
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Predict the simple binary compound that can be formed by the use of electron configuration of the simple ions which are formed by those elements.
Concept Introduction:
Electron configuration describes the positions of electrons of an atom. Depending on that the periodic table is created. Periodic table further defines the simple ion that can be formed by any element. And using those ions, simple binary compounds can be produced.
Order in which orbitals fill to produce the atoms in periodic table as follows:
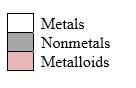
Simplest ion form by each group as follows:
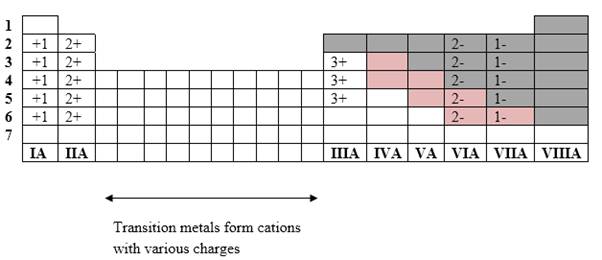
If it’s a compound made by a combination of metal and nonmetal elements, called as ionic compounds.
Ionic chemical compound must have a zero charge. If a compound contains ions;
1. Both positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) must be there.
2. No: of cations and anions collectively should produce a zero-net charge.
Answer to Problem 45CR
Explanation of Solution
Al and Cl
(b)
Interpretation:
Predict the simple binary compound that can be formed by the use of electron configuration of the simple ions which are formed by those elements.
Concept Introduction:
Electron configuration describes the positions of electrons of an atom. Depending on that the periodic table is created. Periodic table further defines the simple ion that can be formed by any element. And using those ions, simple binary compounds can be produced.
Order in which orbitals fill to produce the atoms in periodic table as follows:
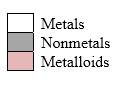
Simplest ion form by each group as follows:
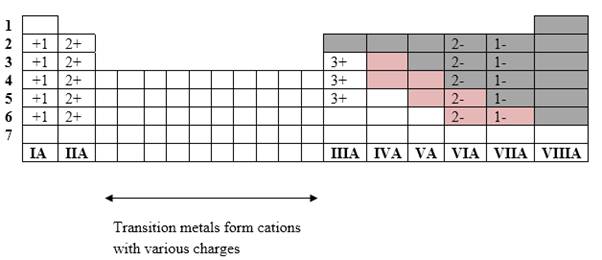
If it’s a compound made by a combination of metal and nonmetal elements, called as ionic compounds.
Ionic chemical compound must have a zero charge. If a compound contains ions;
1. Both positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) must be there.
2. No: of cations and anions collectively should produce a zero-net charge.
Answer to Problem 45CR
Explanation of Solution
Na and N
(c)
Interpretation:
Predict the simple binary compound that can be formed by the use of electron configuration of the simple ions which are formed by those elements.
Concept Introduction:
Electron configuration describes the positions of electrons of an atom. Depending on that the periodic table is created. Periodic table further defines the simple ion that can be formed by any element. And using those ions, simple binary compounds can be produced.
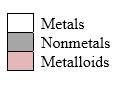
Order in which orbitals fill to produce the atoms in periodic table as follows:
Simplest ion form by each group as follows:
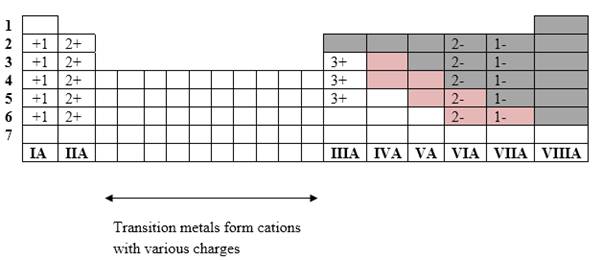
If it’s a compound made by a combination of metal and nonmetal elements, called as ionic compounds.
Ionic chemical compound must have a zero charge. If a compound contains ions;
1. Both positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) must be there.
2. No: of cations and anions collectively should produce a zero-net charge.
Answer to Problem 45CR
Explanation of Solution
Mg and S
(d)
Interpretation:
Predict the simple binary compound that can be formed by the use of electron configuration of the simple ions which are formed by those elements.
Concept Introduction:
Electron configuration describes the positions of electrons of an atom. Depending on that the periodic table is created. Periodic table further defines the simple ion that can be formed by any element. And using those ions, simple binary compounds can be produced.
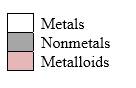
Order in which orbitals fill to produce the atoms in periodic table as follows:
Simplest ion form by each group as follows:
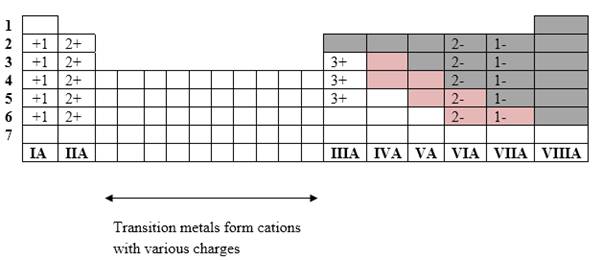
If it’s a compound made by a combination of metal and nonmetal elements, called as ionic compounds.
Ionic chemical compound must have a zero charge. If a compound contains ions;
1. Both positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) must be there.
2. No: of cations and anions collectively should produce a zero-net charge.
Answer to Problem 45CR
CaO.
Explanation of Solution
Ca and O
(e)
Interpretation:
Predict the simple binary compound that can be formed by the use of electron configuration of the simple ions which are formed by those elements.
Concept Introduction:
Electron configuration describes the positions of electrons of an atom. Depending on that the periodic table is created. Periodic table further defines the simple ion that can be formed by any element. And using those ions, simple binary compounds can be produced.
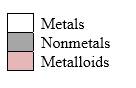
Order in which orbitals fill to produce the atoms in periodic table as follows:
Simplest ion form by each group as follows:
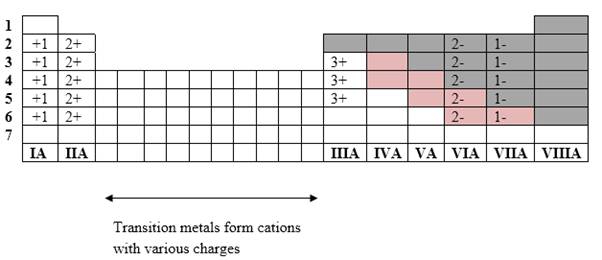
If it’s a compound made by a combination of metal and nonmetal elements, called as ionic compounds.
Ionic chemical compound must have a zero charge. If a compound contains ions;
1. Both positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) must be there.
2. No: of cations and anions collectively should produce a zero-net charge.
Answer to Problem 45CR
Explanation of Solution
K and O
(f)
Interpretation:
Predict the simple binary compound that can be formed by the use of electron configuration of the simple ions which are formed by those elements.
Concept Introduction:
Electron configuration describes the positions of electrons of an atom. Depending on that the periodic table is created. Periodic table further defines the simple ion that can be formed by any element. And using those ions, simple binary compounds can be produced.
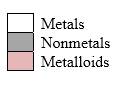
Order in which orbitals fill to produce the atoms in periodic table as follows:
Simplest ion form by each group as follows:
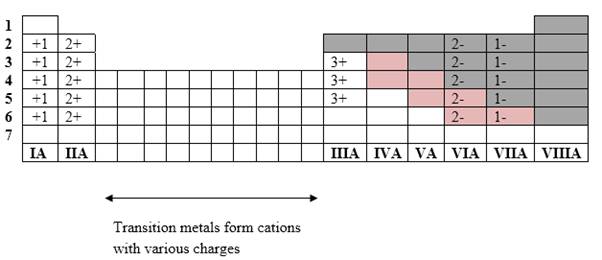
If it’s a compound made by a combination of metal and nonmetal elements, called as ionic compounds.
Ionic chemical compound must have a zero charge. If a compound contains ions;
1. Both positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) must be there.
2. No: of cations and anions collectively should produce a zero-net charge.
Answer to Problem 45CR
Explanation of Solution
Sr and Br
( Simple ion =
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
- 11) The Ksp expression for copper (II) sulfate is: a. [Cu2+][SO4²¯] b. [Cu²+]² [SO4²]² c. [Cu²+]²[SO4²] d. [CuSO4] 12) Which of the following is true about a chemical system in equilibrium? a. All chemical reactions have stopped b. The concentration of reactants is equal to the concertation of products c. The forward and reverse reaction rates become equal d. The system will remain at equilibrium regardless of any external factorsarrow_forward21) Explain the difference between the rate of a reaction and the extent of a reaction. Why are both of these concepts important, if you are a chemical engineer that is trying to develop a process to produce a large volume of a specific type of chemical compound?arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





