
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259989452
Author: Hayt
Publisher: Mcgraw Hill Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 2E
Compute the complex conjugate of each of the following expressions: (a) −1; (b) 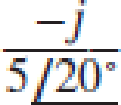 ; (c) 5e−j5 + 2ej3; (d)
; (c) 5e−j5 + 2ej3; (d) 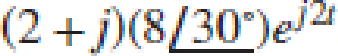 .
.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
"I need something clear written by hand
with steps."
Find Laplace transform and the corresponding ROC for
x(t) = e−3sin(2t) u(t)dt
Three similar coils, connected in star, take a total
power of 1.5 kW, at a power factor of 0.2, from a
three-phase, 400 V, 50 Hz supply. Calculate: (a) the
resistance and inductance of each coil; (b) the line
currents if one of the coils is short-circuited.
(a) Three 20 µF capacitors are star-connected across
a 400 V, 50 Hz, three-phase, three-wire supply.
Calculate the current in each line. (b) If one of the
capacitors is short-circuited, calculate the line cur
rents. (c) If one of the capacitors is open-circuited,
calculate: the line currents and the p.d. across each
of the other two capacitors.
ANS:
1.525 A; 2.64 A, 2.64 A, 4.57 A; 1.32 A, 1.32 A, 0;
210 V
Chapter 14 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Ch. 14.1 - Identify all the complex frequencies present in...Ch. 14.1 - Use real constants A, B, C, , and so forth, to...Ch. 14.2 - Let f (t) = 6e2t [u(t + 3) u(t 2)]. Find the (a)...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 7PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 8PCh. 14.4 - Prob. 9PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 11PCh. 14.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 14.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 14.8 - Find the mesh currents i1 and i2 in the circuit of...Ch. 14.8 - Prob. 17PCh. 14.8 - Prob. 18PCh. 14.9 - Using the method of source transformation, reduce...Ch. 14.9 - Prob. 20PCh. 14.10 - The parallel combination of 0.25 mH and 5 is in...Ch. 14.11 - Prob. 22PCh. 14.11 - Prob. 23PCh. 14.11 - Prob. 24PCh. 14.11 - Prob. 25PCh. 14.12 - Prob. 26PCh. 14 - Determine the conjugate of each of the following:...Ch. 14 - Compute the complex conjugate of each of the...Ch. 14 - Several real voltages are written down on a piece...Ch. 14 - State the complex frequency or frequencies...Ch. 14 - For each of the following functions, determine the...Ch. 14 - Use real constants A, B, , , etc. to construct the...Ch. 14 - The following voltage sources AeBt cos(Ct + ) are...Ch. 14 - Prob. 8ECh. 14 - Compute the real part of each of the following...Ch. 14 - Your new assistant has measured the signal coming...Ch. 14 - Prob. 11ECh. 14 - Prob. 12ECh. 14 - Prob. 13ECh. 14 - Prob. 14ECh. 14 - Prob. 15ECh. 14 - Prob. 16ECh. 14 - Determine F(s) if f (t) is equal to (a) 3u(t 2);...Ch. 14 - Prob. 18ECh. 14 - Prob. 19ECh. 14 - Prob. 20ECh. 14 - Prob. 21ECh. 14 - Evaluate the following: (a)[(2t)]2 at t = 1;...Ch. 14 - Evaluate the following expressions at t = 0: (a)...Ch. 14 - Prob. 24ECh. 14 - Prob. 25ECh. 14 - Prob. 26ECh. 14 - Prob. 27ECh. 14 - Prob. 28ECh. 14 - Prob. 29ECh. 14 - Prob. 30ECh. 14 - Prob. 31ECh. 14 - Prob. 32ECh. 14 - Prob. 33ECh. 14 - Obtain the time-domain expression which...Ch. 14 - Prob. 35ECh. 14 - Prob. 36ECh. 14 - Prob. 37ECh. 14 - Prob. 38ECh. 14 - Prob. 39ECh. 14 - Prob. 40ECh. 14 - Prob. 41ECh. 14 - Obtain, through purely legitimate means, an...Ch. 14 - Prob. 43ECh. 14 - Employ the initial-value theorem to determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 45ECh. 14 - Prob. 46ECh. 14 - Prob. 47ECh. 14 - Prob. 48ECh. 14 - Prob. 49ECh. 14 - Prob. 52ECh. 14 - Determine v(t) for t 0 for the circuit shown in...Ch. 14 - Prob. 54ECh. 14 - Prob. 55ECh. 14 - For the circuit of Fig. 14.54, (a) draw both...Ch. 14 - Prob. 58ECh. 14 - Prob. 59ECh. 14 - Prob. 60ECh. 14 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 14.58, let is1 =...Ch. 14 - Prob. 63ECh. 14 - Prob. 64ECh. 14 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 14.62, determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 67ECh. 14 - Prob. 68ECh. 14 - Determine the poles and zeros of the following...Ch. 14 - Use appropriate means to ascertain the poles and...Ch. 14 - Prob. 71ECh. 14 - For the network represented schematically in Fig....Ch. 14 - Prob. 73ECh. 14 - Prob. 74ECh. 14 - Prob. 75ECh. 14 - Prob. 76ECh. 14 - Prob. 77ECh. 14 - Prob. 78ECh. 14 - Prob. 79ECh. 14 - Prob. 80ECh. 14 - Prob. 81ECh. 14 - Prob. 82ECh. 14 - Design a circuit which produces the transfer...Ch. 14 - Prob. 84ECh. 14 - Prob. 85ECh. 14 - An easy way to get somebodys attention is to use a...Ch. 14 - Prob. 87E
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Which of the following are illegal variable names in Python, and why? x 99bottles july2009 theSalesFigureForFis...
