
Concept explainers
BIO A Cricket Thermometer, by Jiminy
Insects are ectothermic, which means their body temperature is largely determined by the temperature of their surroundings. This can have a number of interesting consequences. For example, the wing coloration in some butterfly species is determined by the ambient temperature, as is the body color of several species of dragonfly. In addition, the wing beat frequency of beetles taking flight varies with temperature due to changes in the resonant frequency of their thorax.
The origin of such temperature effects can be traced back to the fact that molecules have higher speeds and greater energy as temperature is increased (see Chapters 16 and 17). Thus, for example, molecules that collide and react as part of the
One of the most interesting thermal effects is the temperature dependence of chirp rate in certain insects. This behavior has been observed in cone-headed grasshoppers, as well as several types of cricket. A particularly accurate connection between chirp rate and temperature is found in the snowy tree cricket (Oecanthus fultoni Walker), which chirps at a rate that follows the expression N = T − 39, where N is the number of chirps in 13 seconds, and T is the numerical value of the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. This formula, which is known as Dolbear’s law, is plotted in Figure 13-46 (green line) along with data points (blue dots) for the snowy tree cricket.
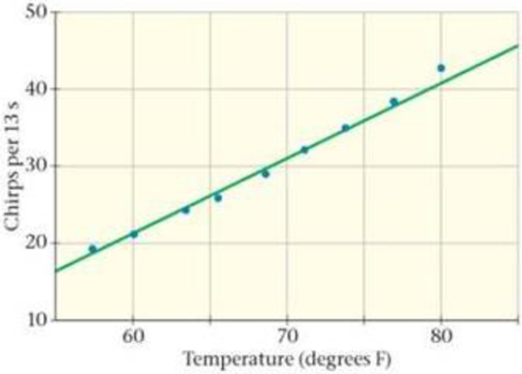
Figure 13-46 Problems 93, 94, 95, and 96
95. • What is the frequency of the cricket’s chirping (in Hz) when the temperature is 68 °F?
- A. 0.45 Hz
- B. 2.2 Hz
- C. 5.2 Hz
- D. 29 Hz
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Physics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





