
Concept explainers
Define each of the following:
a.
b. Brønsted—Lowry acid
c. Lewis acid
Which of the definitions is most general? Write reactions to justify your answer.
(a)
Interpretation: The definition of each term, Arrhenius acid, Bronsted-Lowry acid and Lewis acid is to be given. The most general definition from these terms is to be identified and the reactions are to be given for the justification of answers.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that turns litmus to red. It has a sour taste.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Answer
Arrhenius acid produces hydrogen ions in aqueous solution.
Explanation of Solution
To define: Arrhenius acid.
The substance that produces hydrogen ions in aqueous solution is known as Arrhenius acid.
Arrhenius postulated the concept of acid. According to him “The substance that produces hydrogen ions in aqueous solution is known as acid.”
(b)
Interpretation: The definition of each term, Arrhenius acid, Bronsted-Lowry acid and Lewis acid is to be given. The most general definition from these terms is to be identified and the reactions are to be given for the justification of answers.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that turns litmus to red. It has a sour taste.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Answer
Bronsted-Lowry acids are able to donate a proton.
Explanation of Solution
To define: Bronsted-Lowry acid.
The substance that can donate a proton
Johannes Bronsted and Thomas Lowry proposed a model known as Bronsted-Lowry model. According to this model “The donor of proton
(c)
Interpretation: The definition of each term, Arrhenius acid, Bronsted-Lowry acid and Lewis acid is to be given. The most general definition from these terms is to be identified and the reactions are to be given for the justification of answers.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that turns litmus to red. It has a sour taste.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Answer
Lewis acids can accept a pair of electrons.
The most general definition of acid is given by Bronsted-Lowry model.
Explanation of Solution
To define: Lewis acid.
The chemical species that accepts a pair of non-bonding electrons is known as Lewis acid.
The Gilbert Newton Lewis suggested acid-base theory. According to this theory “The species that can accept a pair of non bonding electrons is known as acid.”
The most general definition of acid is given by Bronsted-Lowry model because this model is applicable to the non-aqueous solution also.
Arrhenius acid,
The substance that produces hydrogen ions in aqueous solution is known as Arrhenius acid.
The dissociation reaction of
The compound
Bronsted-Lowry acid,
The donor of proton
The reaction of
Lowry acid,
The chemical compound that accepts a pair of non-bonding electrons is known as Lewis acid.
The compound
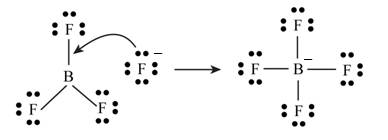
Figure 1
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: AN ATOMS FIRST APPROACH
- 451. Use the diffusion model from lecture that showed the likelihood of mixing occurring in a lattice model with eight lattice sites: Case Left Right A B C Permeable Barrier → and show that with 2V lattice sites on each side of the permeable barrier and a total of 2V white particles and 2V black particles, that perfect de-mixing (all one color on each side of the barrier) becomes increasingly unlikely as V increases.arrow_forward46. Consider an ideal gas that occupies 2.50 dm³ at a pressure of 3.00 bar. If the gas is compressed isothermally at a constant external pressure so that the final volume is 0.500 dm³, calculate the smallest value Rest can have. Calculate the work involved using this value of Rext.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- 2010. Suppose that a 10 kg mass of iron at 20 C is dropped from a heigh of 100 meters. What is the kinetics energy of the mass just before it hits the ground, assuming no air resistance? What is its speed? What would be the final temperature of the mass if all the kinetic energy at impact is transformed into internal energy? The molar heat capacity of iron is Cpp = 25.1J mol-¹ K-1 and the gravitational acceleration constant is 9.8 m s¯² |arrow_forwardell last during 7. Write the isotopes and their % abundance of isotopes of i) Cl ii) Br 8. Circle all the molecules that show Molecular ion peak as an odd number? c) NH2CH2CH2NH2 d) C6H5NH2 a) CH³CN b) CH3OHarrow_forwardCalsulate specific heat Dissolution of NaOH ก ง ง Mass of water in cup Final temp. of water + NaOH Initial temp. of water AT Water AH Dissolution NaOH - "CaicuraORT. AH (NaOH)=-AH( 30g (water) 29.0°C 210°C 8°C (82) 100 3.. =1003.20 Conjosarrow_forward
- Please provide throrough analysis to apply into further problems.arrow_forwardMolecular ion peak: the peak corresponding to the intact morecure (with a positive charge) 4. What would the base peak and Molecular ion peaks when isobutane is subjected to Mass spectrometry? Draw the structures and write the molecular weights of the fragments. 5. Circle most stable cation a) tert-butyl cation b) Isopropyl cation c) Ethyl cation. d)Methyl cationarrow_forwardHow many arrangements are there of 15 indistinguishable lattice gas particles distributed on: a.V = 15 sites b.V = 16 sites c.V = 20 sitesarrow_forward
- For which element is the 3d subshell higher in energy than that 4s subshell? Group of answer choices Zr Ca V Niarrow_forwardii) Molecular ion peak :the peak corresponding to the intact molecule (with a positive charge) What would the base peak and Molecular ion peaks when isobutane is subjected to Mass spectrometry? Draw the structures and write the molecular weights of the fragments. Circle most stable cation a) tert-butyl cation b) Isopropyl cation c) Ethyl cation. d) Methyl cation 6. What does a loss of 15 represent in Mass spectrum? a fragment of the molecule with a mass of 15 atomic mass units has been lost during the ionization Process 7. Write the isotopes and their % abundance of isotopes of i) Clarrow_forwardChoose a number and match the atomic number to your element on the periodic table. For your element, write each of these features on a side of your figure. 1. Element Name and symbol 2. Family and group 3. What is it used for? 4. Sketch the Valence electron orbital 5. What ions formed. What is it's block on the periodic table. 6. Common compounds 7. Atomic number 8. Mass number 9. Number of neutrons- (show calculations) 10. Sketch the spectral display of the element 11.Properties 12. Electron configuration 13. Submit a video of a 3-meter toss in slow-moarrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





