
Campbell Biology: Custom Edition
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781323717271
Author: Urry, Cain, Wasserman, Minorsky, Reece
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 14.3CR
Inheritance patterns are often more complex than predicted by simple
Extensions of Mendelian genetics for a single gene:
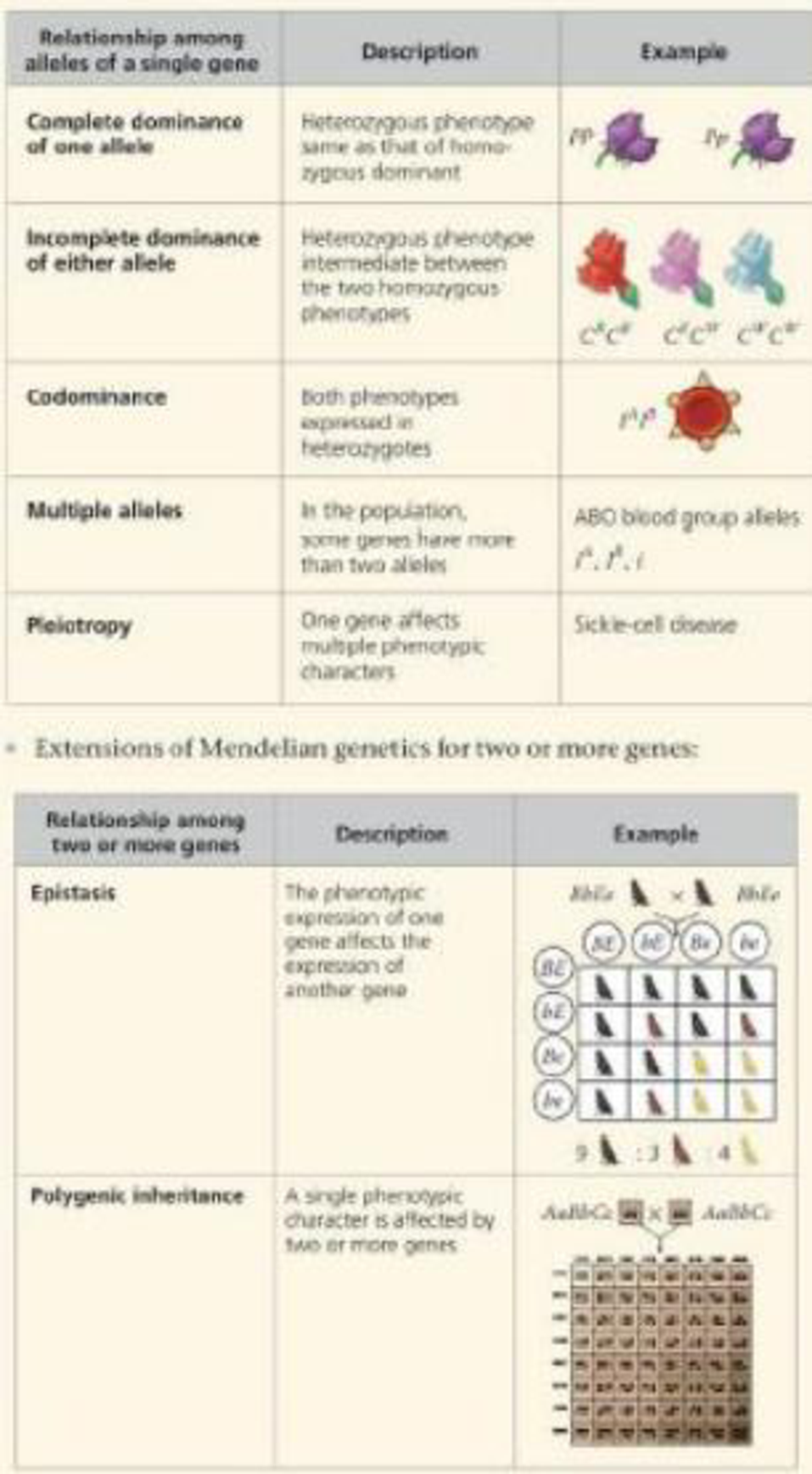
Which genetic relationships listed h the first column of the two tables above are demonstrated by the inheritance pattern of the ABO blood group alleles? For each genetic relationship, explain why this inheritance pattern is or is not an example.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
would this be considered a novel protein and if not how can I fix it so it is and can you draw the corrections please
In as much detail as possible, hand draw a
schematic diagram of the hypothalamic-pituitary-
gonad (HPG) axis in the human male. Be sure to
include all the relevant structures and hormones.
You must define all abbreviations the first time
you use them. Please include (and explain) the
feedback loops.
A negligence action was brought by a mother against a hospital on behalf of her minor daughter. It alleged that when the mother was 13 years of age, the hospital negligently transfused her with Rh-positive blood. The mother's Rh-negative blood was incompatible with and sensitized by the Rh-positive blood. The mother discovered her condition 8 years later during a routine blood screening ordered by her healthcare provider in the course of prenatal care. The resulting sensitization of the mother's blood allegedly caused damage to the fetus, resulting in physical defects and premature birth.
Did a patient relationship with the transfusing hospital exist?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Custom Edition
Ch. 14.1 - DRAW IT Pea plants heterozygous for flower...Ch. 14.1 - WHAT IF? List all gametes that could be made by a...Ch. 14.1 - MAKE CONNECTIONS In some pea plant crosses, the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 1CCCh. 14.2 - Two organisms, with genotypcs BbDD and BBDd, are...Ch. 14.2 - WHAT IF? Three characters (flower color, seed...Ch. 14.3 - What two properties, one structural and one...Ch. 14.3 - If a man with type AB blood marries a woman with...Ch. 14.3 - WHAT IF? A rooster with gray feathers and a hen...Ch. 14.4 - Beth and Tom each have a sibling with cystic...
Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 14.4 - Prob. 3CCCh. 14.4 - MAKE CONNECTIONS In Table 14.1, note the...Ch. 14 - When Mendel did crosses of true-breeding purple-...Ch. 14 - DRAW IT Redraw the Punnett Square on The right...Ch. 14 - Inheritance patterns are often more complex than...Ch. 14 - Both members of a couple know that they are...Ch. 14 - DRAW IT Two pea plants heterozygous for the...Ch. 14 - A man with type A blood marries a woman with type...Ch. 14 - A man has six fingers on each hand and six toes on...Ch. 14 - DRAW IT A pea plant heterozygous for inflated pods...Ch. 14 - Flower position, stem length, and seed shape are...Ch. 14 - Hemochromatosis is an inherited disease caused by...Ch. 14 - The genotype of F1, individuals in a tetrahybrid...Ch. 14 - What is the probability that each of thc following...Ch. 14 - Prob. 9TYUCh. 14 - Prob. 10TYUCh. 14 - In tigers, a recessive allele of a particular gene...Ch. 14 - In maize (com) plants,a dominant allele I inhibits...Ch. 14 - The pedigree belowtraces the inheritance of...Ch. 14 - Imagine that you are a genetic counselor, and a...Ch. 14 - EVOLUTION CONNECTION Over the past half century,...Ch. 14 - SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY You are handed a mystery pea...Ch. 14 - Prob. 17TYUCh. 14 - SYNTHESIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE Just for fun, imagine...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Single penny tossed 20 times and counting heads and tails: Probability (prediction): _______/20 heads ________/...
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
Practice Problem ATTEMPT
Write the rate expressions for each of the following reactions:
(a)
(b)
(c)
Chemistry
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 18. Watch this short youtube video about SARS CoV-2 replication. SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle (Summer 2020) - YouTube.19. What is the name of the receptor that SARS CoV-2 uses to enter cells? Which human cells express this receptor? 20. Name a few of the proteins that the SARS CoV-2 mRNA codes for. 21. What is the role of the golgi apparatus related to SARS CoV-2arrow_forwardState the five functions of Globular Proteins, and give an example of a protein for each function.arrow_forwardDiagram of check cell under low power and high powerarrow_forward
- a couple in which the father has the a blood type and the mother has the o blood type produce an offspring with the o blood type, how does this happen? how could two functionally O parents produce an offspring that has the a blood type?arrow_forwardWhat is the opening indicated by the pointer? (leaf x.s.) stomate guard cell lenticel intercellular space none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue? (stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem ○ phloem none of thesearrow_forward
- Where did this structure originate from? (Salix branch root) epidermis cortex endodermis pericycle vascular cylinderarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College


Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY