
Concept explainers
Draw structural formulas for the products of the following hydrolysis reactions:
a. 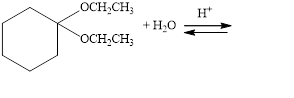
b. 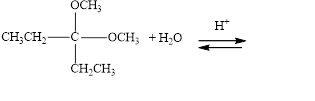
c.
d. 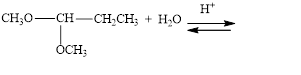
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry For Today: General, Organic, And Biochemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Arrange the following carboxylic acids in order of acidity. CN COOH ба -COOH .COOH .COOH مي سي مي C "CN NOW a b The strongest acid is The second strongest is The third strongest is The weakest acid is darrow_forwardDo not give handwriting solution.arrow_forward16. What is one use for sodium and potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids? Oa. food preservative b. athletes foot treatment C. soaps d. pH buffer e. blood anticoagulantarrow_forward
- Which of the following is the reaction for the acid hydrolysis of ethyl methanoate? 0 0 1 H-C-0-CH₂-CH3 + H₂O -H-C-OH+CH3-CH₂-OH 0 00 0 0 1 H-C-0-CH3 + H₂0 -H-C-OH+CH₂-OH 0 0 1 0 H-C-0-CH2-CH3 + H20 -H-C-0-CH₂-CH3 1 OH OH 0 0 CH3-C-0-CH3 + H20-CH3-C-OH + CH3-OH CH3-C-ONa+CH-OHarrow_forwardWhat product is produced when a hydrolysis reaction occurs with this chemical?arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) of the reaction: Draw Your Solution Ethyl 2-Methylbutanoate Responsible for the smell of ripe apples 1) LIAIH4 2) H3O* ?arrow_forward
- Write equations for the reaction of each compound with H2SO4, a strong protic acid.arrow_forwardWhat is the conjugate acid of CH2ClCOO–? a. CH2ClCOO b. CH2ClCOO2– c. CH2ClCOOH– d. CH2ClCOOH e. H+arrow_forwardWhat is the role of phenolphthalein in the neutralization reaction? Draw the structure of phenolphthalein under acidic and basic conditions.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is the compound that when hydrolyzed produces these two products? X + H₂O* NH + H a. b. C. o Cr Ho C 0arrow_forwardLactic acid, CH3CH(OH)COOH, is a weak monoprotic acid with a melting point of 53 C. It exists as two enantiomers (Sec. 7-2f) that have slightly different Ka values. The D form has a Ka of 1.5 104 and the L form has a Ka of 1.6 104. The D form is synthesized by some bacteria. The L form is produced in muscle cells during anaerobic metabolism in which glucose molecules are broken down into lactic acid and molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are formed. When lactic acid builds up too rapidly in muscle tissue, severe pain results. (a) Which form of lactic acid (D or L) is the stronger acid? Explain your answer. (b) Determine the pKa that would be measured for a 50:50 mixture of the two forms of lactic acid in aqueous solution, pKa = log Ka (c) A solution of D-lactic acid is prepared. Use HL as a general formula for lactic acid, and write the equation for the ionization of lactic acid in water. (d) If 0.100-M solutions of these two acids (D and L) were prepared, calculate what the pH of each solution would be. (e) Before any lactic acid dissolves in the water, what reaction determines the pH? (f) Calculate the pH of a solution made by dissolving 4.46 g D-lactic acid in 500. mL of water. (g) Calculate the volume (mL) of 1.15-M NaOH(aq) required to completely neutralize 4.46 g of pure lactic acid. (h) Calculate the pH of the solution when exactly enough NaOH was added to neutralize all of the lactic acid for (i) the D form; (ii) the L form; and (iii) a 50:50 mixture of the two forms.arrow_forward16-35 (Chemical Connections 16B ) What is an alkaloid? Are all alkaloids basic to litmus?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





