
a.
To find the points of intersection of the orbits of Pluto and the comet.
a.
Answer to Problem 41STP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The orbit of the Pluto modeled by the equation
Calculation:
Graphing the above two equations to find the point of intersection as follows-
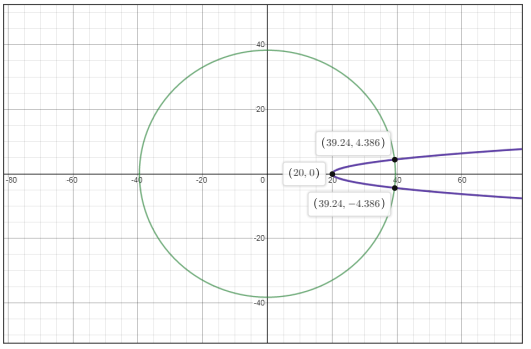
Clearly from the above graph the point of intersection is
b.
To find whether the comet will necessarily hit the Pluto.
b.
Answer to Problem 41STP
Not sure.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The orbit of the Pluto modeled by the equation
Calculation:
As it is visible from the graph, it can’t be sure that it will necessarily hit, it may or may not hit the Pluto.
c.
To find where do the graphs
c.
Answer to Problem 41STP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The orbit of the Pluto modeled by the equation
Calculation:
Let us graph the two equations
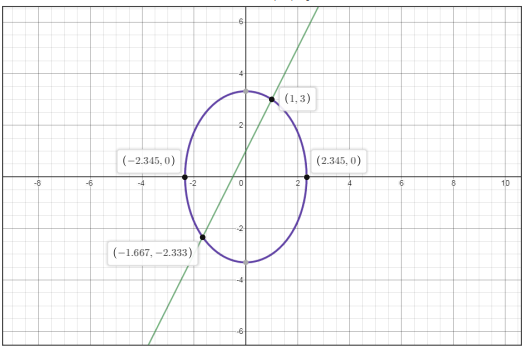
Clearly from the above graph the point of intersection is
d.
To find the coordinates of point that lie on the graphs of both
d.
Answer to Problem 41STP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The orbit of the Pluto modeled by the equation
Calculation:
Let us graph the two equations
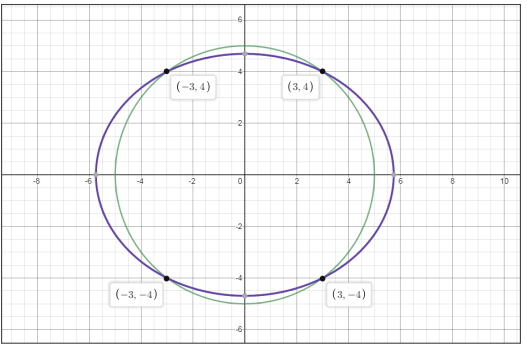
The following are the points that lie on both the graphs-
Chapter 12 Solutions
Algebra 2
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- Find the Laplace Transform of the function to express it in frequency domain form.arrow_forwardPlease draw a graph that represents the system of equations f(x) = x2 + 2x + 2 and g(x) = –x2 + 2x + 4?arrow_forwardGiven the following system of equations and its graph below, what can be determined about the slopes and y-intercepts of the system of equations? 7 y 6 5 4 3 2 -6-5-4-3-2-1 1+ -2 1 2 3 4 5 6 x + 2y = 8 2x + 4y = 12 The slopes are different, and the y-intercepts are different. The slopes are different, and the y-intercepts are the same. The slopes are the same, and the y-intercepts are different. O The slopes are the same, and the y-intercepts are the same.arrow_forward
- Choose the function to match the graph. -2- 0 -7 -8 -9 --10- |--11- -12- f(x) = log x + 5 f(x) = log x - 5 f(x) = log (x+5) f(x) = log (x-5) 9 10 11 12 13 14arrow_forwardWhich of the following represents the graph of f(x)=3x-2? 7 6 5 4 ++ + + -7-6-5-4-3-2-1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -2 3 -5 6 -7 96 7 5 4 O++ -7-6-5-4-3-2-1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -7 765 432 -7-6-5-4-3-2-1 -2 ++ -3 -4 -5 -6 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 2 345 67 -7-6-5-4-3-2-1 2 3 4 5 67 4 -5arrow_forward13) Let U = {j, k, l, m, n, o, p} be the universal set. Let V = {m, o,p), W = {l,o, k}, and X = {j,k). List the elements of the following sets and the cardinal number of each set. a) W° and n(W) b) (VUW) and n((V U W)') c) VUWUX and n(V U W UX) d) vnWnX and n(V WnX)arrow_forward
- 9) Use the Venn Diagram given below to determine the number elements in each of the following sets. a) n(A). b) n(A° UBC). U B oh a k gy ท W z r e t ་ Carrow_forward10) Find n(K) given that n(T) = 7,n(KT) = 5,n(KUT) = 13.arrow_forward7) Use the Venn Diagram below to determine the sets A, B, and U. A = B = U = Blue Orange white Yellow Black Pink Purple green Grey brown Uarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





