
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 15.35P
For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the moment-area method.
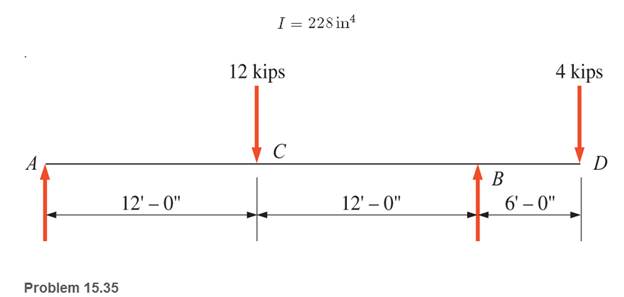
15.35 A structural steel wide-flange section is loaded as shown. Calculate the maximum deflection between the supports and the deflection of the free end. Assume that
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3-55 A multifluid container is connected to a U-tube,
as shown in Fig. P3–55. For the given specific gravities
and fluid column heights, determine the gage pressure at
A. Also determine the height of a mercury column that
would create the same pressure at A. Answers: 0.415 kPa,
0.311 cm
I need help answering parts a and b
Required information
Water initially at 200 kPa and 300°C is contained in a piston-cylinder device fitted with stops. The water is allowed to cool
at constant pressure until it exists as a saturated vapor and the piston rests on the stops. Then the water continues to cool
until the pressure is 100 kPa.
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Water
200 kPa
300°C
On the T-V diagram, sketch, with respect to the saturation lines, the process curves passing through the initial, intermediate, and final states of the water. Label the
T, P, and V values for end states on the process curves.
Please upload your response/solution by using the controls provided below.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 15 - A 14 in.-diameter aluminum rod is bent into a...Ch. 15 - 15.2 Calculate the maximum bending stress produced...Ch. 15 - A 500 -mm-long steel bar having a cross section of...Ch. 15 - 15.4 An aluminum wire has a diameter of in....Ch. 15 - 15.5 A -in.-wide by in.-thick board is bent to a...Ch. 15 - 15.6 A Douglas fir beam is in. wide and in. deep....Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.7PCh. 15 - For Problems 15.7 through 15.14, use the formula...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.7 through 15.14, use the formula...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.7 through 15.14, use the formula...
Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.7 through 15.14, use the formula...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.7 through 15.I4, use the formula...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.7 through 15.14, use the formula...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.7 through 15.14, use the formula...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.15 through 15.26, use the...Ch. 15 - 15.27 Draw the moment diagram by parts for the...Ch. 15 - 15.28 Draw the moment diagram by parts for the...Ch. 15 - 15.29 Draw the moment diagram by parts for the...Ch. 15 - 15.30 For the beam shown, draw the conventional...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - For Problems 15.31 through 15.43, use the...Ch. 15 - 15.49 If the elastic limit of a steel wire is...Ch. 15 - 15.50 Calculate the bending moment required to...Ch. 15 - 15.51 A 6-ft-long cantilever beam is subjected to...Ch. 15 - 15.52 A structural steel wide-flange section is...Ch. 15 - 15.53 A simply supported structural steel...Ch. 15 - 15.54 A structural steel wide-flange shape is...Ch. 15 - A solid, round simply supported steel shaft is...Ch. 15 - Using the moment-area method, check the...Ch. 15 - 15.57 A 1-in.-diameter steel bar is 25 ft long and...Ch. 15 - 15.58 A 102-mm nominal diameter standard-weight...Ch. 15 - I 5.59 Compute the maximum deflection for the...Ch. 15 - An 8-in-wide by 12-in-deep redwood timber beam...Ch. 15 - 15.61 A solid steel shaft 3 in. in diameter and 20...Ch. 15 - 15.62 For the beam shown, draw the conventional...Ch. 15 - 15.63 Rework Problem 15.62 with concentrated loads...Ch. 15 - 15.64 A solid steel shaft 3 in. in diameter and 20...Ch. 15 - 15.65 A structural steel wide-flange section is...Ch. 15 - 15.66 A 6-in.-by-10-in, hem-fir timber beam (S4S)...Ch. 15 - 15.67 A simply supported structural steel...Ch. 15 - Calculate the maximum permissible span length for...Ch. 15 - 15.69 A structural steel wide-flange section 10 ft...Ch. 15 - 15.70 A structural steel wide-flange section...Ch. 15 - 15.71 Determine the deflection at point C and...Ch. 15 - 15.72 Calculate the deflection midway between the...Ch. 15 - 15.73 Derive an expression for the maximum...Ch. 15 - 15.74 Derive an expression for the maximum...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the change in the volume of the cylinder of the refrigerant-134a if the specific volume and enthalpy of R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and -10°C and at the final state of 90.4 kPa and 15°C are as follows: = 0.2418 m³/kg, h₁ = 247.77 kJ/kg 3 v2 = 0.2670 m³/kg, and h₂ = 268.18 kJ/kg The change in the volume of the cylinder is marrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the final pressure of the refrigerant-134a. The final pressure is kPa.arrow_forwardThe hydraulic cylinder BC exerts on member AB a force P directed along line BC. The force P must have a 560-N component perpendicular to member AB. A M 45° 30° C Determine the force component along line AB. The force component along line AB is N.arrow_forward
- ! Required information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. A 15° 25° B T₂ Using trigonometry, determine the required tension T₂ in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical. The required tension is lb.arrow_forwardWhat are examples of at least three (3) applications of tolerance fitting analysis.arrow_forwardThe primary material used in the production of glass products is silica sand. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Which one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forwardIn the lost foam process, the pattern doesn’t need to be removed from the mold. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Tempering eliminates internal stresses in glass. True or Falsearrow_forwardThermoset polymers can be recycled with little to no degradation in properties. True or Falsearrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY