
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:
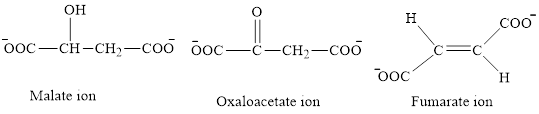
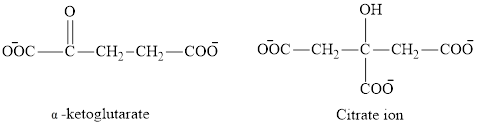
The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:
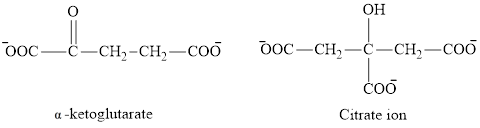
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of metabolic reaction that occur in the human body for completion of functions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions. Polyfunctional carboxylate ions are also the metabolic intermediate formed during metabolic pathways.
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent carboxylic acid.
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:
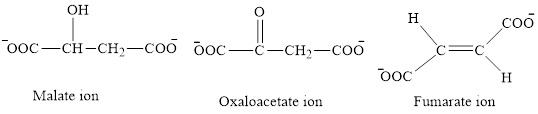
The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:
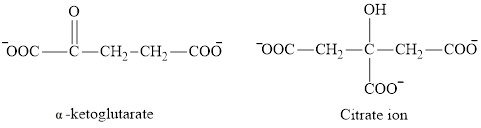
(c)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of metabolic reaction that occur in the human body for completion of functions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions. Polyfunctional carboxylate ions are also the metabolic intermediate formed during metabolic pathways.
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent carboxylic acid.
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:
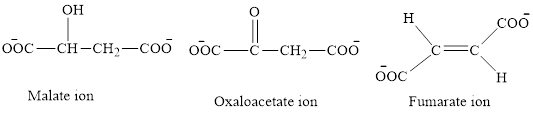
The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of metabolic reaction that occur in the human body for completion of functions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions. Polyfunctional carboxylate ions are also the metabolic intermediate formed during metabolic pathways.
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent carboxylic acid.
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:

The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- PROBLEMS Q1) Label the following salts as either acidic, basic, or neutral a) Fe(NOx) c) AlBr b) NH.CH COO d) HCOON (1/2 mark each) e) Fes f) NaBr Q2) What is the pH of a 0.0750 M solution of sulphuric acid?arrow_forward8. Draw all the resonance forms for each of the fling molecules or ions, and indicate the major contributor in each case, or if they are equivalent (45) (2) -PH2 سمة مدarrow_forwardA J то گای ه +0 Also calculate the amount of starting materials chlorobenzaldehyde and p-chloroacetophenone required to prepare 400 mg of the given chalcone product 1, 3-bis(4-chlorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one molar mass ok 1,3-bis(4-Chlorophenyl) prop-2-en-1-one = 277.1591m01 number of moles= 0.400/277.15 = 0.00144 moles 2 x 0.00 144=0.00288 moves arams of acetophenone = 0.00144 X 120.16 = 0.1739 0.1739x2=0.3469 grams of benzaldehyde = 0.00144X106.12=0.1539 0.1539x2 = 0.3069 Starting materials: 0.3469 Ox acetophenone, 0.3069 of benzaldehyde 3arrow_forward
- 1. Answer the questions about the following reaction: (a) Draw in the arrows that can be used make this reaction occur and draw in the product of substitution in this reaction. Be sure to include any relevant stereochemistry in the product structure. + SK F Br + (b) In which solvent would this reaction proceed the fastest (Circle one) Methanol Acetone (c) Imagine that you are working for a chemical company and it was your job to perform a similar reaction to the one above, with the exception of the S atom in this reaction being replaced by an O atom. During the reaction, you observe the formation of three separate molecules instead of the single molecule obtained above. What is the likeliest other products that are formed? Draw them in the box provided.arrow_forward3. For the reactions below, draw the arrows corresponding to the transformations and draw in the boxes the reactants or products as indicated. Note: Part A should have arrows drawn going from the reactants to the middle structure and the arrows on the middle structure that would yield the final structure. For part B, you will need to draw in the reactant before being able to draw the arrows corresponding to product formation. A. B. Rearrangement ΘΗarrow_forward2. Draw the arrows required to make the following reactions occur. Please ensure your arrows point from exactly where you want to exactly where you want. If it is unclear from where arrows start or where they end, only partial credit will be given. Note: You may need to draw in lone pairs before drawing the arrows. A. B. H-Br 人 C Θ CI H Cl Θ + Br Oarrow_forward
- 4. For the reactions below, draw the expected product. Be sure to indicate relevant stereochemistry or formal charges in the product structure. a) CI, H e b) H lux ligh Br 'Harrow_forwardArrange the solutions in order of increasing acidity. (Note that K (HF) = 6.8 x 10 and K (NH3) = 1.8 × 10-5) Rank solutions from least acidity to greatest acidity. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Least acidity NH&F NaBr NaOH NH,Br NaCIO Reset Greatest acidityarrow_forward1. Consider the following molecular-level diagrams of a titration. O-HA molecule -Aion °° о ° (a) о (b) (c) (d) a. Which diagram best illustrates the microscopic representation for the EQUIVALENCE POINT in a titration of a weak acid (HA) with sodium. hydroxide? (e)arrow_forward
- Answers to the remaining 6 questions will be hand-drawn on paper and submitted as a single file upload below: Review of this week's reaction: H₂NCN (cyanamide) + CH3NHCH2COOH (sarcosine) + NaCl, NH4OH, H₂O ---> H₂NC(=NH)N(CH3)CH2COOH (creatine) Q7. Draw by hand the reaction of creatine synthesis listed above using line structures without showing the Cs and some of the Hs, but include the lone pairs of electrons wherever they apply. (4 pts) Q8. Considering the Zwitterion form of an amino acid, draw the Zwitterion form of Creatine. (2 pts) Q9. Explain with drawing why the C-N bond shown in creatine structure below can or cannot rotate. (3 pts) NH2(C=NH)-N(CH)CH2COOH This bond Q10. Draw two tautomers of creatine using line structures. (Note: this question is valid because problem Q9 is valid). (4 pts) Q11. Mechanism. After seeing and understanding the mechanism of creatine synthesis, students should be ready to understand the first half of one of the Grignard reactions presented in a past…arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis pathway for the following transformations. b) c) d)arrow_forwardThe rate coefficient of the gas-phase reaction 2 NO2 + O3 → N2O5 + O2 is 2.0x104 mol–1 dm3 s–1 at 300 K. Indicate whether the order of the reaction is 0, 1, or 2.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





