
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 4P
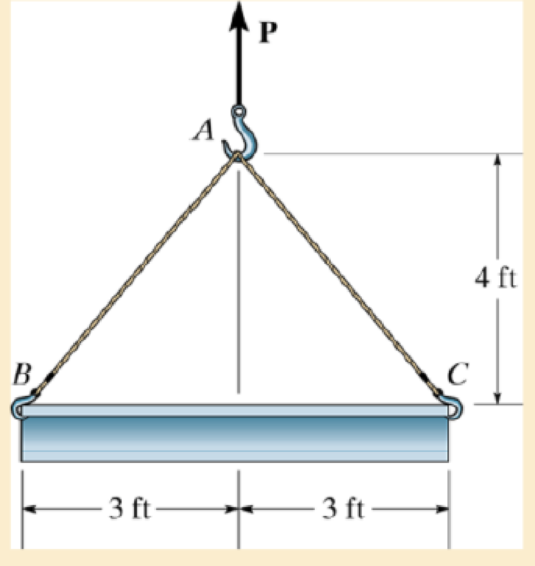
Each of the cables can sustain a maximum tension of 5000 lb. If the uniform beam has a weight of 5000 lb, determine the shortest time possible to lift the beam with a speed of 10 ft/s starting from rest.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The rod of the fixed hydraulic cylinder is moving to the left with a speed of 94 mm/s and this speed is momentarily increasing at a rate
of 440 mm/s each second at the instant when SA = 355 mm. Determine the tension in the cord at that instant. The mass of slider Bis
0.77 kg, the length of the cord is 950 mm, and the effects of the radius and friction of the small pulley at A are negligible. Find results
for cases (a) negligible friction at slider B and (b) p = 0.42 at slider B. The action is in a vertical plane.
220 mm
Answers:
0.77 kg B
(a) Negligible friction: T= i
(b) Uk=0.42:
T= i
N
N
The tractor is used to lift the 170-kg load B with the
24-m-long rope, boom, and pulley system. The tractor
travels to the right with an acceleration of 4 m/s² and
has a velocity of 5 m/s at the instant SA = 5 m. When
SA = 0, SB = 0. (Figure 1)
Figure
12 m
-SA
1 of 1
Part A
Determine the tension in the rope at this instant.
Express your answer to three significant figu
T =
Value
N
Submit Previous Answers Request Answ
X Incorrect; Try Again
If the motor draws in the cable with an acceleration of 3 m/s^2, determine the reactions at the supports A and B. The beam has a uniform mass of 30 kg/m, and the crate has a mass of 200 kg. Neglect the mass of the motor and pulleys.
Chapter 15 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 15 - The 0.5kg ball strikes the rough ground and...Ch. 15 - Prob. 2FPCh. 15 - Prob. 3FPCh. 15 - The wheels of the 1.5-Mg car generate the traction...Ch. 15 - Prob. 5FPCh. 15 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 3PCh. 15 - Each of the cables can sustain a maximum tension...Ch. 15 - Crates A and B weigh 100 lb and 50 lb,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 8P
Ch. 15 - Prob. 9PCh. 15 - During operation the jack hammer strikes the...Ch. 15 - For a short period of time, the frictional driving...Ch. 15 - The 2.5-Mg van is traveling with a speed of 100...Ch. 15 - Prob. 14PCh. 15 - The towing force acting on the 400-kg safe varies...Ch. 15 - Prob. 18PCh. 15 - Prob. 19PCh. 15 - If it takes 35 s for the 50-Mg tugboat to increase...Ch. 15 - Prob. 23PCh. 15 - The balloon has a total mass of 400 kg including...Ch. 15 - Prob. 26PCh. 15 - Prob. 30PCh. 15 - Prob. 7FPCh. 15 - The cart and package have a mass of 20 kg and 5...Ch. 15 - The 5-kg block A has an initial speed of 5 m/s as...Ch. 15 - Prob. 10FPCh. 15 - Prob. 11FPCh. 15 - The cannon and support without a projectile have a...Ch. 15 - The 5-Mg bus B is traveling to the right at 20...Ch. 15 - Prob. 36PCh. 15 - A railroad car having a mass of 15 Mg is coasting...Ch. 15 - A ballistic pendulum consists of a 4-kg wooden...Ch. 15 - Prob. 39PCh. 15 - Prob. 43PCh. 15 - Prob. 44PCh. 15 - Prob. 45PCh. 15 - The 30-Mg freight car A and 15-Mg freight car B...Ch. 15 - Blocks A and B have masses of 40 kg and 60 kg,...Ch. 15 - Block A has a mass of 5 kg and is placed on the...Ch. 15 - Solve Prob. 15-53 if the coefficient of kinetic...Ch. 15 - Prob. 56PCh. 15 - Prob. 13FPCh. 15 - Prob. 14FPCh. 15 - The 30-lb package A has a speed of 5 ft/s when it...Ch. 15 - The ball strikes the smooth wall with a velocity...Ch. 15 - Prob. 17FPCh. 15 - Prob. 18FPCh. 15 - Prob. 58PCh. 15 - Prob. 59PCh. 15 - Prob. 61PCh. 15 - Prob. 62PCh. 15 - Prob. 63PCh. 15 - Prob. 64PCh. 15 - A 1-lb ball A is traveling horizontally at 20 ft/s...Ch. 15 - Prob. 69PCh. 15 - Prob. 73PCh. 15 - Two smooth disks A and B each have a mass of 0.5...Ch. 15 - Prob. 75PCh. 15 - The cue ball A is given an initial velocity (vA)1...Ch. 15 - Prob. 78PCh. 15 - Prob. 79PCh. 15 - A ball of negligible size and mass m is given a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 81PCh. 15 - The 20-lb box slides on the surface for which k =...Ch. 15 - Prob. 84PCh. 15 - Prob. 85PCh. 15 - Prob. 90PCh. 15 - Prob. 92PCh. 15 - Disks A and B have a mass of 15 kg and 10 kg,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 19FPCh. 15 - Prob. 20FPCh. 15 - Initially the 5-kg block is moving with a constant...Ch. 15 - Prob. 22FPCh. 15 - Prob. 23FPCh. 15 - Prob. 24FPCh. 15 - Determine the angular momentum HO of the 6-lb...Ch. 15 - Determine the angular momentum HP of the 6-lb...Ch. 15 - Prob. 96PCh. 15 - Determine the angular momentum Hp, of each of the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 98PCh. 15 - Determine the angular momentum Hp of the 3-kg...Ch. 15 - The 800-lb roller-coaster car starts from rest on...Ch. 15 - The 800-lb roller-coaster car starts from rest on...Ch. 15 - If the rod of negligible mass is subjected