
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118921876
Author: Pritchard, Philip J.; Leylegian, John C.; Bhaskaran, Rajesh
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 20P
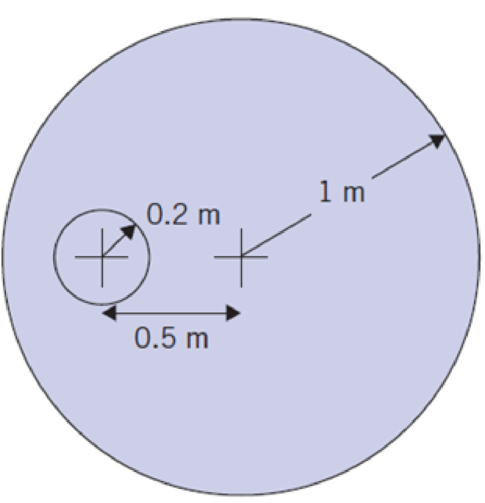
An object traveling in atmospheric air emits two pressure waves at different times. At an instant in time, the waves appear as in the figure. Determine the velocity and Mach number of the object and its current location.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A ship of 10 000 tonne displacement has a waterplanearea of 1300 m2. The ship loads in water of 1.010 t/m3 andmoves into water of 1.026 t/m3. Find the change in meandraught
A ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water.
A ship has 300 tonne of cargo in the hold, 24 m forward ofmidships. The displacement of the vessel is 6000 tonne and its centre of gravity is 1.2 m forward of midships.Find the new position of the centre of gravity if this cargo ismoved to an after hold, 40 m from midships
Chapter 12 Solutions
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 12 - Air is expanded in a steady flow process through a...Ch. 12 - Five kilograms of air is cooled in a closed tank...Ch. 12 - Air is contained in a piston-cylinder device. The...Ch. 12 - Calculate the power delivered by the turbine per...Ch. 12 - If hydrogen flows as a perfect gas without...Ch. 12 - A 1-m3 tank contains air at 0.1 MPa absolute and...Ch. 12 - Air enters a turbine in steady flow at 0.5 kg/s...Ch. 12 - Natural gas, with the thermodynamic properties of...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide flows at a speed of 10 m/s in a...Ch. 12 - In an isothermal process, 0.1 cubic feet of...
Ch. 12 - Calculate the speed of sound at 20C for (a)...Ch. 12 - An airplane flies at 550 km/hr at 1500 m altitude...Ch. 12 - Actual performance characteristics of the Lockheed...Ch. 12 - For a speed of sound in steel of 4300 m/s,...Ch. 12 - Determine and plot the Mach number of an...Ch. 12 - Investigate the effect of altitude on Mach number...Ch. 12 - The grandstand at the Kennedy Space Center is...Ch. 12 - Use data for specific volume to calculate and plot...Ch. 12 - An object traveling in atmospheric air emits two...Ch. 12 - An object traveling in atmospheric air emits two...Ch. 12 - While at the seashore, you observe an airplane...Ch. 12 - The temperature varies linearly from sea level to...Ch. 12 - Prob. 23PCh. 12 - A photograph of a bullet shows a Mach angle of 32....Ch. 12 - An F-4 aircraft makes a high-speed pass over an...Ch. 12 - All aircraft passes overhead at 3 km altitude. The...Ch. 12 - A supersonic aircraft flies at 3 km altitude at a...Ch. 12 - For the conditions of Problem 12.27, find the...Ch. 12 - The Concorde supersonic transport cruised at M =...Ch. 12 - Plot the percentage discrepancy between the...Ch. 12 - Compute the air density in the undisturbed air and...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide flows in a duct at a velocity of 90...Ch. 12 - If nitrogen at 15C is flowing and the stagnation...Ch. 12 - An aircraft cruises at M = 0.65 at 10 km altitude...Ch. 12 - High-speed aircraft use air data computers to...Ch. 12 - A supersonic wind tunnel test section is designed...Ch. 12 - Oxygen flows in a passage at a pressure of 25...Ch. 12 - What is the pressure on the nose of a bullet...Ch. 12 - Prob. 39PCh. 12 - Air flows in an insulated duct. At point the...Ch. 12 - Consider steady, adiabatic flow of air through a...Ch. 12 - Air passes through a normal shock in a supersonic...Ch. 12 - A Boeing 747 cruises at M = 0:87 at an altitude of...Ch. 12 - Space debris impact is a real concern for...Ch. 12 - A CO2 cartridge is used to propel a toy rocket....Ch. 12 - Nitrogen flows from a large tank, through a...Ch. 12 - Air flows from the atmosphere into an evacuated...Ch. 12 - Oxygen discharges from a tank through a convergent...Ch. 12 - The hot gas stream at the turbine inlet of a JT9-D...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide discharges from a tank through a...Ch. 12 - Air at 100F and 100 psia in a large tank flows...Ch. 12 - Calculate the required diameter of a convergent...Ch. 12 - Steam flows steadily and isentropically through a...Ch. 12 - Nitrogen flows through a diverging section of duct...Ch. 12 - At a section in a passage, the pressure is 30...Ch. 12 - In a given duct flow M = 2.0; the velocity...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Five pounds of air per second discharge from a...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a...Ch. 12 - Air, at an absolute pressure of 60.0 kPa and 27C,...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide flows from a tank through a...Ch. 12 - A convergent-divergent nozzle of 50-mm tip...Ch. 12 - Air flows adiabatically through a duct. At the...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Atmospheric air at 98.5 kPa and 20C is drawn into...Ch. 12 - The exit section of a convergent-divergent nozzle...Ch. 12 - Air flowing isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Air flows from a large tank at p = 650 kPa...Ch. 12 - A converging nozzle is connected to a large tank...Ch. 12 - Air at 0C is contained in a large tank on the...Ch. 12 - A large tank initially is evacuated to 10 kPa...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Air enters a converging-diverging nozzle at 2 MPa...Ch. 12 - Prob. 75PCh. 12 - A jet transport aircraft, with pressurized cabin,...Ch. 12 - A converging-diverging nozzle, with a throat area...Ch. 12 - Air, at a stagnation pressure of 7.20 MPa absolute...Ch. 12 - A small rocket motor, fueled with hydrogen and...Ch. 12 - Testing of a demolition explosion is to be...Ch. 12 - A total-pressure probe is placed in a supersonic...Ch. 12 - Air flows steadily through a long, insulated...Ch. 12 - Air discharges through a convergent-divergent...Ch. 12 - A normal shock wave exists in an airflow. The...Ch. 12 - Air approaches a normal shock at V1 = 900 m/s, p1...Ch. 12 - Air approaches a normal shock at M1 = 2.5, with...Ch. 12 - Air undergoes a normal shock. Upstream, T1 = 35C,...Ch. 12 - If, through a normal shock wave in air, the...Ch. 12 - The stagnation temperature in an airflow is 149C...Ch. 12 - A supersonic aircraft cruises at M = 2.2 at 12 km...Ch. 12 - The Concorde supersonic transport flew at M = 2.2...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is the difference between the names defined in an ML let construct from the variables declared in a C bloc...
Concepts Of Programming Languages
ICA 17-24
The decay of a radioactive isotope can be theoretically modeled with the following equation, where C0...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
A contractor uses a blueprint to build a set of identical houses. Are classes analogous to the blueprint or the...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
What is a ToolTip?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Fill in the blanks in each of the following statements: A relation that has no partial functional dependencies ...
Modern Database Management
List in chronological order the major events that take place when a process is interrupted.
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Sketch and describe how ships are supported in dry dock. When and where does the greatest amount of stresses occur?arrow_forwardSketch and desribe a balanced rudder and how it is suspendedarrow_forwardA ship 140 m long and 18 m beam floats at a draught of9 m. The immersed cross-sectionai areas at equai intervais are 5,60, 116, 145, 152, 153, 153, 151, 142, 85 and 0 m2 respectively.Calculate:(a) displacement(b) block coefficient(c) midship section area coefficient(d) prismatic coefficient.arrow_forward
- A steamer has waterplane area 1680m2 recorded in water with relative denisty 1.013. Displacement = 1200 t, calculate difference in draught in salwater reltive denisity 1.025.arrow_forwardrelative velocity 11.72 m/s is correct, need help finding the angle pleasearrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the two automobiles 2 s after A has passed through the intersection.arrow_forward
- A box barge 65 m long and 12 m wide floats at a draught of5.5 m in sea water. Calculate:(a) the displacement of the barge,(b) its draught in fresh waterarrow_forwardwhat is the angle of the velocity of block B? velocity is 7.46 in/s Determine the acceleration and angle of block B. (Round the acceleration value to three decimal places.)arrow_forwardDetermine the relative velocity of B with respect to A.arrow_forward
- Generate the kinematic diagram of the following mechanism. Then, draw their graphs and calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula.arrow_forwardAn elastic bar of length L = 1m and cross section A = 1cm2 spins with angular velocity ω about an axis, as shown in the figure below. The radial acceleration at a generic point x along the bar is a(x) = ω2x, where ω= 100rad/s is the angular velocity. The bar is pinned on the rotation axis at x = 0. A mass M = 1kg is attached to the right end of the bar. Due to the radial acceleration, the bar stretches along x with displacement function u(x). The displacement u(x) solves the BVP (strong form) sketched below: d dx (σ(x)) + ρa(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = E du dx Hooke’s law (1) u(0) =?? essential BC σ(L) =?? natural BC where σ(x) is the axial stress in the rod, ρ= 2700kg /m3 is the mass density, and E = 70GPa is the Young’s modulus 1. Define appropriate BCs for the strong BVP 2. Find the solution of the strong BVP analytically 3. Derive the weak form of the BVP.arrow_forwardGruebler's formula for the following mechanism?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Intro to Compressible Flows — Lesson 1; Author: Ansys Learning;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OgR6j8TzA5Y;License: Standard Youtube License