
Concept explainers
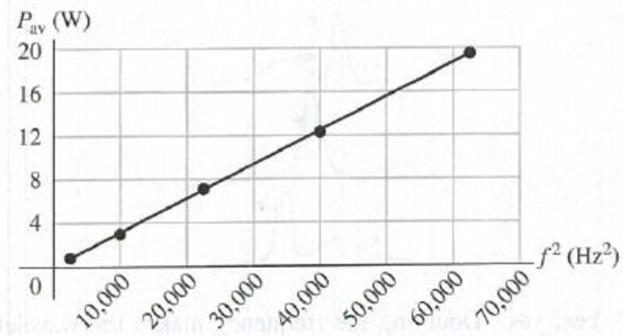
DATA You are measuring the frequency dependence of the average power Pav transmitted by traveling waves on a wire. In your experiment you use a wire with linear mass density 3.5 g/m. For a transverse wave on the wire with amplitude 4.0 mm. you measure Pav (in watts) as a function of the frequency f of the wave (in Hz). You have chosen to plot Pav as a function of f2 (Fig. F15.76). (a) Explain why values of Pav plotted versus f2 should be well fit by a straight line. (b) Use the slope of the straight-line fit to the data shown in Fig P15.76 to calculate the speed of the waves. (c) What angular frequency ω would result in Pav = 10.0 W?
Figure P15.76
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Conceptual Integrated Science
- You place your ear onto a steel railroad track and hear the sound of a distant train through the rails Δt = 2.7 seconds before you do through the air. The speed of sound in steel is vs = 6100 m/s, and and the air temperature is 36° C. Find the distance, D, to the train in meters.arrow_forwardA pulsar is a type of rotating neutron star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation. Imagine a pulsar that is moving toward Earth at a speed of 875.500 km/s. It emits mostly radio waves with a wavelength (at the source) of 124.000 cm. What is the observed wavelength of this radiation on Earth? (Assume the Earth is stationary. Consider the speed of light c = 3.00000 108 m/s. Give your answer to at least six significant figures.)______________ cmarrow_forwardThe mathematical form of a wave packet formed by linear superposition of sinusoidal waves with constant amplitude A and wave numbers in the range k - Ak to k + A k is: rx + Ax S** а. y(x,t) = Acos (k't – o't) dk X- Ax b. rk+ Ak y(x,t) = / k - Ak Acos (k'x – w't) dk' w + A O c. y(x,t) = S** Acos (k'x – o't) do' ω-Δω O d. y(x,t) i+ At Acos (k'x – o't) dt' 1- Atarrow_forward
- E16P1arrow_forwardA sinusoidal wave of Vmax = 10 V and T= 40 ms periodic time, Calculate the following: Veff=Vrms of this wave: The frequency f : Write the equation of this wave using V=Vmax sin [ (2πf)]tarrow_forwardAs we said, sound waves can be modeled with sine waves. The standard musical pitch is the A440 which means that the musical note A4 has a frequency of 440 Hz. So this note oscillates once every seconds and it could be modeled using the curve y = sin(440- 2nt) = sin(880nt). For each of the following musical notes, what would w be if we wanted to model the sound wave with y = sin(wt)? !! %3D (a) (i) C4, (261.63 Hz (iii) E4, (329.63 Hz) (v) G4, (392 Hz) (ii) D4, (293.66 Hz) (iv) F4, (349.23 Hz) (vi) B4, (493.88 Hz)arrow_forward
- A pulsar is a type of rotating neutron star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation. Imagine a pulsar that is moving toward Earth at a speed of 743.000 km/s. It emits mostly radio waves with a wavelength (at the source) of 137.000 cm. What is the observed wavelength of this radiation on Earth? (Assume the Earth is stationary. Consider the speed of light c = 3.00000 x 108 m/s. Give your answer to at least six significant figures.) 4.0 cm Additional Materialsarrow_forwardAM radio signals are broadcast at frequencies between 550 kHz (kilohertz) and 1600 kHz and travel at 3 x 10^8 m/s. a) What is the range of wavelengths for those signals? b) FM frequencies range between 88 MHz (megahertz) and 108 MHz and travel at the the same speed. What is the range of the FM frequencies.arrow_forwardConsider electromagnetic waves in free space. What is the wavelength of a wave that has the following frequencies? (a) 4.74 x 10¹¹ Hz m (b) 7.52 x 1016 Hz marrow_forward
- If the propagation speed of the wave is 1*10^7 m/s in a coaxial transmission line whose conductors are filled with dielectric material, what is the phase velocity of the wave in Mm/s (megameters/second)?arrow_forwardWrite your understanding about coherent waves. A steel wire in a piano has a length of L = 0.9m and a mass of m = 5.4 g. To what tension T must this wire be stretched so that its fundamental а. vibration possess a frequency f= 261.6 Hz? b. The equation of a plane sound wave is, y(x, t) = 6.0 × 10-6 sin(5.7x – 1500t). Find the frequency, the wavelength and the velocity of the wave. Compare the wavelength with the amplitude of the oscillations and the wave velocity with the amplitude of the velocity of the oscillations. What is the phase shift between the oscillations of two points 30.0 cm apart in the direction of the sound wave?arrow_forwardAM radio signals are broadcast at frequencies between 550 kHz (kilohertz) and 1600 kHz and travel at 3 x 10^8 m/s. a) What is the range of wavelengths for those signals? b) FM frequencies range between 88 MHz (megahertz) and 108 MHz and travel at the same speed. What is the wavelength range of the FM frequencies.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





