
Concept explainers
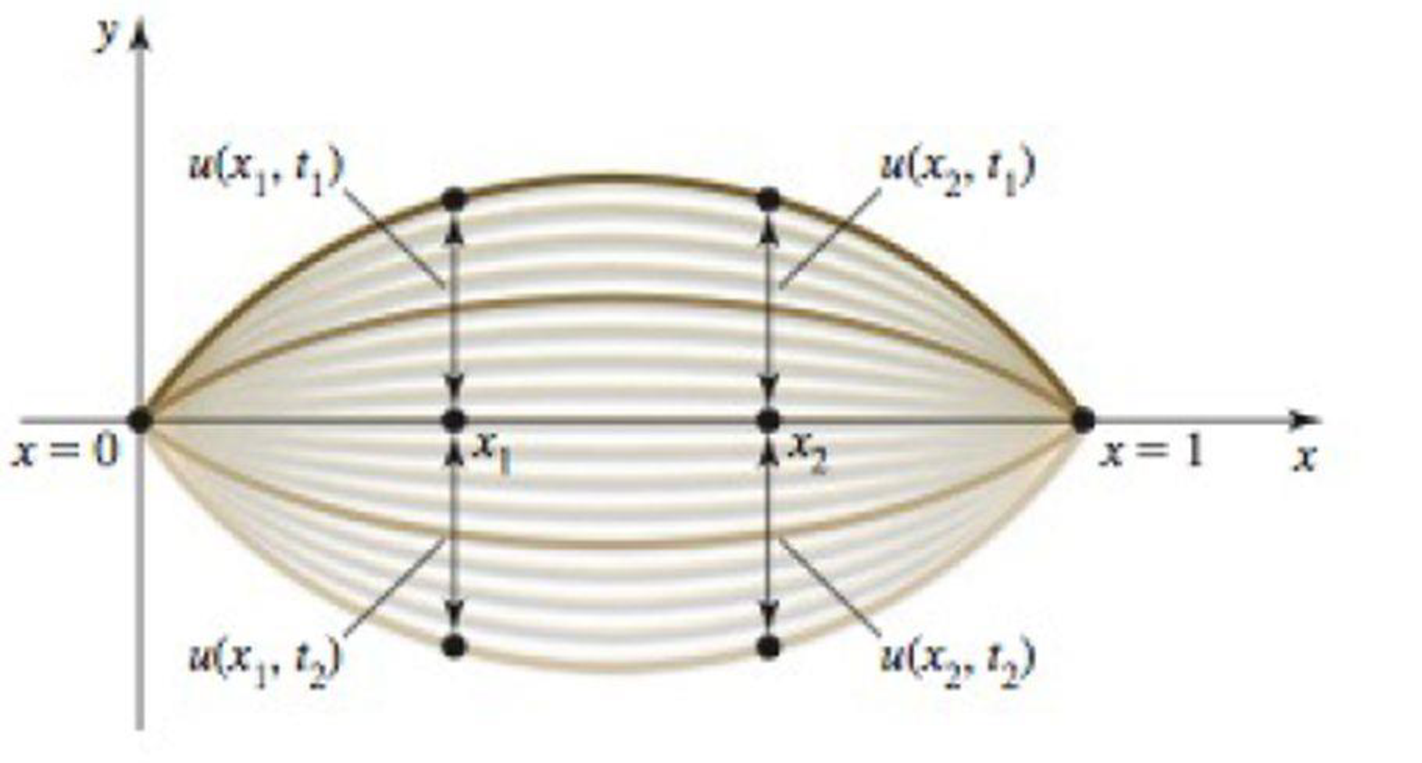
Wave on a string Imagine a string that is fixed at both ends (for example, a guitar string). When plucked, the string forms a standing wave. The displacement u of the string varies with position x and with time t. Suppose it is given by u = f(x, t) = 2 sin (πx) sin (πt/2), for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 and t ≥ 0 (see figure). At a fixed point in time, the string forms a wave on [0, 1]. Alternatively, if you focus on a point on the string (fix a value of x), that point oscillates up and down in time.
a. What is the period of the motion in time?
b. Find the rate of change of the displacement with respect to time at a constant position (which is the vertical velocity of a point on the string).
c. At a fixed time, what point on the string is moving fastest?
d. At a fixed position on the string, when is the string moving fastest?
e. Find the rate of change of the displacement with respect to position at a constant time (which is the slope of the string).
f. At a fixed time, where is the slope of the string greatest?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 12 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual, Single Variable for Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- 1. The graph of ƒ is given. Use the graph to evaluate each of the following values. If a value does not exist, state that fact. и (a) f'(-5) (b) f'(-3) (c) f'(0) (d) f'(5) 2. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = g(x) at x = 5 if g(5) = −3 and g'(5) = 4. - 3. If an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = f(x) at the point where x 2 is y = 4x — 5, find ƒ(2) and f'(2).arrow_forwardDoes the series converge or divergearrow_forwardDoes the series converge or divergearrow_forward
- Diverge or converarrow_forwardCan you help explain what I did based on partial fractions decomposition?arrow_forwardSuppose that a particle moves along a straight line with velocity v (t) = 62t, where 0 < t <3 (v(t) in meters per second, t in seconds). Find the displacement d (t) at time t and the displacement up to t = 3. d(t) ds = ["v (s) da = { The displacement up to t = 3 is d(3)- meters.arrow_forward
- Let f (x) = x², a 3, and b = = 4. Answer exactly. a. Find the average value fave of f between a and b. fave b. Find a point c where f (c) = fave. Enter only one of the possible values for c. c=arrow_forwardplease do Q3arrow_forwardUse the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forward
- Find the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forwarda -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning

