
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Terminal
The addition of
In presence of peroxide,
Answer to Problem 12.65P
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown below.
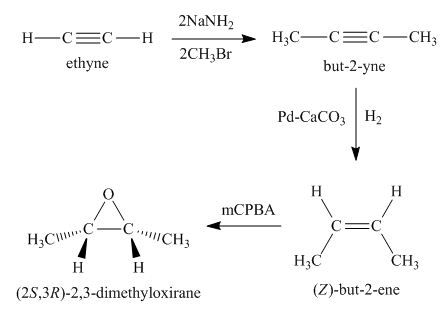
Explanation of Solution
Synthesis of the given compound is shown below.

Figure 1
In the first step, acetylene is converted to
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Terminal alkynes can be converted into internal alkynes by forming new
In presence of sodium metal in ammonia, the alkyne is reduced to
Answer to Problem 12.65P
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown below.
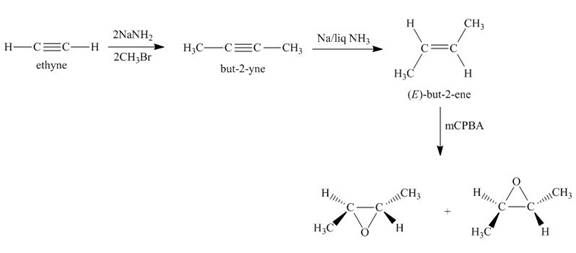
Explanation of Solution
Synthesis of the given compound is shown below.
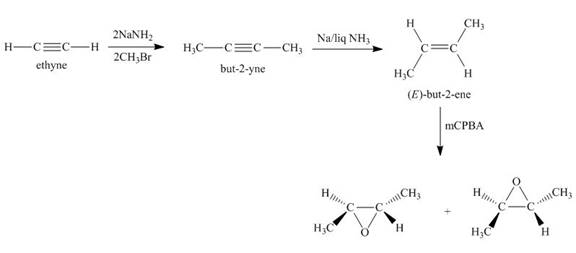
Figure 2
In the first step, acetylene is converted to
In the final step,
In the final step,
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Terminal alkynes can be converted into internal alkynes by forming new
The addition of
Addition of two hydroxyl groups on double bond to form
Answer to Problem 12.65P
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown below.
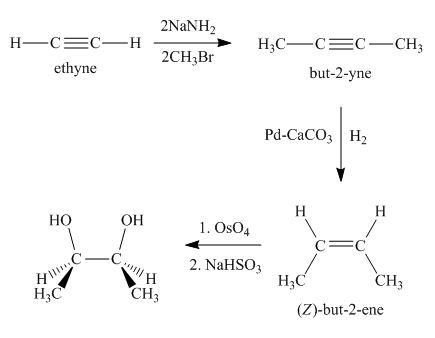
Explanation of Solution
Synthesis of the given compound is shown below.

Figure 3
In the first step, acetylene is converted to
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is to be devised.
Concept introduction: Terminal alkynes can be converted into internal alkynes by forming new
The addition of
In presence of peroxide, alkene is oxidized to epoxide. This is known as epoxidation. The weak pi bond of alkene and weak
Answer to Problem 12.65P
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown below.
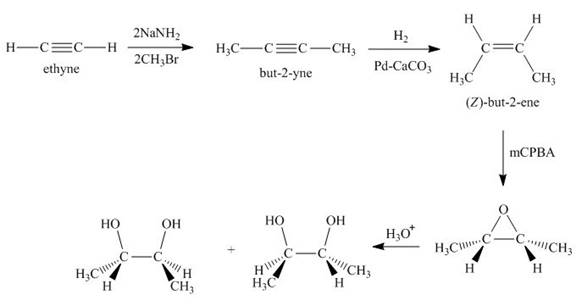
Explanation of Solution
Synthesis of the given compound is shown below.

Figure 4
In the first step, acetylene is converted to
Synthesis of the given compound from acetylene and other required reagents is shown in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





