
Concept explainers
What
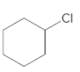
a.
(a)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
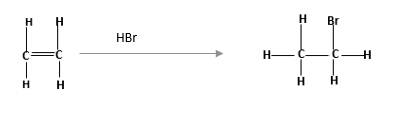
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 59P
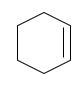
Starting alkene-
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction:
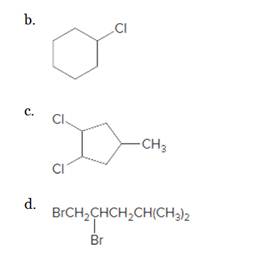
(b)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 59P
Starting alkene −
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction;
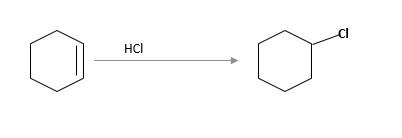
(c)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
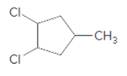
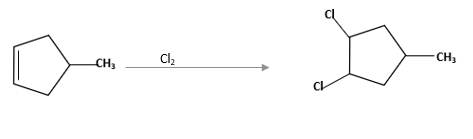
Answer to Problem 59P
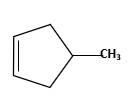 Starting alkene −
Starting alkene −
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction;
(d)
Interpretation:
The starting material and the reagents needed to prepare following alkyl halide should be determined:

Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 59P
Starting alkene −
Reagent -
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated alkene molecules react with
Refer to the below reaction:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- Which alkane most readily undergoes thermal decomposition? Note that C-H bonds are usually stronger than C-C bonds. O ethane O dimethylpropane O propane O methylpropanearrow_forwardThis type of hydrocarbons contain at least one double or triple bond. Unsaturated hydrocarbons Saturated hydrocarbons Polyunsaturated hydrocarbons O Supersaturated hydrocarbons The most acidic among the hydrocarbons. Alkynes Alkenes Alkanes Arenes The number of secondary carbon(s) in this compound. CH3 CH,-C CHCH, CH3 CIarrow_forwardEach of the following hydrocarbons contains a single functional group. Which is an alkene? O C3H5 O C3H6 O C3H8 O C3H7arrow_forward
- Identify the alkene from the following four molecules. HC. CH HC. CHa CHs CH CH3 2.arrow_forwardCompounds with two carbonyl groups are named as alkane diones, for example: R 2,3-butanedione The compound above is an artificial flavor added to microwave popcorn and movie-theater popcorn to simulate the butter flavor. Interestingly, this very same compound is also known to contribute to body odor. Name the following compounds: cyclohexane-1,3-dione cycloheptane-1,4-dione gily nonane-2,8-dionearrow_forwardWhat functional group distinguishes each of the following hydrocarbon derivatives? a. halohydrocarbons b. alcohols c. ethers d. aldehydes e. ketones f. carboxylic acids g. esters h. amines Give examples of each functional group. What prefix or suffix is used to name each functional group? What are the bond angles in each? Describe the bonding in each functional group. What is the difference between a primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol? For the functional groups in ah, when is a number required to indicate the position of the functional group? Carboxylic acids are often written as RCOOH. What does COOH indicate and what does R indicate? Aldehydes are sometimes written as RCHO. What does CHO indicate?arrow_forward
- Name each alkyne: a.CH3CHCHCH2CH2CH3arrow_forwardName and draw a structural formula for the product of each alkene addition reaction. (a) (b)arrow_forwardWhat are aromatic hydrocarbons? Benzene exhibits resonance. Explain. What are the bond angles in benzene? Give a detailed description of the bonding in benzene. The electrons in benzene are delocalized, while the electrons in simple alkenes and alkynes are localized. Explain the difference.arrow_forward
- Mark the correct statements about the structural features of alkenes and alkynes. * A- Free rotation is not possible around a double or triple bond. B- A triple bond is shorter and stronger than a double bond. C- A pi-bond can only form by overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent atoms if these atoms are from the same element. D- The pi-bond in an alkene is weaker than the sigma bond because the sideways overlap of p-orbitals is less than the head-to-head overlap of sp² hybrid orbitals. E- All the bond angles in an alkyne are 180°.arrow_forwardWhich reagent is needed to change an alkyne to an alkane? * Н:0+, Hg (COОH)2 N2, Pt Ог, Pd Н, Pt What reaction takes place when an alcohol is produced during the net addition of water across the double bond of an alkene? * Dehydrogenation Hydrogenation Dehydration Hydrationarrow_forwardname: Consider the image. H-C- H H name: a H :S: H H C H H H H H What is the IUPAC name for the thiol shown as a Lewis structure in the image? C-Harrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning  World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