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
The ____________ is always transparent.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain the advantages of three-phase supply for distribution purposes. (b) Assuming the relationship between the line and phase values of currents and voltages, show that the active power input to a three-phase balanced load is √3VI cos φ, where V and I are line quantities. (c) Three similar inductors, each of resistance 10 Ω and inductance 0.019 H, are delta-connected to a three-phase, 400 V, 50 Hz sinusoidal supply. Calcu late: the value of the line current; the power factor and the active power input to the circuit. ANS: 59.5 A, 0.858 lag, 35.5 kWarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forwardA three-phase, 400 V, star-connected motor has an output of 50 kW, with an efficiency of 90 per cent and a power factor of 0.85. Calculate the line current. Sketch a phasor diagram showing the voltages and currents. If the motor windings were connected in mesh, what would be the correct voltage of a three phase supply suitable for the motor? ANS: 90.8 A, 240 Varrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardShow with the aid of a phasor diagram that for both star- and delta-connected balanced loads, the total active power is given by √3VI cos φ, where V and I are the line values of voltage and current respectively and φ is the angle between phase values of voltage and current. A balanced three-phase load consists of three coils, each of resistance 4 Ω and inductance 0.02 H. Determine the total active power when the coils are (a) star-connected, (b) delta-connected to a 400 V, three phase, 50 Hz supply. ANS:11.56 kW, 34.7 kWarrow_forwardThe load connected to a three-phase supply comprises three similar coils connected in star. The line currents are 25 A and the apparent and active power inputs are 20 kVA and 11 kW respectively. Find the line and phase voltages, reactive power input and the resistance and reactance of each coil. If the coils are now con nected in delta to the same three-phase supply, calculate the line currents and the active power taken. ANS : 462 V, 267 V, 16.7 kvar, 5.87 Ω, 8.92 Ω; 75 A, 33 kWarrow_forward
- A three-phase delta-connected load, each phase of which has an inductive reactance of 40 Ω and a resistance of 25 Ω, is fed from the secondary of a three-phase star-connected transformer which has a phase voltage of 230 V. Draw the circuit diagram of the system and calculate: (a) the current in each phase of the load; (b) the p.d. across each phase of the load; (c) the current in the transformer secondary windings; the total active power taken from the supply and its power factor.arrow_forwardDerive the numerical relationship between the line and phase currents for a balanced three-phase delta connected load. Three coils are connected in delta to a three-phase, three-wire, 400 V, 50 Hz supply and take a line current of 5 A 0.8 power factor lagging. Calculate the resistance and inductance of the coils. If the coils are star-connected to the same supply, calculate the line current and the total power. Calculate the line cur rents if one coil becomes open-circuited when the coils are connected in star. Ans: 110.7 Ω, 0.264 H; 1.67 A, 926 W; 1.445 A, 1.445 A, 0arrow_forwardDerive, for both star- and delta-connected systems, an expression for the total power input for a balanced three-phase load in terms of line voltage, line current and power factor. The star-connected secondary of a transformer supplies a delta-connected motor taking a power of 90 kW at a lagging power factor of 0.9. If the volt age between lines is 600 V, calculate the current in the transformer winding and in the motor winding. Draw circuit and phasor diagrams, properly labelled, showing all voltages and currents in the transformer secondary and the motor. ANS: . 96.2 A, 55.6 Aarrow_forward
- Deduce the relationship between the phase and the line voltages of a three-phase star-connected generator. If the phase voltage of a three-phase star-connected generator is 200 V, what will be the line voltages: (a) when the phases are correctly connected; (b) when the connections to one of the phases are reversed? ans: 346 V; 346 V, 200 V, 200 Varrow_forwardQ2: Given a discrete sequence x(n) = [1,-1,2,4, 1, 3,-1,1] and its spectrum X(k): i. Show that: X(k) =G(k)+WH(k) k=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 where G(k) = DFT[g(n)] and H(k) = DFT[h(n)], g(n) and h(n) are even and odd components of x(n) respectively. ii. Compute G(k) and H(k) using the method of computation of DFTS of two real sequences. (15 marks)arrow_forwardQ2: Given a discrete sequence x(n) = [1,-1,2,4, 1, 3,-1,1] and its spectrum X(k): i. Show that: X(k) = G(k)+WH(k) k = 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 where G(k) = DFT[g(n)] and H(k) = DFT[h(n)], g(n) and h(n) are even and odd components of x(n) respectively. ii. Compute G(k) and H(k) using the method of computation of DFTS of two real sequences.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Inductors Explained - The basics how inductors work working principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KSylo01n5FY;License: Standard Youtube License