
Concept explainers
Grace Greenberg, production planner for Science and Technology Labs, in New Jersey, has the master production plan shown below:
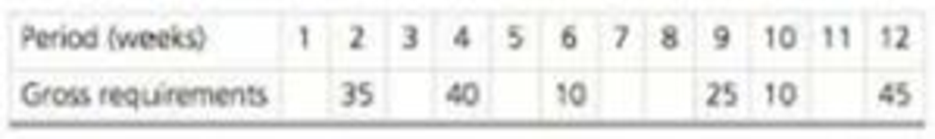
Lead time = 1 period; setup cost = $200; holding cost = $10 per week; stockout cost = $10 per week. Develop an ordering plan and costs for Grace, using these techniques:
a) Lot-for-lot.
b) EOQ.
c) POQ.
d) Which plan has the lowest cost?
a)
To determine: The ordering plan and cost for Lot for lot.
Introduction:
Lot for Lot:
The lot for lot method of requirements plan is the process where the planned order release will be equal to the net requirement of the period.
Net requirements plan:
The net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
Answer to Problem 27P
The cost for Lot for lot is $1,200.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
Holding cost = $10 / week
Setup cost = $200
Lead time = 1 period
Stockout cost = $10 / week
Lot for lot:
Net requirements plan:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | |||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| Ending inventory | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | |||||||
Week 2:
The gross requirement is 35 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 35. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 35 in week 1 which will be the planned order receipt in week 2.
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 40 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 40. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 40 in week 3 which will be the planned order receipt in week 4.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 10 in week 5 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6.
Week 9:
The gross requirement is 25 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 25. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 25 in week 8 which will be the planned order receipt in week 9. There is no ending inventory.
Week 10:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 10 in week 9 which will be the planned order receipt in week 10.
Week 12:
The gross requirement is 45 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 45. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 45 in week 11 which will be the planned order receipt in week 12. There is no ending inventory.
Number of planned orders = 6
Inventory holding units= 0
Formula to calculate total cost of the plan:
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by adding the product of number of planned order and setup cost with the product of inventory holding period and holding cost.
Hence, the cost for Lot for lot is $1,200.
b)
To determine: The ordering plan and cost for EOQ.
Introduction:
Economic order quantity (EOQ):
The economic order quantity is the number of units a firm must add to their stock while making each order. The notion of EOQ is to reduce the total cost of inventory of the firm.
Net requirements plan:
The net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
Answer to Problem 27P
The cost for EOQ is $2,370.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
Holding cost = $10 / week
Setup cost = $200
Lead time = 1 period
Stockout cost = $10 / week
Formula to calculate EOQ:
Calculation of EOQ:
The EOQ can be rounded off to 23 units.
Net requirements plan:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | |||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | 11 | 11 | 17 | 17 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 18 | 18 | ||
| Ending inventory | 11 | 11 | 17 | 17 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 137 | |
| Net requirement | 35 | 29 | 0 | 18 | 5 | 27 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 46 | 46 | 0 | 23 | 23 | 46 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 46 | 46 | 23 | 23 | 46 | ||||||||
Week 2:
The gross requirement is 35 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 35. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 46 (1 Lot = 23) in week 1 which will be the planned order receipt in week 2. The ending inventory is 11 which will be available at week 3.
Week 3:
The on hand inventory is 11. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 3 is 11 which will be available at week 4.
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 40 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 11. Hence, the net requirement is 29. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 46 (1 Lot = 23) in week 3 which will be the planned order receipt in week 4. The ending inventory is 17 which will be available at week 5.
Week 5:
The on hand inventory is 17. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 5 is 17 which will be available at week 6.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 17. Hence, the net requirement is 0. Therefore there will be no planned order assembly. The ending inventory is 7 which will be available at week 7.
Week 7:
The on hand inventory is 7. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 7 is 7 which will be available at week 8.
Week 8:
The on hand inventory is 7. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 8 is 7 which will be available at week 9.
Week 9:
The gross requirement is 25 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 7. Hence, the net requirement is 18. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 23 (1 Lot = 23) in week 8 which will be the planned order receipt in week 9. The ending inventory is 5 which will be available at week 10.
Week 10:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 5. Hence, the net requirement is 5. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 23 (1 Lot = 23) in week 9 which will be the planned order receipt in week 10. The ending inventory is 18 which will be available at week 11.
Week 11:
The on hand inventory is 18. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 11 is 18 which will be available at week 12.
Week 12:
The gross requirement is 45 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 18. Hence, the net requirement is 27. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 46 (1 Lot = 23) in week 11 which will be the planned order receipt in week 12. The ending inventory is 19 which will be available in the next week.
Number of planned order releases = 5
Total Ending inventory = 137
Calculation of total setup cost:
Calculation of total holding cost:
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by summing the total setup cost and total holding cost.
Hence, the total cost for EOQ is $2,370
c)
To determine: The ordering plan and cost for POQ.
Introduction:
Periodic order quantity (POQ):
The POQ is the standard quantity of units that will be ordered over a fixed period of time. This method is followed when the usage of raw materials is consistent and is predictable.
Net requirements plan:
The net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
Answer to Problem 27P
The cost for POQ is $1,100.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
Holding cost = $10 / week
Setup cost = $200
Lead time = 1 period
Stockout cost = $10 / week
Net requirements plan:
The planned ordered release in the POQ plan is planned in a way such that the demand for next two periods is satisfied.
Net requirements plan:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | |||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Ending inventory | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | |
| Net requirement | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 45 | ||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 35 | 40 | 10 | 35 | 45 | ||||||||
| Planned order release | 35 | 40 | 10 | 35 | 45 | ||||||||
Week 2:
The gross requirement is 35 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 35. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 35 in week 1 which will be the planned order receipt in week 2. There is no ending inventory.
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 40 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 40. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 40 in week 3 which will be the planned order receipt in week 4. There is no ending inventory.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 10. Therefore, the planned order release will be 10 in week 5 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6. There is no ending inventory.
Week 9:
The gross requirement is 25 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 25. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 35 in week 8 which will be the planned order receipt in week 9. The ending inventory is 10 which will be available at week 10.
Week 10:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 10. Hence, the net requirement is 0. Therefore there will be no planned order inventory.
Week 12:
The gross requirement is 45 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 45. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 45 in week 11 which will be the planned order receipt in week 12. There is no ending inventory.
Number of planned orders = 5
Inventory holding units= 10
Formula to calculate total cost of the plan:
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by adding the product of number of planned order and setup cost with the product of inventory holding period and holding cost.
Hence, the cost for POQ is $1,100.
d)
To determine: The plan which has the lowest cost.
Answer to Problem 27P
The plan which has the lowest cost is POQ.
Explanation of Solution
The total cost for Lot for lot is $1,200. The total cost for EOQ is $2,370. The total cost for POQ is $1,100. The total cost is less for POQ when compared with EOQ and Lot for lot. ($1,100 < $2,370, $1,200)
Hence, the plan which has the lowest cost is POQ.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- CASE STUDY 9-1 Was Robert Eaton a Good Performance Management Leader? R obert Eaton was CEO and chairman of Chrys- ler from 1993 to 1998, replacing Lee Iacocca, who retired after serving in this capacity since 1978. Eaton then served as cochairman of the newly merged DaimlerChrysler organization from 1998 to 2000. In fact, Eaton was responsible for the sale of Chrysler Corporation to Daimler-Benz, thereby creating DaimlerChrysler. With 362,100 employees, DaimlerChrysler had achieved revenues of €136.4 billion in 2003. DaimlerChrysler's passenger car brands included Maybach, Mercedes-Benz, Chrysler, Jeep, Dodge, and Smart. Commercial vehicle brands included Mercedes-Benz, Freightliner, Sterling, Western Star, and Setra. From the beginning of his tenure as CEO, Eaton communicated with the people under him. He immediately shared his plans for the future with his top four executives, and upon the advice of his colleague, Bob Lutz, decided to look around the company before making any hasty…arrow_forwardCritically assess Martin’s coaching style.arrow_forwardCompare Robert Eaton’s performance management leadership presented in the case against the performance management leadership principles, functions, and behaviors. What recommendations can be made about what he might do more effectively? Explain and defend your answer.arrow_forward
