
Concept explainers
Answer the following questions about compound A, represent in the given ball-and-stick model.
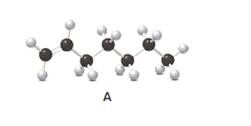
- Convert A to a condensed structure and give its IUPAC name.
- What product is formed when A is treated with H2 in the presence of metal catalyst?
- What product is formed when A is treated with H2O in the presence of H2SO4?
- What
polymer is formed when A ispolymerized ?
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of the molecule A should be converted to a condensed structure and IUPAC name of the molecule should be given.
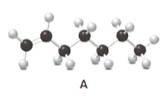 = (
= (
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
In alkene nomenclature, the longest C chain will be considered as the parent/ main C chain. At the end of the alkane suffix -ene is added. The longest chain which includes the carbon-carbon double bond will be considered as the main carbon chain. The numbering of the main C chain is starting from the first substituent by giving the lower number to that substituent and as well as the double bond should get the lower number. All the substituents should be numbered and named. Two or more identical substituents should be indicated by using appropriate prefixes as di-. Names of the substituents should be alphabetized. Each substituent should have a position number which is mentioned in the main C chain.
Answer to Problem 95P
Condensed structure −
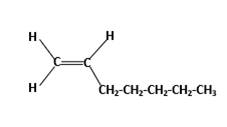
IUPAC name −Heptene
Explanation of Solution
In alkenes, there is a carbon-carbon double bond and different groups are connected to the two carbons. In most of the alkenes; out of four binding positions of carbon-carbon double bond, two of them are bind with two hydrogen atoms and the other two binding positions bind with two different alkyl groups. In this molecule, carbon atoms are represented in black and hydrogen atoms are represented in white color. The structure of a chemical compound is the arrangement of atoms and bonds in the space.
Condensed structure −
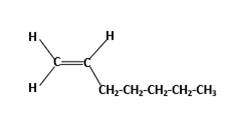
In this molecule, the main carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon double bond is a seven-membered chain and there are no substituents in this molecule. According to the numbering of the main chain double bond gets the lowest number and it is number 1. Hence, the IUPAC name of the molecule is heptene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that contain a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 95P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 95P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Refer to the below reaction;
(d)
Interpretation:
The resulting polymer should be identified after polymerization of
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond inside a molecule.
Polymers are high molecular weight macromolecules which formed from covalently bonded monomer molecules.
Answer to Problem 95P
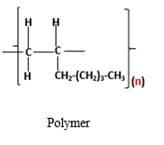
Explanation of Solution
Polymers are high molecular weight macromolecules which formed from covalently bonded monomer molecules. When forming polymers from alkene monomers, the weak bond which is in the carbon-carbon double bond is broken and new strong bond will form to connect the monomer molecules together. Hence; weak bond of the carbon-carbon double bond of

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- The following 'H NMR spectrum was taken with a 750 MHz spectrometer: 1.0 0.5 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 ' 2.0 1.0 0.0 (ppm) What is the difference Av in the frequency of RF ac Δν ac radiation absorbed by the a and c protons? (Note: it's not equal to the difference in chemical shifts.) Round your answer to 2 significant digits, and be sure it has an appropriate unit symbol. = O O a will shift left, c will shift right. O a will shift right, c will shift left. a and c will both shift left, with more space between them. Suppose a new spectrum is taken with a 500 MHz spectrometer. What will be true about this new spectrum? O a and c will both shift left, with less space between them. O a and c will both shift right, with more space between them. O a and c will both shift right, with less space between them. Which protons have the largest energy gap between spin up and spin down states? O None of the above. ○ a Ob Explanation Check C Ar B 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved.…arrow_forwardWhat mass of Na2CO3 must you add to 125g of water to prepare 0.200 m Na2CO3? Calculate mole fraction of Na2CO3, mass percent, and molarity of the resulting solution. MM (g/mol): Na2CO3 105.99; water 18.02. Final solution density is 1.04 g/mL.arrow_forward(ME EX2) Prblms Can you please explain problems to me in detail, step by step? Thank you so much! If needed color code them for me.arrow_forward
- Experiment #8 Electrical conductivity & Electrolytes. Conductivity of solutions FLINN Scientific Scale RED LED Green LED LED Conductivity 0 OFF OFF 1 Dim OFF 2 medium OFF 3 Bright Dim Low or Nowe Low Medium High 4 Very Bright Medium nd very high AA Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ SE=Strong Electrolyte, FE = Fair Electrolyte CWE = Weak Electrolyte, NE= Noni Electrolyte, #Solutions 1 0.1 M NaCl 2/1x 102 M NaCl, 3/1X103 M Nall Can Prediction M Observed Conductivity Very bright red Bright red Dim red you help me understand how I'm supposed to find the predictions of the following solutions? I know this is an Ionic compound and that the more ions in a solution means it is able to carry a charge, right? AAAA Darrow_forward(SE EX 2) Prblsm 4-7: Can you please explain problems 4-7 and color code if needed for me. (step by step) detail explanationsarrow_forward(SE EX 2) Problems 8-11, can you please explain them to me in detail and color-code anything if necessary?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning


