
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The substitutive name and common name of
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by
Rules for writing IUPAC name from the structural formula are given below.
- First, identify the longest carbon chain.
- The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
- Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
- Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents is present.
- Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The common name of the compound
Explanation of Solution
The compound
The compound
The number on the carbon atoms in the compound is shown below.
The compound is
The common name of the compound
(b)
Interpretation:
The substitutive name and common name of
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of the organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing IUPAC name from the structural formula are given below.
- First, identify the longest carbon chain.
- The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
- Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
- Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents is present.
- Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The common name of the compound
Explanation of Solution
The compound
The compound
The number on the carbon atoms in the compound is shown below.
The compound is alkyne. Therefore, -yne will be present as the suffix. The triple bond is present on the fifth carbon atom. The compound has ten-carbon atom long chain. Therefore, the substitutive name of the compound is
The common name of the compound
(c)
Interpretation:
The substitutive name of compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of the organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing IUPAC name from the structural formula are given below.
- First, identify the longest carbon chain.
- The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
- Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
- Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents is present.
- Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The substitutive name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown below.
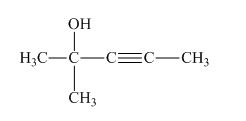
Figure 1
The compound has five carbon atom in the longest chain. Therefore, pent- will be used in the root name. The number of the carbon atoms will be started from the carbon atom which gives the lowest number to hydroxyl group in the chain.
The number on the carbon atoms in the compound is shown below.
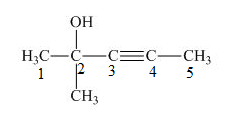
Figure 2
The compound has methyl group and hydroxyl group. Therefore, -yne will be present as primary suffix and –ol will be present on as secondary suffix. The methyl group is resent at the second carbon. Therefore, methyl will be used as prefix. The triple bond is present on the third carbon atom and hydroxyl group is present on the second carbon atom. Therefore, the substitutive name of the compound is
The substitutive name of the given compound is
(d)
Interpretation:
The substitutive name of compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of the organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing IUPAC name from the structural formula are given below.
- First, identify the longest carbon chain.
- The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
- Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
- Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents is present.
- Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The substitutive name of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown below.
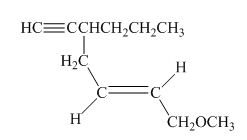
Figure 3
The compound has seven carbon atom in the longest chain. Therefore, hept- will be used in root name. The number of the carbon atoms will be started from the carbon atom which gives lowest number to propyl group in the chain.
The number on the carbon atoms in the compound is shown below.
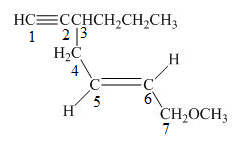
Figure 4
The compound has propyl group and methoxy group. Therefore, methoxy and propyl will be present as suffix. The propyl group is present at the third carbon. The triple bond is present on the first carbon atom and double bond is present at the fifth carbon atom. Therefore, the substitutive name of the compound is
The substitutive name of the given compound is
(e)
Interpretation:
The substitutive name of compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of the organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing IUPAC name from the structural formula are given below.
- First, identify the longest carbon chain.
- The next step is to identify the groups attached to the longest chain.
- Identify the position, location, and a number of the substituents bonded to the carbon chain.
- Use prefix di, tri, tetra if the same type of substituents is present.
- Name the substituents in alphabetical order.
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The substitutive name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is shown below.
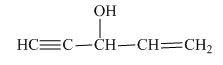
Figure 5
The compound has five carbon atom in the longest chain. Therefore, pent- will be used in root name. The number of the carbon atoms will be started from the carbon atom which gives lowest number to double bond in the chain.
The number on the carbon atoms in the compound is shown below.
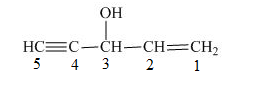
Figure 6
The compound has hydroxyl group. Therefore, hydroxyl will be present as prefix. The hydroxyl group is present at the third carbon. The triple bond is present on the fifth carbon atom and double bond is present at the first carbon atom. Therefore, the substitutive name of the compound is
The substitutive name of the given compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- please help fill in the tablearrow_forwardAnswer F pleasearrow_forward4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
- What is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forwardPLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when possarrow_forward. M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forward
- Please use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forwardBriefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forward
- Answe Answer A and B pleasearrow_forward3. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: Isoelectric point Amino Acid Arginine 10.76 Glutamic Acid 3.22 Tryptophan 5.89 A. Define isoelectric point. B. The most basic amino acid is C. The most acidic amino acid is sidizo zoarrow_forward3. A gas mixture contains 50 mol% H2 and 50 mol% He. 1.00-L samples of this gas mixture are mixed with variable volumes of O2 (at 0 °C and 1 atm). A spark is introduced to allow the mixture to undergo complete combustion. The final volume is measured at 0 °C and 1 atm. Which graph best depicts the final volume as a function of the volume of added O2? (A) 2.00 1.75 Final Volume, L 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 2.00 (B) 1.75 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50- 0.25 0.00 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 2 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2 2.00 2.00 (C) (D) 1.75 1.75 1.50 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