- In the context of the material in Chapter 9, provide a critical analysis of the decisions that Henry has made in assigning Martin to this role.arrow_forwardpanies (pp. 80-118). New York, NY: Times Books, specifically Chap. 4, "Robert Eaton and Robert Lutz; The Copilots." CASE STUDY 9-2 Performance Management Leadership at Henry's Commercial Sales and Leasing H enry is the owner of a small real estate agency that handles the sale and leasing of commercial property. He has two real estate agents working in the office, along with himself. He also has two customer service representatives (CSRs), each of whom has a real estate license, and one receptionist who has worked for the company for about three months. Henry has recently decided that he needs another customer service representative. He hasarrow_forwardDiscuss possible solutions to help Tara become an effective CSR. What should martin be doing to help her?arrow_forward
- What are the ethical challenges regarding employees (i.e., diversity, discrimination, sexual harassment, privacy, employee theft, bad leadership, etc.) that Apple Inc. has faced over the past five to ten years and that they should prepare to face in the next five to ten years. Once a developed list of challenges is created, consider how having faced those challenges will impact and be impacted by the social cause you've selected. Propose the findings on the ethical challenges faced by Apple Inc. in recent history and the near future. Analyze ways in which each challenge was (and/or could be) appropriately handled and areas for improvement. Evaluate the ethical/moral aspects of Apple Inc. that protected it from ethical challenges in the past and could protect it in the future. Assess how ethical challenges and handling of ethical challenges could positively or negatively impact the charitable cause are selected and how the selection of your social cause could positively or negatively…arrow_forwardBy selecting Cigna Accredo pharmacy that i identify in my resand compare the current feedback system against the “Characteristics of a Good Multiple Source Feedback Systems” described in section 8-3-3. What can be improved? As a consultant, what recommendations would you make?arrow_forwardScenario You have been given a task to create a demand forecast for the second year of sales of a premium outdoor grill. Accurate forecasts are important for many reasons, including for the company to ensure they have the materials they need to create the products required in a certain period of time. Your objective is to minimize the forecast error, which will be measured using the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) with a goal of being below 25%. You have historical monthly sales data for the past year and access to software that provides forecasts based on five different forecasting techniques (Naïve, 3-Month Moving Average, Exponential Smoothing for .2, Exponential Smooth for .5, and Seasonal) to help determine the best forecast for that particular month. Based on the given data, you will identify trends and patterns to create a more accurate forecast. Approach Consider the previous month's forecast to identify which technique is most effective. Use that to forecast the next…arrow_forward
- Approach Consider the previous month's forecast to identify which technique is most effective. Use that to forecast the next month. Remember to select the forecasting technique that produces the forecast error nearest to zero. For example: a. Naïve Forecast is 230 and the Forecast Error is -15. b. 3-Month Moving Forecast is 290 and the Forecast Error is -75. c. Exponential Smoothing Forecast for .2 is 308 and the Forecast Error is -93. d. Exponential Smoothing Forecast for .5 is 279 and the Forecast Error is -64. e. Seasonal Forecast is 297 and the Forecast Error is -82. The forecast for the next month would be 230 as the Naïve Forecast had the Forecast Error closest to zero with a -15. This forecasting technique was the best performing technique for that month. You do not need to do any external analysis-the forecast error for each strategy is already calculated for you in the tables below. Naïve Month Period Actual Demand Naïve Forecast Error 3- Month Moving Forecast 3- Month Moving…arrow_forwardScenario You have been given a task to create a demand forecast for the second year of sales of a premium outdoor grill. Accurate forecasts are important for many reasons, including for the company to ensure they have the materials they need to create the products required in a certain period of time. Your objective is to minimize the forecast error, which will be measured using the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) with a goal of being below 25%. You have historical monthly sales data for the past year and access to software that provides forecasts based on five different forecasting techniques (Naïve, 3-Month Moving Average, Exponential Smoothing for .2, Exponential Smooth for .5, and Seasonal) to help determine the best forecast for that particular month. Based on the given data, you will identify trends and patterns to create a more accurate forecast. Approach Consider the previous month's forecast to identify which technique is most effective. Use that to forecast the next…arrow_forwardUse the internet to obtain crash safety ratings for passenger vehicles. Then, answer thesequestions:a. Which vehicles received the highest ratings? The lowest ratings?b. How important are crash-safety ratings to new car buyers? Does the degree of importancedepend on the circumstances of the buyer?c. Which types of buyers would you expect to be the most concerned with crash-safety ratings?d. Are there other features of a new car that might sway a buyer from focusing solely on crashsafety? If so, what might they be?arrow_forward
- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning





