
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
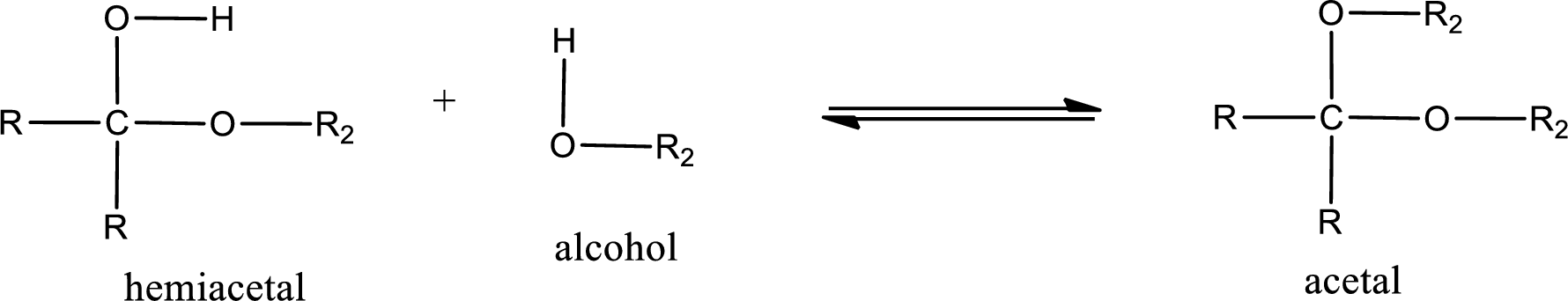
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
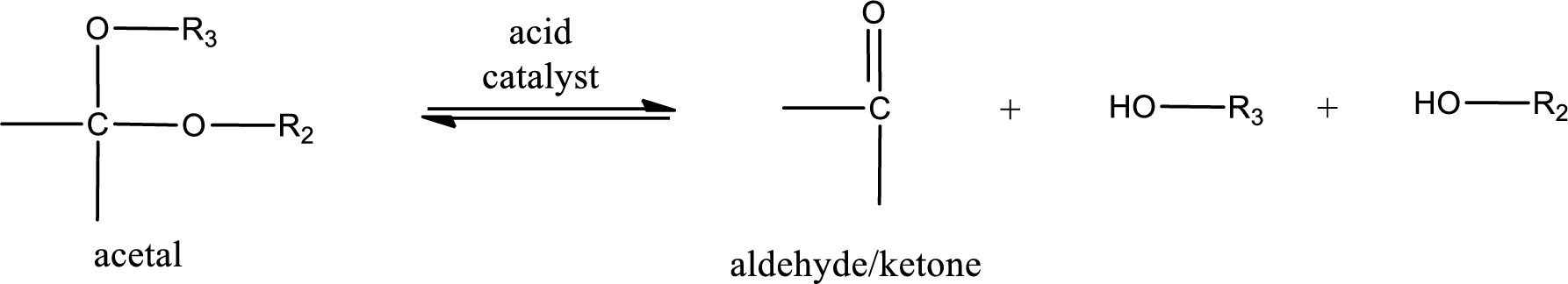
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which the compound splits into two or more fragments when water is added to the compound in presence of acid or base as catalyst. Acetals undergo hydrolysis to give the respective starting materials from which it is formed.
