
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172364
Author: Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 9SCQ
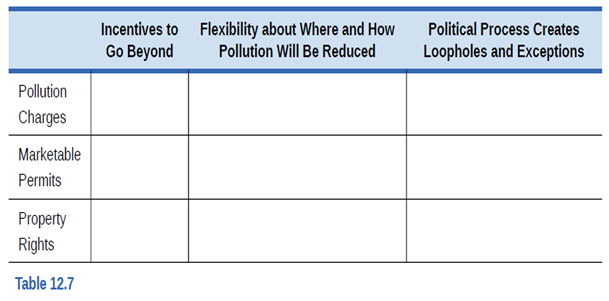
The rows in Table 12.7 show three market-oriented tools for reducing pollution. The columns of the table show three complaints about command-and-control regulation. Fill in the table by stating briefly how each market-oriented tool addresses each of the three concerns.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Should Maureen question the family about the history of the home? Can Maureen access public records for proof of repairs?
3. Distinguish between a direct democracy and a representative democracy. Use appropriate
examples to support your answers.
[4]
4. Explain the distinction between outputs and outcomes in social service delivery [2]
5. A R1000 tax payable by all adults could be viewed as both a proportional tax and a
regressive tax. Do you agree? Explain.
[4]
6. Briefly explain the displacement effect in Peacock and Wiseman's model of government
expenditure growth and provide a relevant example of it in the South African context. [5]
7. Explain how unbalanced productivity growth may affect government expenditure and
briefly comment on its relevance to South Africa.
[5]
8. South Africa has recently proposed an increase in its value-added tax rate to 15%, sparking
much controversy. Why is it argued that value-added tax is inequitable and what can be
done to correct the inequity?
[5]
9. Briefly explain the difference between access to education and the quality of education,
and why we should care about the…
20. Factors 01 pro
B. the technological innovations available to companies.
A. the laws that regulate manufacturers.
C. the resources used to create output
D. the waste left over after goods are produced.
21. Table 1.1 shows the tradeoff between different combinations of missile production and home
construction, ceteris paribus. Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both
missiles and houses. Then answer the indicated question(s).
Combination
Number of
houses
Opportunity cost
of houses in
Number of
missiles
terms of missiles
J
0
4
K
10,000
3
L
17,000
2
1
M
21,000
0
N
23,000
Opportunity cost
of missiles in
terms of houses
Tutorials-Principles of Economics
m health care
Chapter 12 Solutions
Principles of Economics 2e
Ch. 12 - Identify the following situations as an example of...Ch. 12 - Identify whether the market supply curve will...Ch. 12 - For each of your answers to Exercise 12.2, will...Ch. 12 - Table 12.5 provides the supply and demand...Ch. 12 - Consider two approaches to reducing emissions of...Ch. 12 - Classify the following pollution-control policies...Ch. 12 - An emissions tax on a quantity of emissions from a...Ch. 12 - Four films called Elm, Maple, Oak, and (Shelly,...Ch. 12 - The rows in Table 12.7 show three market-oriented...Ch. 12 - Suppose a city releases 16 million gallons of raw...
Ch. 12 - The state of Colorado requires oil and gas...Ch. 12 - Consider the case of global environmental problems...Ch. 12 - A country called Sherwood is very heavily covered...Ch. 12 - What is an externality?Ch. 12 - Give an example of a positive externality and an...Ch. 12 - What is the difference between private costs and...Ch. 12 - In a market without environmental regulations,...Ch. 12 - What is command-and-control environmental...Ch. 12 - What are the three problems that economists have...Ch. 12 - What is a pollution charge and what incentive does...Ch. 12 - What is a marketable permit and what incentive...Ch. 12 - What are better-defined property rights and what...Ch. 12 - As the extent of environmental protection expands,...Ch. 12 - As the extent of environmental protection expands,...Ch. 12 - What are the economic tradeoffs between low-income...Ch. 12 - What arguments d0 low-income countries make in...Ch. 12 - In the tradeoff between economic output and...Ch. 12 - What does a point inside the production...Ch. 12 - Suppose you want to put a dollar value on the...Ch. 12 - Would environmentalists favor command-and-control...Ch. 12 - Consider two ways of protecting elephants from...Ch. 12 - Will a system of marketable permits work with...Ch. 12 - Is zero pollution possible under a marketable...Ch. 12 - Is zero pollution an optimal goal? Way or why not?Ch. 12 - From an economic perspective, is it sound policy...Ch. 12 - Recycling is a relatively inexpensive solution to...Ch. 12 - Can extreme levels of pollution hurt the economic...Ch. 12 - How can high-income countries benefit from...Ch. 12 - Technological innovations shift the production...Ch. 12 - Show the market for cigarettes in equilibrium,...Ch. 12 - Refer to Table 12.2. The externality created by...Ch. 12 - Table 12.12, shows the supply and demand...Ch. 12 - A city currently emits 15 million gallons (MG) of...Ch. 12 - In the Land of Purity, there is only one form of...
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
(NPV calculation) Calculate the NPV given the following free cash flows if the appropriate required rate of ret...
Foundations Of Finance
The meaning of stock’s alpha and its interpretation. Introduction: Stock is a type of security in a company tha...
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
1-13. Identify a product, either a good or a service, that will take advantage of this opportunity. Although yo...
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
4. JC Manufacturing purchase d inventory for $ 5,300 and al so paid a $260 freight bill. JC Manufacturing retur...
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
Determine the FW of the following engineering project when the MARR is 15% per year. Is the project acceptable?...
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Discussion Questions 1. What characteristics of the product or manufacturing process would lead a company to us...
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a small open economy with a floating exchange rate, the supply of real money balances is fixed and a rise in government spending ______ Group of answer choices Raises the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market Raises the interest rate, so that income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market.arrow_forwardSuppose a country with a fixed exchange rate decides to implement a devaluation of its currency and commits to maintaining the new fixed parity. This implies (A) ______________ in the demand for its goods and a monetary (B) _______________. Group of answer choices (A) expansion ; (B) contraction (A) contraction ; (B) expansion (A) expansion ; (B) expansion (A) contraction ; (B) contractionarrow_forwardAssume a small open country under fixed exchanges rate and full capital mobility. Prices are fixed in the short run and equilibrium is given initially at point A. An exogenous increase in public spending shifts the IS curve to IS'. Which of the following statements is true? Group of answer choices A new equilibrium is reached at point B. The TR curve will shift down until it passes through point B. A new equilibrium is reached at point C. Point B can only be reached in the absence of capital mobility.arrow_forward
- A decrease in money demand causes the real interest rate to _____ and output to _____ in the short run, before prices adjust to restore equilibrium. Group of answer choices rise; rise fall; fall fall; rise rise; fallarrow_forwardIf a country's policy makers were to continously use expansionary monetary policy in an attempt to hold unemployment below the natural rate , the long urn result would be? Group of answer choices a decrease in the unemployment rate an increase in the level of output All of these an increase in the rate of inflationarrow_forwardA shift in the Aggregate Supply curve to the right will result in a move to a point that is southwest of where the economy is currently at. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forward
- An oil shock can cause stagflation, a period of higher inflation and higher unemployment. When this happens, the economy moves to a point to the northeast of where it currently is. After the economy has moved to the northeast, the Federal Reserve can reduce that inflation without having to worry about causing more unemployment. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forwardThe long-run Phillips Curve is vertical which indicates Group of answer choices that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and the price level. None of these that in the long-run, the economy returns to a 4 percent level of inflation.arrow_forwardSuppose the exchange rate between the British pound and the U.S. dollar is £1 = $2.00. The U.S. government implementsU.S. government implements a contractionary fiscal policya contractionary fiscal policy. Illustrate the impact of this change in the market for pounds. 1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new demand line. 2.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new supply line. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required objects.arrow_forward
- Just Part D please, this is for environmental economicsarrow_forward3. Consider a single firm that manufactures chemicals and generates pollution through its emissions E. Researchers have estimated the MDF and MAC curves for the emissions to be the following: MDF = 4E and MAC = 125 – E Policymakers have decided to implement an emissions tax to control pollution. They are aware that a constant per-unit tax of $100 is an efficient policy. Yet they are also aware that this policy is not politically feasible because of the large tax burden it places on the firm. As a result, policymakers propose a two- part tax: a per unit tax of $75 for the first 15 units of emissions an increase in the per unit tax to $100 for all further units of emissions With an emissions tax, what is the general condition that determines how much pollution the regulated party will emit? What is the efficient level of emissions given the above MDF and MAC curves? What are the firm's total tax payments under the constant $100 per-unit tax? What is the firm's total cost of compliance…arrow_forward2. Answer the following questions as they relate to a fishery: Why is the maximum sustainable yield not necessarily the optimal sustainable yield? Does the same intuition apply to Nathaniel's decision of when to cut his trees? What condition will hold at the equilibrium level of fishing in an open-access fishery? Use a graph to explain your answer, and show the level of fishing effort. Would this same condition hold if there was only one boat in the fishery? If not, what condition will hold, and why is it different? Use the same graph to show the single boat's level of effort. Suppose you are given authority to solve the open-access problem in the fishery. What is the key problem that you must address with your policy?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you


 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning



Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:Cengage Learning
