
Concept explainers
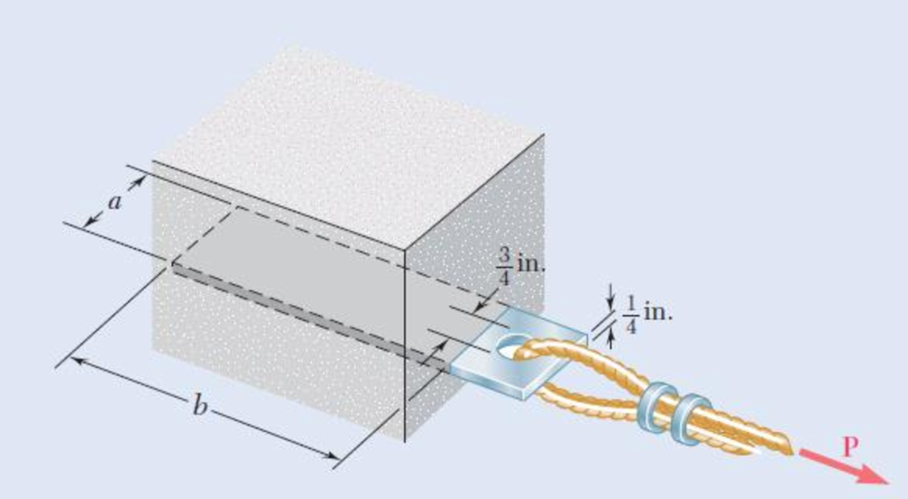
Determine the factor of safety for the cable anchor in Prob. 1.49 when P = 2.5 kips, knowing that a = 2 in. and b = 6 in.
1.49 A steel plate
Fig. P1.49
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardaversity of Baoyion aculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023, st Course, 1st Attempt Stage: 3rd Subject: Heat Transfer I Date: 2023\01\23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Q4: A thick slab of copper initially at a uniform temperature of 20°C is suddenly exposed to radiation at one surface such that the net heat flux is maintained at a constant value of 3×105 W/m². Using the explicit finite-difference techniques with a space increment of Ax = = 75 mm, determine the temperature at the irradiated surface and at an interior point that is 150 mm from the surface after 2 min have elapsed. Q5: (12.5 M) A) A steel bar 2.5 cm square and 7.5 cm long is initially at a temperature of 250°C. It is immersed in a tank of oil maintained at 30°C. The heat-transfer coefficient is 570 W/m². C. Calculate the temperature in the center of the bar after 3 min. B) Air at 90°C and atmospheric pressure flows over a horizontal flat plate at 60 m/s. The plate is 60 cm square and is maintained at a…arrow_forwardUniversity of Baby on Faculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023. 1 Course, 1" Attempt Stage 3 Subject Heat Transfer I Date: 2023 01 23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Notes: Q1: • • Answer four questions only Use Troles and Appendices A) A flat wall is exposed to an environmental temperature of 38°C. The wall is covered with a layer of insulation 2.5 cm thick whose thermal conductivity is 1.4 W/m. C, and the temperature of the wall on the inside of the insulation is 315°C. The wall loses heat to the environment by convection. Compute the value of the convection heat-transfer coefficient that must be maintained on the outer surface of the insulation to ensure that the outer-surface temperature does not exceed 41°C. B) A vertical square plate, 30 cm on a side, is maintained at 50°C and exposed to room air at 20°C. The surface emissivity is 0.8. Calculate the total heat lost by both sides of the plate. (12.5 M) Q2: An aluminum fin 1.5 mm thick is placed on a circular tube…arrow_forward
- Solve this and show all of the workarrow_forwardNeed helparrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





