
(a)
Interpretation:
The compound that has higher solubility in water among the given pair has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom.
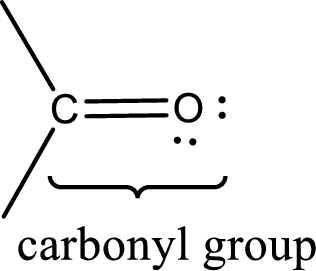
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that contains a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom bonded to it. Aldehyde that has one and two carbon atoms are gas at room temperature. The physical state of aldehyde that contains three carbon atoms to eleven carbon atoms that are not branched is liquid at room temperature. Aldehydes that contain more than eleven carbon atoms are solid at room temperature.
Ketones contain a carbonyl group that contains two carbon atoms bonded to it. For a compound to be ketone, a minimum of three carbon atom is required. Ketones that contain three carbon atoms to eight carbon atoms which have the carbonyl group at the second carbon atom are liquid at room temperature.
Solubility of aldehydes and ketones depend upon the length of the carbon chain. Those contain less than six carbon atoms are soluble in both water and organic solvents. Aldehydes and ketones that contain six or more carbon atoms are not soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents only. Solubility of smaller ketones and aldehydes are result of the hydrogen bond formation between the lone pairs of oxygen atom and the hydrogen atom in the water molecule.
(b)
Interpretation:
The compound that has higher solubility in water among the given pair has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
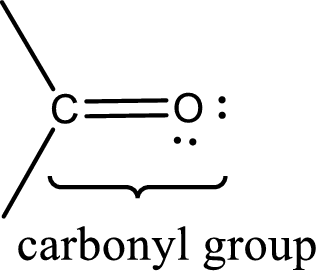
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that contains a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom bonded to it. Aldehyde that has one and two carbon atoms are gas at room temperature. The physical state of aldehyde that contains three carbon atoms to eleven carbon atoms that are not branched is liquid at room temperature. Aldehydes that contain more than eleven carbon atoms are solid at room temperature.
Ketones contain a carbonyl group that contains two carbon atoms bonded to it. For a compound to be ketone, a minimum of three carbon atom is required. Ketones that contain three carbon atoms to eight carbon atoms which have the carbonyl group at the second carbon atom are liquid at room temperature.
Solubility of aldehydes and ketones depend upon the length of the carbon chain. Those contain less than six carbon atoms are soluble in both water and organic solvents. Aldehydes and ketones that contain six or more carbon atoms are not soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents only. Solubility of smaller ketones and aldehydes are result of the hydrogen bond formation between the lone pairs of oxygen atom and the hydrogen atom in the water molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Select all of the following that the ablation (knockout) or ectopoic expression (gain of function) of Hox can contribute to. Another set of wings in the fruit fly, duplication of fingernails, ectopic ears in mice, excess feathers in duck/quail chimeras, and homeosis of segment 2 to jaw in Hox2a mutantsarrow_forwardSelect all of the following that changes in the MC1R gene can lead to: Changes in spots/stripes in lizards, changes in coat coloration in mice, ectopic ear formation in Siberian hamsters, and red hair in humansarrow_forwardPleiotropic genes are genes that (blank) Cause a swapping of organs/structures, are the result of duplicated sets of chromosomes, never produce protein products, and have more than one purpose/functionarrow_forward
- A loss of function mutation in Pitx1 enhancers can cause (blank) Removal of Pitx1 exons and growth of ectopic hindlimbs, growth of extra ectopic forelimbs, loss of forelimb specification and development, and loss of hindlimb specification and developmentarrow_forwardHox1a most likely contributes to (blank) patterning in the developing embryo? Ventral, posterior, limb or anteriorarrow_forwardSelect all of the following that can help establish Hox gene expression boundaries (things that affect Hox and not things that Hox affects). Retinoic acid, anterior/posterior axis, fibroblast growth factors, vagal neural crest, and enhancersarrow_forward
- Ectopic expression of Hox often results in (blank) phenotypes. (Blank) transformations are characterized by the replacement of one body part/structure with another. Hoxeotic, homealoneotic, joexotic, or homeoticarrow_forwardWhat's the difference when drawing omega-6 and omega-3?arrow_forward. Consider a base substitution mutation that occurred in a DNA sequence that resulted in a change in the encoded protein from the amino acid glutamic acid to aspartic acid. Normally the glutamic acid amino acid is located on the outside of the soluble protein but not near an active site. O-H¨ A. What type of mutation occurred? O-H B. What 2 types of chemical bonds are found in the R-groups of each amino acid? The R groups are shaded. CH2 CH2 CH2 H2N-C-COOH H2N-C-COOH 1 H Glutamic acid H Aspartic acid C. What 2 types of bonds could each R-group of each of these amino acids form with other molecules? D. Consider the chemical properties of the two amino acids and the location of the amino acid in the protein. Explain what effect this mutation will have on this protein's function and why.arrow_forward
- engineered constructs that consist of hollow fibers are acting as synthetic capillaries, around which cells have been loaded. The cellular space around a single fiber can be modeled as if it were a Krogh tissue cylinder. Each fiber has an outside “capillary” radius of 100 µm and the “tissue” radius can be taken as 200 µm. The following values apply to the device:R0 = 20 µM/secaO2 = 1.35 µM/mmHgDO2,T = 1.67 x 10-5 cm2/secPO2,m = 4 x 10-3 cm/secInstead of blood inside the fibers, the oxygen transport and tissue consumption are being investigated by usingan aqueous solution saturated with pure oxygen. As a result, there is no mass transfer resistance in the synthetic“capillary”, only that due to the membrane itself. Rather than accounting for pO2 variations along the length ofthe fiber, use an average value in the “capillary” of 130 mmHg.Is the tissue fully oxygenated?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help with question. thank you You are studying the expression of the lac operon. You have isolated mutants as described below. In the presence of glucose, explain/describe what would happen, for each mutant, to the expression of the lac operon when you add lactose AND what would happen when the bacteria has used up all of the lactose (if the mutant is able to use lactose).5. Mutations in the lac operator that strengthen the binding of the lac repressor 200 fold 6. Mutations in the promoter that prevent binding of RNA polymerase 7. Mutations in CRP/CAP protein that prevent binding of cAMP8. Mutations in sigma factor that prevent binding of sigma to core RNA polymerasearrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help and there is an attached image. Thank you. A bacteria has a gene whose protein/enzyme product is involved with the synthesis of a lipid necessary for the synthesis of the cell membrane. Expression of this gene requires the binding of a protein (called ACT) to a control sequence (called INC) next to the promoter. A. Is the expression/regulation of this gene an example of induction or repression?Please explain:B. Is this expression/regulation an example of positive or negative control?C. When the lipid is supplied in the media, the expression of the enzyme is turned off.Describe one likely mechanism for how this “turn off” is accomplished.arrow_forward

 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





