
Concept explainers
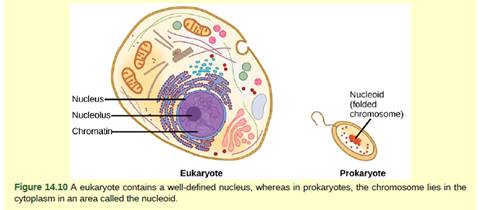
Figure 14.10 In eukaryotic cells, DNA and RNA synthesis occur in a separate compartment from protein synthesis. In prokaryotic cells, both processes occur together. What advantages might there be to separating the processes? What advantages might there be to having them occur together?
To review:
The advantages of separate processes of DNA synthesis, transcription and translation in eukaryotes and the same occurring together in prokaryotes.
Introduction:
Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms lacking a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles. Eukaryotes are either unicellular or multicellular organisms with a well-defined nucleus covered by a nuclear membrane, showing nucleoplasm and nucleolus along with the membrane-bound organelles in their cytoplasm like the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, chloroplast. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes also differ in the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Explanation of Solution
In prokaryotes, the synthesis of DNA and RNA occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. No compartmentalization in prokaryotes makes the synthesis of RNA and proteins to occur simultaneously, helping in their quicker synthesis and allowing the cell to reproduce at a quicker rate. This quicker reproduction can bring changes in the cell and can help the cells to evolve.
In eukaryotes, the synthesis of DNA takes place in the nucleus of the cell by a process called the replication of DNA. The synthesis of RNA occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. The advantages of this separation are that more complex proteins and RNA products are formed separately by a set of specific steps with minimum damage to them. This also prevents the interaction of these molecules among themselves and helps in regulating the gene expression.
Thus, the separation of DNA and RNA synthesis from the synthesis of proteins in eukaryotes helps in the formation of the complex products with minimum damage and their synthesis in prokaryotes occurring together makes them reproduce quickly.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
BIOLOGY 2E
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- identify the indicated cell in white arrowarrow_forwardGloeocaspa Genus - diagram a colony and label the sheath, cell wall, and cytoplasm. Oscillatoria Genus - Diagram a trichome, and label the shealth and individual cells Nostoc Genus- diagram a sketch of the colonoy microscopically from low power to the left of the drawing. Draw a filament showing intercalary heterocysts, and vegatative cells to the right of the drawing Merismopedia Genus- diagram a sketch of the colony. draw and label a filament showing the colony, cell wall, and sheath. Gloeotrichia Genus- diagram a habit sketch of the colony. draw a filament showing the heterocyst, akimetes and vegatative cells of the filamentarrow_forwardOf this list shown, which genus does the image belong toarrow_forward
- As a medical professional, it is important to be able to discuss how genetic processes such as translation regulation can directly affect patients. Think about some situations that might involve translation regulation. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: Why is translation regulation important? What are some examples of translation regulation in humans? Select one of the examples you provided and explain what happens when translation regulation goes wrong.arrow_forwardThe metabolic pathway below is used for the production of the purine nucleotides adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP) in eukaryotic cells. Assume each arrow represents a reaction catalyzed by a different enzyme. Using the principles of feedback inhibition, propose a regulatory scheme for this pathway that ensures an adequate supply of both AMP and GMP, and prevents the buildup of Intermediates A through G when supplies of both AMP and GMP are adequate.arrow_forwardQUESTION 27 Label the structures marked A, B, C and explain the role of structure A. W plasma membrane For the toolbar, press ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN+F10 (Mac). BIUS ☐ Paragraph Π " ΩΘΗ Β Open Sans, a... 10pt EEarrow_forward
- examples of synamptomorphyarrow_forwardexamples of synamtomorphy.arrow_forwardE. Bar Graph Use the same technique to upload the completed image. We will use a different type of graph to derive additional information from the CO2 data (Fig A1.6.2) 1. Calculate the average rate of increase in COz concentration per year for the time intervals 1959-1969, 1969- 1979, etc. and write the results in the spaces provided. The value for 1959-1969 is provided for you as an example. 2. Plot the results as a bar graph. The 1959-1969 is plotted for you. 3. Choose the graph that looks the most like yours A) E BAR GRAPH We will use a different type of graph to derive additional information from the CU, data (rig. nive). Average Yearly Rate of Observatory, Hawall interval Rate of increase per year 1959-1969 0.9 1969-1979 1979-1989 1989-1999 1999-2009 Figure A1.6.2 1999-2009 *- mrame -11- -n4 P2 جية 1989-1999 1979-1989 1969-1979 1959-1969 This bar drawn for you as an example 1.0 CO, Average Increase/Year (ppmv) B) E BAR GRAPH We will use a different type of graph to derive…arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