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
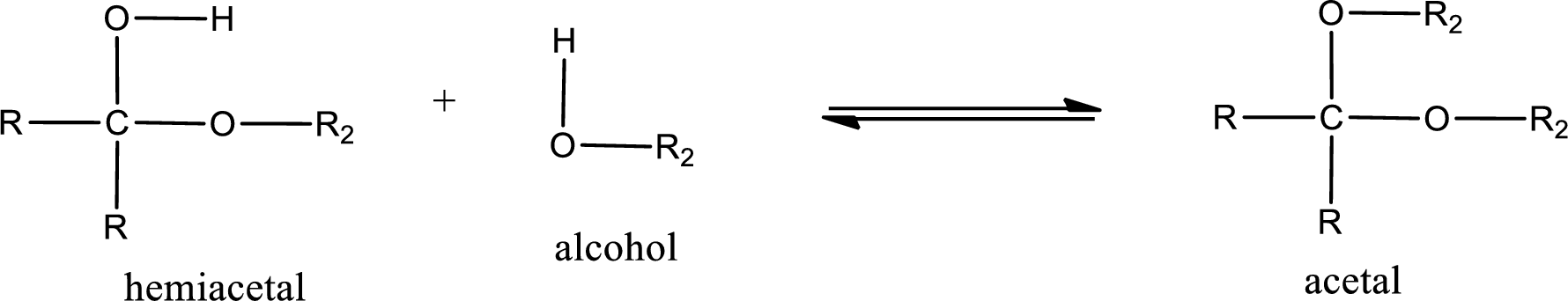
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
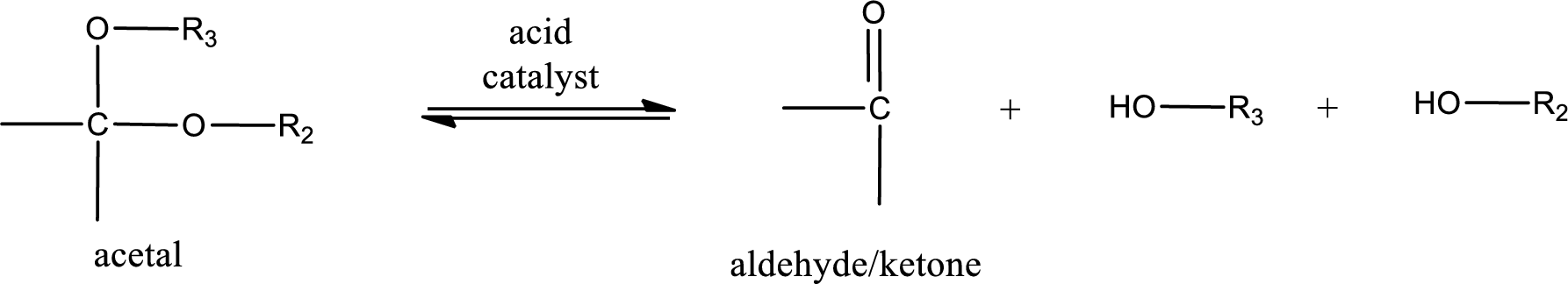
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which the compound splits into two or more fragments when water is added to the compound in presence of acid or base as catalyst. Acetals undergo hydrolysis to give the respective starting materials from which it is formed.
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
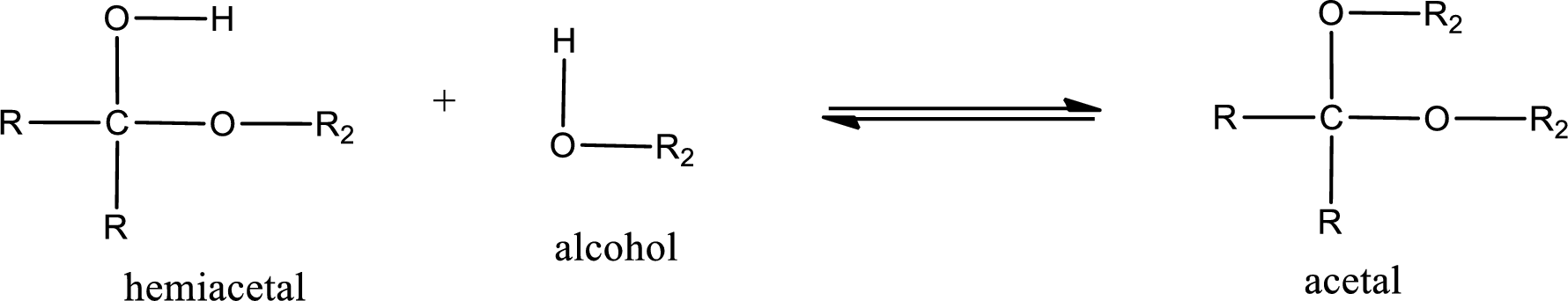
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
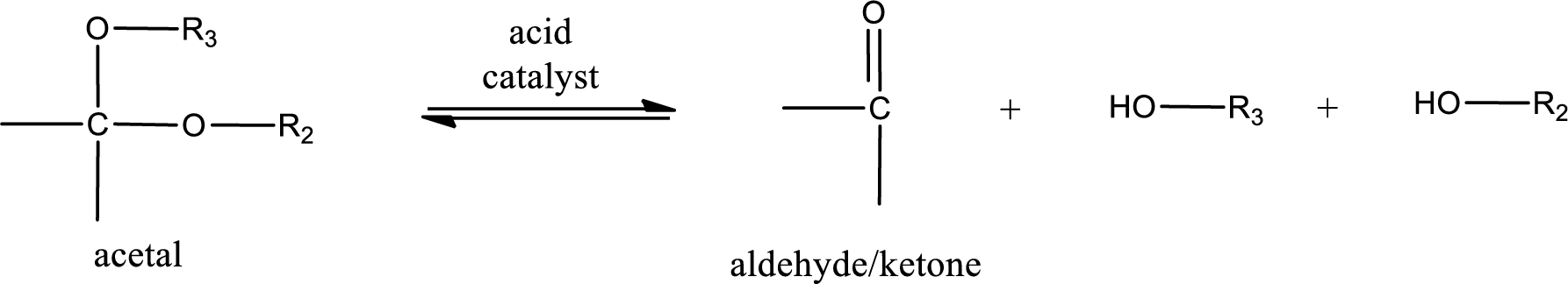
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which the compound splits into two or more fragments when water is added to the compound in presence of acid or base as catalyst. Acetals undergo hydrolysis to give the respective starting materials from which it is formed.
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
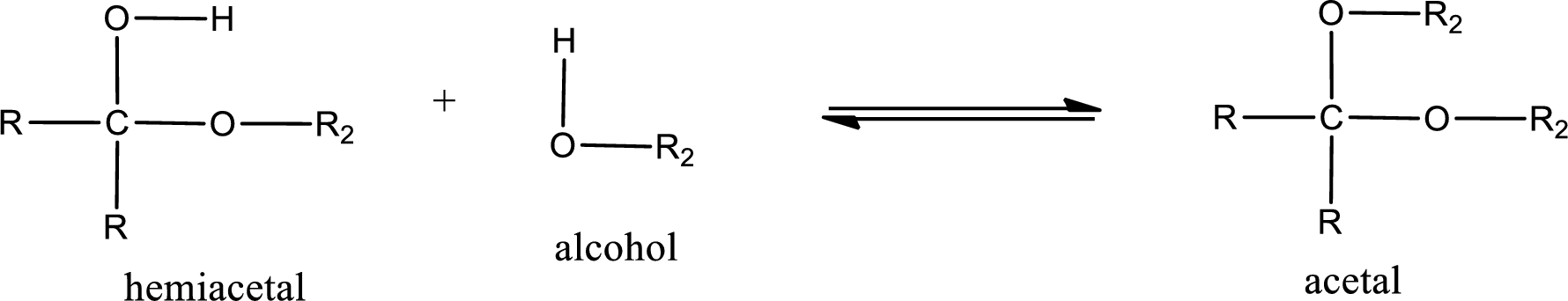
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
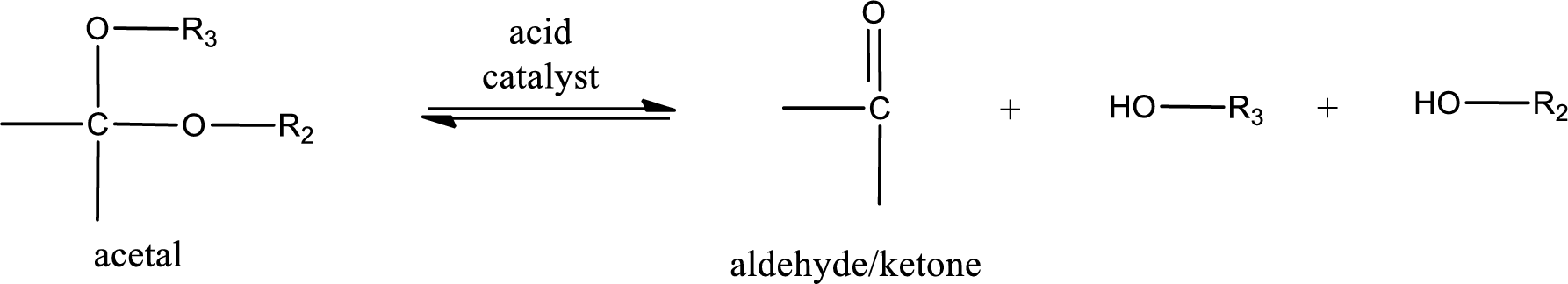
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 15 Solutions
General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry, Hybrid (with Owlv2 Quick Prep For General Chemistry Printed Access Card)
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





