
(a)
Interpretation:
The missing products have to be predicted and the balanced equation has to be written for the decomposition and chlorination of diborane to boron trichloride.
Concept Introduction:
Decomposition reaction:
It is an elimination reaction. When a saturated reactant becomes an unsaturated (presence of double bond) product, the reaction is said to be elimination reaction. In elimination reaction, two products are formed from one reactant.
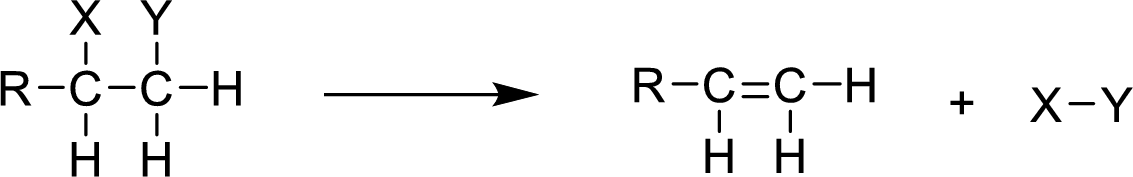
Chlorination:
The addition halogens to the organic compounds is said to be halogenation and the addition of chlorine atoms to the organic compound is said to be chlorination.
(b)
Interpretation:
The missing products has to be predicted and the balanced equation has to be written for the combustion of Pentaborane (
Concept Introduction:
Combustion reaction:
When hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water, the reaction is said to be combustion.
(c)
Interpretation:
The missing products has to be predicted and the balanced equation has to be written for the hydrolysis of trisilane (
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis:
Addition of water molecule to the reactant to form the product is known as hydrolysis.
(d)
Interpretation:
The missing products has to be predicted and the balanced equation has to be written for the complete halogenation of disilane with
Concept Introduction:
Halogenation:
The addition halogens (
(e)
Interpretation:
The missing products have to be predicted and the balanced equation has to be written for the thermal decomposition of
Concept Introduction:
Thermal decomposition:
It is an elimination reaction which occurs in presence of light. When a saturated reactant becomes an unsaturated (presence of double bond) product, the reaction is said to be elimination reaction. In elimination reaction, two products are formed from one reactant.
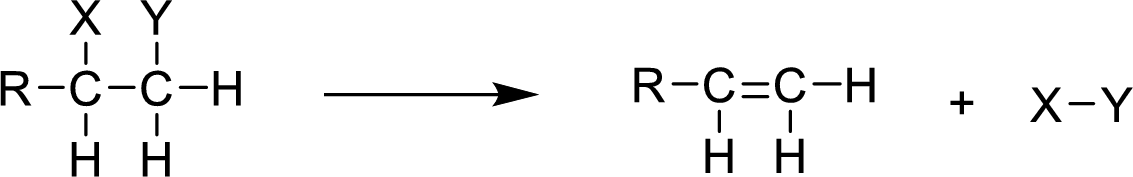
(f)
Interpretation:
The missing products has to be predicted and the balanced equation has to be written for the hydrolysis of
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis:
Addition of water molecule to the reactant to form the product is known as hydrolysis.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change - Standalone book
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 9arrow_forwardalekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forward
- x + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forwardS: Using a phase diagram leksogi/x/sl.exe/1ou-IgNs kr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZdHYU+80XL-5alyVp O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure se the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 1.6 atm. pressure (atm) 32- 16- solid liquid 0. gas 100 200 temperature (K) 300 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. 10 Explanation Check § Q Search J 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Researrow_forward151.2 254.8 85.9 199.6 241.4 87.6 242.5 186.4 155.8 257.1 242.9 253.3 256.0 216.6 108.7 239.0 149.7 236.4 152.1 222.7 148.7 278.2 268.7 234.4 262.7 283.2 143.6 QUESTION: Using this group of data on salt reduced tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forward
- Results Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unloc xb Success Confirmation of Q x O Google Pas alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCavJ17dZtpxbFD0Qggd1J O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Gabr 3/5 he pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 101. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample sublime? Use the phase diagram of X below to nd your answer. pressure (atm) 24- 12 solid liquid gas 200 400 temperature (K) 600 ote: your answer must be within 0.15 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm Thanation Check © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center I Q Search L³ ملةarrow_forward301.7 348.9 193.7 308.6 339.5 160.6 337.7 464.7 223.5 370.5 326.6 327.5 336.1 317.9 203.8 329.8 221.9 331.7 211.7 309.6 223.4 353.7 334.6 305.6 340.0 304.3 244.7 QUESTION: Using this group of data on regular tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardSearch Results Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unlo x b Success Confirmation of Q aleks.com/alekscgi/x/sl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTIOHz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCav States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 0. 32- 16 solid liquid gas 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Дос Xarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