to a...Ch. 15 - The amusement park ride consists of a 200-kg car...Ch. 15 - An earth satellite of mass 700 kg is launched into...Ch. 15 - Prob. 115PCh. 15 - Prob. 116PCh. 15 - Prob. 119PCh. 15 - The gauge pressure of water at A is 150.5 kPa....Ch. 15 - Prob. 121PCh. 15 - The fountain shoots water in the direction shown....Ch. 15 - A plow located on the front of a locomotive scoops...Ch. 15 - Prob. 124PCh. 15 - Water is discharged from a nozzle with a velocity...Ch. 15 - Prob. 127PCh. 15 - Prob. 128PCh. 15 - Sand drops onto the 2-Mg empty rail car at 50 kg/s...Ch. 15 - Prob. 133PCh. 15 - A rocket has an empty weight of 500 lb and carries...Ch. 15 - Prob. 135PCh. 15 - Prob. 138PCh. 15 - The missile weighs 40 000 lb. The constant thrust...Ch. 15 - Prob. 140PCh. 15 - Prob. 1RPCh. 15 - Prob. 2RPCh. 15 - Prob. 3RPCh. 15 - Prob. 4RPCh. 15 - The 200-g projectile is fired with a velocity of...Ch. 15 - Block A has a mass of 3 kg and is sliding on a...Ch. 15 - Two smooth billiard balls A and B have an equal...Ch. 15 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The steel ingot has a mass of 1940 kg. It travels along the conveyor at a speed v= 0,2 m/s when it collides with the "nested" spring assembly. If the stiffness of the outer spring is Ka= 5 kN/m, determine the required stiffness Kb of the inner spring so that the motion of the ingot is stopped at the moment the front, C, of the ingot is 0.3 m from the wall. (Answer in kN/m) 0.5 m -0.45 m kB k Barrow_forwardThe 250-N block rests upon a level plane for which fk = 0.2. It is pulled by force P= 100N inclined at 20o with the horizontal. Find the velocity of the block after it moves 20m starting from rest.arrow_forwardA cart has a mass of 1.5 kg. It is given some initial push toward a sensor and is slowed by a hanging mass which makes the cart turn around and speed up as it returns to its original position. This situation is illustrated in the attached image. If the acceleration towards the sensor is 0.5 m/s2 and the accaleration away from the sensor is 0.15 m/s2, a. draw the free body diagrams for the cart moving towards the sensor and away from the sensor. b. Write Newton's law for both situations and solve for the frictional force and for the force from the hanging mass.arrow_forward
- solve, answer is provided, show all steps.arrow_forwardThe super-container vessel has a total mass displacement of 23000 long tons. This vessel towed by a tugboat with α=20⁰ angle with horizontal. If a constant tension is applied as F=320 kN by the tugboat, please calculate the time to bring the vessel to a speed of 2 knot from the rest. At these low speeds, please neglect the hull resistance that created by the motion. Note: (1 long tons = 1016.05 kg, 1 knot=1.151 mi/hr= 0.5144 m/s)arrow_forwardThe roller coaster car has a mass of 700 kg, including its passenger. If it starts from the top of the hill A with a speed v A = 3 m/s, determine the minimum height h of the hill crest so that the car travels around the inside loops without leaving the track. Neglect friction, the mass of the wheels, and the size of the car. What is the normal reaction on the car when the car is at B find the Max g-force on passenger, bank angle the force required to slow down the motion and the time the force is applied must be determined to bring the coaster to rest. The maximum G-load experienced by a person should be no more than 5 g and fint the bank angle B h 15 marrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardPlease draw the free body diagram and each step of the work please and thank youarrow_forwardThe 150-lb car of an amusement partk ride is connected to a rotating telescopic boom. When r = 15 ft, the car is moving on a horizontal circular path with a speed of 30 ft/s. If the boom is shortened at a rate of 3 ft/s, determine the speed of the car when r = 10 ft. Also, find the work done by the axial for F along the boom. Neglect the size of the car and the mass of the boom.arrow_forward
- Determine the maximum vertical height h which the rollercoaster will reach on the second slope. Include an FBD for the rollercoaster while it is ascending (going up) the slope on the right. Use conservation of energy.arrow_forward3. The smooth 160-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a negligible diameter. It is carried on a truck as shown. Determine the maximum acceleration which the truck can have without causing the normal reaction at A to be zero (i.e. lifting the pipe). Also determine the horizontal and vertical components of force which the truck exerts on the pipe at B at that acceleration. 20 ft 5 ft B 12 ftarrow_forwardDetermine the skier's speed when he reaches point B on the smooth slope. Also, what is the normal force on the skier's skis at BB? What is the skier's rate of increase in speed at BB?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License