
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
![]()
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given aldehyde is ethanal.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
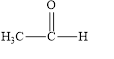
Figure 1
The given compound is aldehyde. The first step in the naming of aldehyde is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of two
The given aldehyde is ethanal.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given aldehyde is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
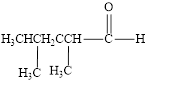
Figure 2
The given compound is aldehyde. The first step in the naming of aldehyde is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of five
The given aldehyde is
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given ketone is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
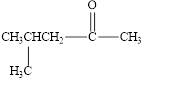
Figure 3
The given compound is ketone. The first step in the naming of ketone is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of five
The given ketone is
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given aldehyde is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
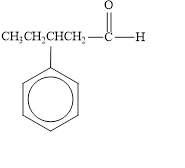
Figure 4
The given compound is aldehyde. The first step in the naming of aldehyde is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of five
The given aldehyde is
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given cyclic ketone is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
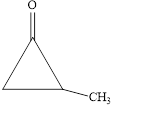
Figure 5
The given compound is cyclic ketone. The first step in the naming of ketone is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of three
The given cyclic ketone is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry For Today: General, Organic, And Biochemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Can I get help on drawing my arrowsarrow_forwardCan I get helpp drawing my arrowsarrow_forwardWhich of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forward
- Please explain how to calculate the pH.arrow_forwardI'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forwardWe discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





