
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 83P
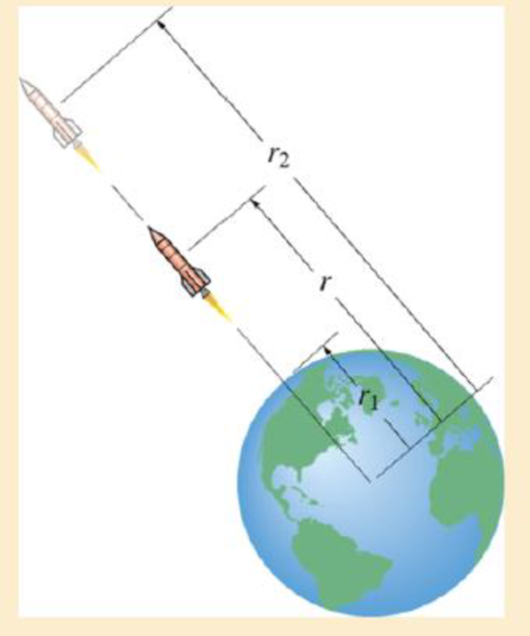
A rocket of mass m is fired vertically from the surface of the earth, i e., at r = r1. Assuming that no mass is lost as it travels upward, determine the work it must do against gravity to reach a distance r2. The force of gravity is F = GMem/r2. (Eq. 13-1, where Me is the mass of the earth and r the distance between the rocket and the center of the earth.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Answer all the calculations questions, if you are not not expert please don't attempt, don't use artificial intelligence
Please measure the size of the following object, and then
draw the front, top and side view in the AutoCAD
(including the printing)
just one arrow
for this one
30
Question 5
Calculate the Moment about the point B in
Nx m
B
500 N
A
2 m
1.2 m
0.8 m
300 N
7
Chapter 14 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 14 - Prob. 1FPCh. 14 - If the motor exerts a constant force of 300 N on...Ch. 14 - If the motor exerts a force of F = (600 + 2s2) N...Ch. 14 - The 1.8-Mg dragster is traveling at 125 m/s when...Ch. 14 - When s = 0.5 m, the spring is unstretched and the...Ch. 14 - The 5-lb collar is pulled by a cord that passes...Ch. 14 - Prob. 2PCh. 14 - The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown....Ch. 14 - Determine the required height h of the roller...Ch. 14 - When the driver applies the brakes of a light...
Ch. 14 - Prob. 7PCh. 14 - The force F, acting in a constant direction on the...Ch. 14 - The 2-lb brick slides down a smooth roof, such...Ch. 14 - The two blocks A and B have weights WA = 60 lb and...Ch. 14 - A small box of mass m is given a speed of v=14gr...Ch. 14 - Prob. 18PCh. 14 - If the cord is subjected to a constant force of F=...Ch. 14 - The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists...Ch. 14 - The 25-lb block has an initial speed of v0 = 10...Ch. 14 - At a given instant the 10-lb block A is moving...Ch. 14 - Prob. 25PCh. 14 - The catapulting mechanism is used to propel the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 27PCh. 14 - Prob. 31PCh. 14 - When the 150-lb skier is at point A he has a speed...Ch. 14 - Prob. 39PCh. 14 - Prob. 40PCh. 14 - If the contact surface between the 20-kg block and...Ch. 14 - Prob. 8FPCh. 14 - Prob. 9FPCh. 14 - Prob. 10FPCh. 14 - Prob. 11FPCh. 14 - Prob. 12FPCh. 14 - The jeep has a weight of 2500 lb and an engine...Ch. 14 - Determine the power Input for a motor necessary to...Ch. 14 - An automobile having a mass of 2 Mg travels up a 7...Ch. 14 - Prob. 45PCh. 14 - To dramatize the loss of energy in an automobile,...Ch. 14 - Escalator steps move with a constant speed of 0.6...Ch. 14 - Prob. 48PCh. 14 - The 1000-lb elevator is hoisted by the pulley...Ch. 14 - The sports car has a mass of 2.3 Mg, and while it...Ch. 14 - Prob. 54PCh. 14 - Prob. 55PCh. 14 - The 50-lb block rests on the rough surface for...Ch. 14 - The 2-kg pendulum bob is released from rest when...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14FPCh. 14 - Prob. 15FPCh. 14 - Prob. 16FPCh. 14 - The 75-lb block is released from rest 5 ft above...Ch. 14 - Prob. 18FPCh. 14 - The girl has a mass of 40 kg and center of mass at...Ch. 14 - The 30-lb block A is placed on top of two nested...Ch. 14 - The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the...Ch. 14 - The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s to the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 71PCh. 14 - The roller coaster car has a mass of 700 kg,...Ch. 14 - The roller coaster car has a mass of 700 kg,...Ch. 14 - Prob. 76PCh. 14 - The roller coaster car having a mass m is released...Ch. 14 - The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and an...Ch. 14 - Prob. 79PCh. 14 - Prob. 80PCh. 14 - When s = 0, the spring on the firing mechanism is...Ch. 14 - If the mass of the earth is Me, show that the...Ch. 14 - A rocket of mass m is fired vertically from the...Ch. 14 - The 4-kg smooth collar has a speed of 3 m/s when...Ch. 14 - Prob. 85PCh. 14 - Prob. 87PCh. 14 - Prob. 90PCh. 14 - The roller coaster car has a speed of 15 ft/s when...Ch. 14 - Prob. 1RPCh. 14 - The small 2-lb collar starting from rest at A...Ch. 14 - Prob. 3RPCh. 14 - Prob. 4RPCh. 14 - Prob. 5RPCh. 14 - Prob. 6RPCh. 14 - Prob. 7RPCh. 14 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given that an L-shaped member (OAB) can rotate about OA, determine the moment vector created by the force about the line OA at the instant shown in the figure below. OA lies in the xy-plane, and the AB part is vertical. Express your answer as a Cartesian vector.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the moment created by the force about the point A.arrow_forward= MMB 241- Tutorial 1.pdf 2/3 80% + + 10. Determine a ats = 1 m v (m/s) 4 s (m) 2 11. Draw the v-t and s-t graphs if v = 0, s=0 when t=0. a (m/s²) 2 t(s) 12. Draw the v-t graph if v = 0 when t=0. Find the equation v = f(t) for each a (m/s²) 2 segment. 2 -2 13. Determine s and a when t = 3 s if s=0 when t = 0. v (m/s) 2 t(s) t(s) 2arrow_forward
- Q.5) A cylinder is supported by spring AD and cables AB and AC as shown. The spring has an at rest length (unstretched length) of 4 meters. If the maximum allowable tension in cables AB and AC is 200 N, determine (a) the largest mass (kg) of cylinder E the system can support, (b) the necessary spring constant (stiffness) to maintain equilibrium, and (b) the tension (magnitude) in each cable when supporting the maximum load found in part (a). B 4 m 3 m A E 1 m 3 m D 5 marrow_forwardDetermine the moment created by the force about the point O. Express your answer as a Cartesian vector.arrow_forward4. An impeller rotating at 1150 rpm has the following data: b, = 1 ¼ in., b2 = ¾ in., d, = 7 in., d2 = 15 in., B1 = 18", B2 = 20°, cross-sectional area A = Db if vane thickness is neglected. Assuming radial inlet flow, determine the theoretical capacity in gpm head in ft horsepower 5. If the impeller in Problem (4) develops an actual head of 82 ft and delivers 850 gpm at the point of maximum efficiency and requires 22 BHP. Determine overall pump efficiency virtual velocities V2 and W2arrow_forward
- (30 pts) Problem 1 A thin uniform rod of mass m and length 2r rests in a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius r. A moment M mgr 4 is applied to the rod. Assume that the bowl is fixed and its rim is in the horizontal plane. HINT: It will help you to find the length l of that portion of the rod that remains outside the bowl. M 2r a) How many degrees of freedom does this system have? b) Write an equation for the virtual work in terms of the angle 0 and the motion of the center of mass (TF) c) Derive an equation for the variation in the position of the center of mass (i.e., Sŕƒ) a. HINT: Use the center of the bowl as the coordinate system origin for the problem. d) In the case of no applied moment (i.e., M 0), derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation e) In the case of an applied moment (i.e., M = mgr = -) derive an equation that can be used to 4 solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation. f) Can…arrow_forwardPlease show all work step by steparrow_forwardCopyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall 2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also a pin at F. E 400 mm 15° D B 30 mm² 80 mm/ 20 mm 15° $15° 20 mm 400 mm 15° 100 N 100 N 15°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY