
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260916942
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.1, Problem 14.17P
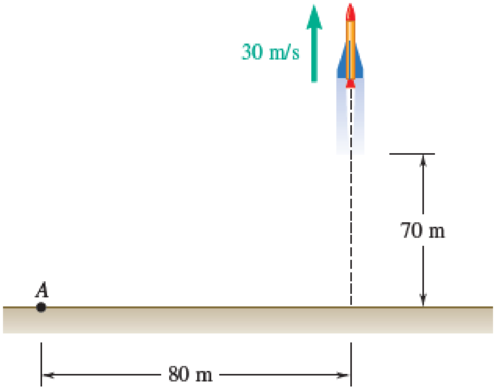
A 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and reaches an altitude of 70 m with a speed of 30 m/s at the end of powered flight, time t = 0. As the rocket approaches its maximum altitude, it explodes into two parts of masses mA = 0.7 kg and mB = 1.3 kg. Part A is observed to strike the ground 80 m west of the launch point at t = 6 s. Determine the position of part B at that time.
Fig. P14.17
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
0 = 6
a = 25
t = 3
Y
b = 30
x
Solve this problem and show all of the work
b = 25
y
t = 2
a=10
C = 25
Chapter 14 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
Ch. 14.1 - A 30-g bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at...Ch. 14.1 - An airline employee tosses two suitcases in rapid...Ch. 14.1 - Car A weighing 4000 lb and car B weighing 3700 lb...Ch. 14.1 - Two swimmers A and B, of weight 190 lb and 125 lb,...Ch. 14.1 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand side by side...Ch. 14.1 - A 40-Mg boxcar A is moving in a railroad...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical cars A and B are at rest on a...Ch. 14.1 - A 20-kg base satellite deploys three...Ch. 14.1 - For the satellite system of Prob. 14.9, assuming...
Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three particles A, B, and C....Ch. 14.1 - For the system of particles of Prob. 14.13,...Ch. 14.1 - A 13-kg projectile is passing through the origin O...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.16PCh. 14.1 - A 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and...Ch. 14.1 - An 18-kg cannonball and a 12-kg cannonball are...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.21PCh. 14.1 - Two spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a...Ch. 14.1 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.24PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.25PCh. 14.1 - In a scattering experiment, an alpha particle A is...Ch. 14.1 - Derive the relation HO=rmv+HG between the angular...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.28PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.29PCh. 14.1 - Show that the relation MA=HA, where HA is defined...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost due to friction and the...Ch. 14.2 - In Prob. 14.3, determine the energy lost (a) when...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.33PCh. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost as a result of the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.35PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.36PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.37PCh. 14.2 - Ball B is suspended from a cord of length l...Ch. 14.2 - A 15-lb block B starts from rest and slides on the...Ch. 14.2 - A 40-lb block B is suspended from a 6-ft cord...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.41PCh. 14.2 - 14.41 and 14.42 In a game of pool, ball A is...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.43PCh. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.45PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.46PCh. 14.2 - Four small disks A, B, C, and D can slide freely...Ch. 14.2 - In the scattering experiment of Prob. 14.26, it is...Ch. 14.2 - Three identical small spheres, each weighing 2 lb,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small spheres A, B, and C, each of mass m,...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.51PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.52PCh. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 3 kg and 1.5 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 2 kg and 1 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.56PCh. 14.3 - A stream of water with a density of = 1000 kg/m3...Ch. 14.3 - A jet ski is placed in a channel and is tethered...Ch. 14.3 - Tree limbs and branches are being fed at A at the...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.60PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.61PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.62PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.63PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.64PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.65PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.66PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.67PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.68PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.69PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.70PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.71PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.72PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.73PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.74PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.75PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.76PCh. 14.3 - The propeller of a small airplane has a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.78PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.79PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.80PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.81PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.82PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.83PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.84PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.85PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.86PCh. 14.3 - Solve Prob. 14.86, assuming that the chain is...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.88PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.89PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.90PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.91PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.92PCh. 14.3 - A rocket sled burns fuel at the constant rate of...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.94PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.95PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.96PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.97PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.98PCh. 14.3 - Determine the distance traveled by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - A rocket weighs 2600 lb, including 2200 lb of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the altitude reached by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.102PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.103PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.104PCh. 14 - Three identical cars are being unloaded from an...Ch. 14 - A 50-kg mother and her 26-kg son are sledding down...Ch. 14 - An 80-Mg railroad engine A coasting at 6.5 km/h...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.108RPCh. 14 - Mass C, which has a mass of 4 kg, is suspended...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.110RPCh. 14 - A 6000-kg dump truck has a 1500-kg stone block...Ch. 14 - For the ceiling-mounted fan shown, determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.113RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.114RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.115RPCh. 14 - A chain of length l and mass m falls through a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- reading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forward
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY