
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118921876
Author: Pritchard, Philip J.; Leylegian, John C.; Bhaskaran, Rajesh
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 19P
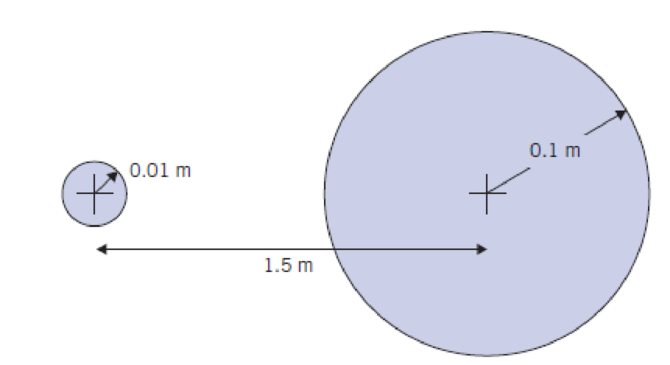
An object traveling in atmospheric air emits two pressure waves at different times. At an instant in time, the waves appear as in the figure. Determine the velocity and Mach number of the object and its current location.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Qu. 3 The automobile is originally at rest s = 0. If it then starts to increase its speed at
i = (0.05t2)ft/s?, where t is in seconds, determine the magnitudes of its velocity and acceleration at s
= 550 ft.
please show all work from dynamics step by step formula
question 5 and 6 from dynamics I need to show all work step by step problems
Study Area
Document Sharing
User Settings
Access Pearson
mylabmastering.pearson.com
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a
nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material.
The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle
penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1)
Part A
P Course Home
b My Questions | bartleby
Review
Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it
strikes the first barrel.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
1 of 1
36
μΑ
S =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
?
Next >
Chapter 12 Solutions
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 12 - Air is expanded in a steady flow process through a...Ch. 12 - Five kilograms of air is cooled in a closed tank...Ch. 12 - Air is contained in a piston-cylinder device. The...Ch. 12 - Calculate the power delivered by the turbine per...Ch. 12 - If hydrogen flows as a perfect gas without...Ch. 12 - A 1-m3 tank contains air at 0.1 MPa absolute and...Ch. 12 - Air enters a turbine in steady flow at 0.5 kg/s...Ch. 12 - Natural gas, with the thermodynamic properties of...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide flows at a speed of 10 m/s in a...Ch. 12 - In an isothermal process, 0.1 cubic feet of...
Ch. 12 - Calculate the speed of sound at 20C for (a)...Ch. 12 - An airplane flies at 550 km/hr at 1500 m altitude...Ch. 12 - Actual performance characteristics of the Lockheed...Ch. 12 - For a speed of sound in steel of 4300 m/s,...Ch. 12 - Determine and plot the Mach number of an...Ch. 12 - Investigate the effect of altitude on Mach number...Ch. 12 - The grandstand at the Kennedy Space Center is...Ch. 12 - Use data for specific volume to calculate and plot...Ch. 12 - An object traveling in atmospheric air emits two...Ch. 12 - An object traveling in atmospheric air emits two...Ch. 12 - While at the seashore, you observe an airplane...Ch. 12 - The temperature varies linearly from sea level to...Ch. 12 - Prob. 23PCh. 12 - A photograph of a bullet shows a Mach angle of 32....Ch. 12 - An F-4 aircraft makes a high-speed pass over an...Ch. 12 - All aircraft passes overhead at 3 km altitude. The...Ch. 12 - A supersonic aircraft flies at 3 km altitude at a...Ch. 12 - For the conditions of Problem 12.27, find the...Ch. 12 - The Concorde supersonic transport cruised at M =...Ch. 12 - Plot the percentage discrepancy between the...Ch. 12 - Compute the air density in the undisturbed air and...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide flows in a duct at a velocity of 90...Ch. 12 - If nitrogen at 15C is flowing and the stagnation...Ch. 12 - An aircraft cruises at M = 0.65 at 10 km altitude...Ch. 12 - High-speed aircraft use air data computers to...Ch. 12 - A supersonic wind tunnel test section is designed...Ch. 12 - Oxygen flows in a passage at a pressure of 25...Ch. 12 - What is the pressure on the nose of a bullet...Ch. 12 - Prob. 39PCh. 12 - Air flows in an insulated duct. At point the...Ch. 12 - Consider steady, adiabatic flow of air through a...Ch. 12 - Air passes through a normal shock in a supersonic...Ch. 12 - A Boeing 747 cruises at M = 0:87 at an altitude of...Ch. 12 - Space debris impact is a real concern for...Ch. 12 - A CO2 cartridge is used to propel a toy rocket....Ch. 12 - Nitrogen flows from a large tank, through a...Ch. 12 - Air flows from the atmosphere into an evacuated...Ch. 12 - Oxygen discharges from a tank through a convergent...Ch. 12 - The hot gas stream at the turbine inlet of a JT9-D...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide discharges from a tank through a...Ch. 12 - Air at 100F and 100 psia in a large tank flows...Ch. 12 - Calculate the required diameter of a convergent...Ch. 12 - Steam flows steadily and isentropically through a...Ch. 12 - Nitrogen flows through a diverging section of duct...Ch. 12 - At a section in a passage, the pressure is 30...Ch. 12 - In a given duct flow M = 2.0; the velocity...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Five pounds of air per second discharge from a...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a...Ch. 12 - Air, at an absolute pressure of 60.0 kPa and 27C,...Ch. 12 - Carbon dioxide flows from a tank through a...Ch. 12 - A convergent-divergent nozzle of 50-mm tip...Ch. 12 - Air flows adiabatically through a duct. At the...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Atmospheric air at 98.5 kPa and 20C is drawn into...Ch. 12 - The exit section of a convergent-divergent nozzle...Ch. 12 - Air flowing isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Air flows from a large tank at p = 650 kPa...Ch. 12 - A converging nozzle is connected to a large tank...Ch. 12 - Air at 0C is contained in a large tank on the...Ch. 12 - A large tank initially is evacuated to 10 kPa...Ch. 12 - Air flows isentropically through a converging...Ch. 12 - Air enters a converging-diverging nozzle at 2 MPa...Ch. 12 - Prob. 75PCh. 12 - A jet transport aircraft, with pressurized cabin,...Ch. 12 - A converging-diverging nozzle, with a throat area...Ch. 12 - Air, at a stagnation pressure of 7.20 MPa absolute...Ch. 12 - A small rocket motor, fueled with hydrogen and...Ch. 12 - Testing of a demolition explosion is to be...Ch. 12 - A total-pressure probe is placed in a supersonic...Ch. 12 - Air flows steadily through a long, insulated...Ch. 12 - Air discharges through a convergent-divergent...Ch. 12 - A normal shock wave exists in an airflow. The...Ch. 12 - Air approaches a normal shock at V1 = 900 m/s, p1...Ch. 12 - Air approaches a normal shock at M1 = 2.5, with...Ch. 12 - Air undergoes a normal shock. Upstream, T1 = 35C,...Ch. 12 - If, through a normal shock wave in air, the...Ch. 12 - The stagnation temperature in an airflow is 149C...Ch. 12 - A supersonic aircraft cruises at M = 2.2 at 12 km...Ch. 12 - The Concorde supersonic transport flew at M = 2.2...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Examine the following classes. The table lists the variables that are members of the Third class (some are inhe...
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
In Exercises 49 through 54, find the value of the given function. Math.Round(2.6)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Find the no-load value of υo in the circuit shown.
Find υo when RL is 150 Ω.
How much power is dissipated in th...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
ICA 8-20
A eutectic alloy of two metals contains the specific percentage of each metal that gives the lowest po...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Consider the following C program void fun (void) { int a, b, c; / defiinition.1 / . . . while (. . .) int b, c,...
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Describe the purpose of a database.
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Water is the working fluid in an ideal Rankine cycle. Saturated vapor enters the turbine at 12 MPa, and the condenser pressure is 8 kPa. The mass flow rate of steam entering the turbine is 50 kg/s. Determine: (a) the net power developed, in kW. (b) the rate of heat transfer to the steam passing through the boiler, in kW. (c) the percent thermal efficiency. (d) the mass flow rate of condenser cooling water, in kg/s, if the cooling water undergoes a temperature increase of 18°C with negligible pressure change in passing through the condenser.arrow_forward4. The figure below shows a bent pipe with the external loading FA 228 lb, and M₁ = M₂ = 1 kip-ft. The force Fernal loading FA = 300 lb, FB: parallel to the y-axis, and and yc = 60°. = 125 lb, Fc = acts parallel to the x-z plane, the force FB acts Cartesian resultan Coordinate direction angles of Fc are ac = 120°, ẞc = 45°, a. Compute the resultant force vector of the given external loading and express it in EST form. b. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the origin, O, and express it in Cartesian vector form. Use the vector method while computing the moments of forces. c. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the line OA and express it in Cartesian vector form. :00 PM EST k ghoufran@buffaternal du 2 ft M₁ A 40° FA M2 C 18 in 1 ft Fc 25 houfran@bald.edu - Feb 19, 3 ft FBarrow_forwardThe differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe? c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40)arrow_forward
- Auto Controls Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. με ? VB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ☐ о Α NB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. The crate is originally at rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is μk = 0.2. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of 8.1 m/s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 500 N 1 of 1 Α S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forward
- The differential equation of a DC motor can be described by the following equation Find the transfer function between the applied voltage ( Va)and the motor speed (thetadot m). What is the steady state speed of the motor after a voltage (Va = 10V) has been applied. Find the transfer function between the applied voltage (Va) and the shaft angle (thetadot m) .arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review The sports car has a mass of 2.5 Mg and accelerates at 6 m/s², starting from rest. (Figure 1) If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind is FD = (10v) N, where v is the velocity in m/s, determine the power supplied to the engine when t = 5 s. The engine has a running efficiency of € = 0.66. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 о Α ? P = Value Units Submit Request Answer Return to Assignment Provide Feedbackarrow_forward
- Access Pearson Study Area mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Document Sharing User Settings The car in (Figure 1) having a mass of 2 Mg is originally traveling at 2 m/s. Assume 0 = 22°. Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review Determine the distance it must be towed by a force F = 4 kN in order to attain a speed of 6 m/s. Neglect friction and the mass of the wheels. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Α ? S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forwardDerive the Laplace transform of the following functions. Use the definition of Laplace transform. f(t)=sin4t and f(t)=cos2t Auto Controlsarrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Marbles having a mass of 5 g fall from rest at A through the glass tube and accumulate in the can at C. (Figure 1) Figure Aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Intro to Compressible Flows — Lesson 1; Author: Ansys Learning;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OgR6j8TzA5Y;License: Standard Youtube License