
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The change in the items due to the change in the lead time of item G.
Introduction:
Net requirements plan:
The Net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the Gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the
a)
Answer to Problem 16P
The change will take place only with item G because it has no children. The Lead time of 4 weeks will preempt the Planned order release by 1 one week.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- 10 units for service and production department for B and F.
- 10 units of A at week 8.
- Lead time of G has been changed to 4 weeks.
| Part | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
| On hand | 0 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 10 |
Product structure:
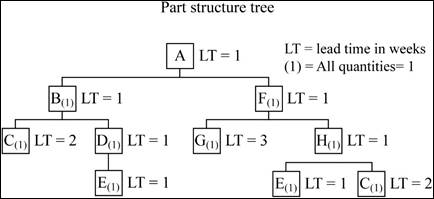
Net requirements plan:
Item A:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 10 | |||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (0) | 0 | |||||||
| Net requirement | 10 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 10 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 10 | |||||||
Week 8:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 7 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 8.
Item B:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item B | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 10 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (2) | 2 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 8 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 8 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 8 | 10 | ||||||
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 2. Hence, the Net requirement is 8. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 8 in week 5 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6.
Week 7:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 10 in week 6 which will be the planned order receipt in week 7.
Item F:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item F | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 10 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (5) | 5 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 5 | 10 | ||||||
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 5. Hence, the Net requirement is 5. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 5 in week 5 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Week 7:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 6 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 7.
Item D:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item D | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 8 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (5) | 5 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 3 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 8 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B. The on-hand inventory is 5. Hence, the Net requirement is 3. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 3 in week 4 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 5 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item G (Lead Time = 3):
| Week | ||||||||
| Item G | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (1) | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 4 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 5 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 1. Hence, the Net requirement is 4. The lead time is 3 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 4 in week 2 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 3 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 3 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item G (Lead Time = 4):
| Week | ||||||||
| Item G | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (1) | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 4 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 5 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 1. Hence, the Net requirement is 4. The lead time is 4 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 4 in week 1 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 4 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 2 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item H:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item H | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (10) | 10 | 5 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 5 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 5 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 5 | |||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 5 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 10. Hence, the Net requirement is 0. Therefore, there will be no Planned order release. The excess inventory will be available in week 6.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 5. Hence, the Net requirement is 5. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 5 in week 5 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item C:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item C | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 13 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (10) | 10 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 3 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 13 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B and H. The on-hand inventory is 10. Hence, the Net requirement is 3. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 3 in week 3 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B and H. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 4 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item E:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item E | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 3 | 15 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (4) | 4 | 1 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 14 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 14 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 14 | |||||||
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 3 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of D. The on-hand inventory is 4. Hence, the Net requirement is 0. Therefore, there will be no Planned order release. The excess inventory will be available in week 5.
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 15 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of H. The on-hand inventory is 1. Hence, the Net requirement is 14. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 14 in week 4 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Hence, the change will take place only with item G because it has no children. The Lead time of 4 weeks will preempt the Planned order release by 1 one week.
b)
To determine: The implications of the production plan because of change in the lead time of item G.
Introduction:
Net requirements plan:
The Net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the Gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the Scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
b)
Answer to Problem 16P
The production plan will be altered such that item F and four units of A will be delayed by 1 week.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- 10 units for service and production department for B and F.
- 10 units of A at week 8.
- Lead time of G has been changed to 4 weeks.
| Part | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
| On Hand | 0 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 10 |
Product structure:
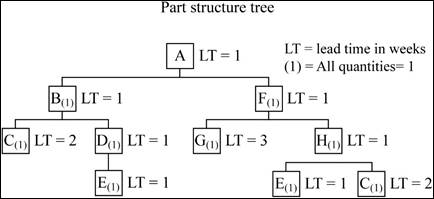
Net requirements plan:
Item A:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 10 | |||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (0) | 0 | |||||||
| Net requirement | 10 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 10 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 10 | |||||||
Week 8:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 7 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 8.
Item B:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item B | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 10 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (2) | 2 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 8 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 8 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 8 | 10 | ||||||
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 2. Hence, the Net requirement is 8. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 8 in week 5 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Week 7:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 6 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 7.
Item F:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item F | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 10 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (5) | 5 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 5 | 10 | ||||||
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 5. Hence, the Net requirement is 5. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 5 in week 5 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Week 7:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of A. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 6 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 7.
Item D:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item D | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 8 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (5) | 5 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 3 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 8 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B. The on-hand inventory is 5. Hence, the Net requirement is 3. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 3 in week 4 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 5 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item G (Lead Time = 3):
| Week | ||||||||
| Item G | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (1) | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 4 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 5 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 1. Hence, the Net requirement is 4. The lead time is 3 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 4 in week 2 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 3 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 3 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item G (Lead Time = 4):
| Week | ||||||||
| Item G | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (1) | 1 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 4 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 4 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 5 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 1. Hence, the Net requirement is 4. The lead time is 4 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 4 in week 1 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 4 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 2 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item H:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item H | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 5 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (10) | 10 | 5 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 5 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 5 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 5 | |||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 5 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 10. Hence, the Net requirement is 0. Therefore, there will be no Planned order release. The excess inventory will be available in week 6.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of F. The on-hand inventory is 5. Hence, the Net requirement is 5. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 5 in week 5 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item C:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item C | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 13 | 10 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (10) | 10 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order receipt | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Planned order release | 3 | 10 | ||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 13 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B and H. The on-hand inventory is 10. Hence, the Net requirement is 3. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 3 in week 3 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of B and H. The on-hand inventory is 0. Hence, the Net requirement is 10. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 10 in week 4 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 6.
Item E:
| Week | ||||||||
| Item E | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Gross requirements | 3 | 15 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||
| On-hand (4) | 4 | 1 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 14 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 14 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 14 | |||||||
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 3 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of D. The on-hand inventory is 4. Hence, the Net requirement is 0. Therefore, there will be no Planned order release. The excess inventory will be available in week 5.
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 15 (1 assembly) derived from the Planned order release of H. The on-hand inventory is 1. Hence, the Net requirement is 14. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the Planned order release will be 14 in week 4 which will be the Planned order receipt in week 5.
If this week is week 1 of the production plan, the increase in the lead time will make that only 1 assembly of G will be available for F in week 5. Hence, item F and consequently 4 units of item A will be delayed by a time of 1 week.
c)
To determine: The options the
c)
Explanation of Solution
Options the production manager has to manage these changes:
The production manager can do the following. They are:
- The production manager can inform the customer in advance that the 4 units will be delayed by a time of 1 week.
- The production manager can ask the supplier of item G to expedite the production or the delivery.
- The production manager can reduce the time take for production of item F or A.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- Following their early success and growth, Listo hired a number of new managers and employees. In response to the expansion of staff, Listo reorganized by adding layers of supervisors and managers between executive management and line staff; however, growth occurred so rapidly that proper training was not provided to the new employees. Management was less concerned with the employees’ opinions and was more focused on production and profit. Instead of enlisting employees’ opinions, more directive orders were given. The change and increased complexity associated with adding new layers to the hierarchy resulted in the organization’s goals and objectives becoming unclear. Employees began to complain about the new bureaucratic processes and the slow pace of decision-making. While the organization has been growing in size, productivity has slowed and quality has decreased. The turnover rate is higher than it has ever been, and the number of sick days that people take has doubled over the past…arrow_forwardFollowing their early success and growth, Listo hired a number of new managers and employees. In response to the expansion of staff, Listo reorganized by adding layers of supervisors and managers between executive management and line staff; however, growth occurred so rapidly that proper training was not provided to the new employees. Management was less concerned with the employees’ opinions and was more focused on production and profit. Instead of enlisting employees’ opinions, more directive orders were given. The change and increased complexity associated with adding new layers to the hierarchy resulted in the organization’s goals and objectives becoming unclear. Employees began to complain about the new bureaucratic processes and the slow pace of decision-making. While the organization has been growing in size, productivity has slowed and quality has decreased. The turnover rate is higher than it has ever been, and the number of sick days that people take has doubled over the past…arrow_forwardDiscuss in detail any five types of authority. give citations and referencearrow_forward
- Can you guys help me with this? Thank you! Business Environment: Provide insights into the guidelines for conducting business in the chosen country and working there as an expatriate. This information is vital for understanding the practicalities of engagement in that particular environment. The country in here is India Put the answer as bullet points, provide sources that have relevant information for the answer on economic factorsarrow_forwardCan you guys help me with this? Thank you! Intriguing Facts: Incorporate engaging facts about the country that enhance its value and uniqueness within the global supply chain landscape. These can include cultural anecdotes, technological innovations, or historical achievements. The country in here is India Put the answer as bullet points, provide sources that have relevant information for the answer on economic factorsarrow_forwardCan you guys help me with this? Thank you! Economic Factors: Evaluate the country's economic performance by analyzing key indicators such as GDP (Gross Domestic Product), GDP per capita, exports, and imports. These metrics provide insight into the country's economic prowess and its position in global trade. The country in here is India Put the answer as bullet points, provide sources that have relevant information for the answer on economic factorsarrow_forward
- provide scholarly reseach and define legal and complince risk and reputational risk in banking. Additionally 1. What more can be done about it 2. the department where the risk is exposed to 3. what strategy can be used 4. responsible personarrow_forwardRead the case in the link below and Develop a risk management programme appropriate for this case using the attached template. https://finopsinfo.com/investors/citis-900m-blunder-casts-light-on-poor-loan-ops/arrow_forwardDo the inherent differences between private and public sector objectives—profit versus publicgood—render private sector category management practices unsuitable for public sectorpurchasing, where open tendering is the norm?You have now undergone the Category Management classes and your superiors have requestedfor your input on how to integrate some of the learnings into the public sector policy. Discuss and elaborate what are the activities and governance you would introduce in yourrecommendations without violating the principle of transparency and accountability withinyour organisation. This is based on Singapore context. Pls provide a draft with explanation, examples and useful links for learning purposes. Citations will be good too. This is a module in SUSS called category management and supplier evaluationarrow_forward
- provide scholarly answers for what risk was associated with the Citibank bank loosing 50 million in August 2020arrow_forwardConclusion: The report recommendations and broad conclusion to the essay. TOTAL 5 100arrow_forwardAs part of your new role, as a strategy consultant and member of the steering committee, discuss what logistics and transportation strategies you will execute to achieve operational efficiencies and facilitate economic growth in SA. The committee would like to have a implementable strategic transport and logistics plan to realise the roadmap vision based on the subsection numbering given below! QUESTION ONE Introduction: Must include an overview and history of South Africa's Road, rail and freight transport network. Marks 5arrow_forward
- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning  Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,





