...Ch. 15 - Prob. 135PCh. 15 - Prob. 138PCh. 15 - The missile weighs 40 000 lb. The constant thrust...Ch. 15 - Prob. 140PCh. 15 - Prob. 1RPCh. 15 - Prob. 2RPCh. 15 - Prob. 3RPCh. 15 - Prob. 4RPCh. 15 - The 200-g projectile is fired with a velocity of...Ch. 15 - Block A has a mass of 3 kg and is sliding on a...Ch. 15 - Two smooth billiard balls A and B have an equal...Ch. 15 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (read image)arrow_forwardQu 2 Schematically plot attractive, repulsive, and net energies versus interatomic separation for two atoms or ions. Note on this plot the equilibrium separation (distance) ro and the bonding energy Eo. Qu 3 How many atoms (or molecules) are in one mole of the substance? Qu 4 Mole, in the context of this book, is taken in units of gram-mole. On this basis, how many atoms are there in a pound-mole of a substance? Qu 5 The atomic radii of Mg* and F ions are 0.072 and 0.133 nm, respectively. Calculate the force of attraction between these two ions at their equilibrium interionic separation (i.e., when the ions just touch one another). What is the force of repulsion at this same separation distance?show all work step by step problems formulaarrow_forwardQu 4 Silver has FCC crystal structure at room temperature, and a lattice constant, a, of 0.407 nm. Draw a reduced sphere silver unit cell in the grids provided below, clearly label the lattice dimensions. Within the unit cell you drew, shade the (1 0 0) plane. How many atoms are contained within the (1 0 0) plane? Calculate the area of (1 0 0) plane in [nm?]. Express your answer in [nm?] to three significant figures. Calculate the planar density of the (1 0 0) plane in [atoms/nm?]. Express the answer in atoms/nm to three significant figures. show all work step by steparrow_forward
- Can I get help on this question?arrow_forwardDuring some actual expansion and compression processes in piston–cylinder devices, the gases have been observed to satisfy the relationship PVn = C, where n and C are constants. Calculate the work done when a gas expands from 350 kPa and 0.03 m3 to a final volume of 0.2 m3 for the case of n = 1.5. The work done in this case is kJ.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide contained in a piston–cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m3. During the process, the pressure and volume are related by P = aV–2, where a = 6 kPa·m6. Calculate the work done on carbon dioxide during this process. The work done on carbon dioxide during this process is kJ.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY