
Concept explainers
You’re working for the summer with an ornithologist who knows you’ve studied physics. She asks you for a noninvasive way to measure birds’ masses. You propose using a bird feeder in the shape of a 50-cm-diameter disk of mass 340 g, suspended by a wire with torsional constant 5.00 N·m/rad (Fig. 13.36). Two birds land on opposite sides and the feeder goes into torsional oscillation at 2.6 Hz. Assuming the birds have the same mass, what is it?
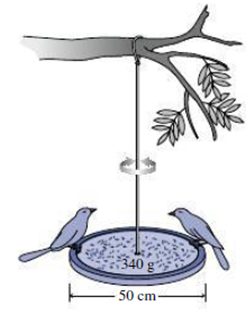
FIGURE 13.36 Problem 82
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essential University Physics Volume 1, Loose Leaf Edition (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- help and explain how to find the answerarrow_forwardWhat is the equivalent resistance between points A and B of the network shown in the figure? A • 12 B 4.0 6.0 Ω 8.0 Ωarrow_forwardAccording to the provided information answer the question accorrding to grade 11 physics Jerry has decided to give up his part-time job for a new career, cat-burglar! Jerry loves the idea of dressing up like a cat all day and of course the chance of meeting Cat Woman! On Jerry's first "job" he figures out his escape plan. He travels 3.0 km south for 15 minutes and then 8.0 km west for 1.5 hours before reaching his house. Draw a sketch diagram of the path he took with all the appropriate labels.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





