
(a)
Interpretation:
The relationship between the given isomers needs to be established.
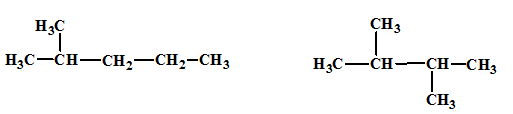
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are two or more compounds which have the same formula but different structures and properties. Constitutional isomers are structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of the constituent atoms.
(b)
Interpretation:
The relationship between the given isomers needs to be established.
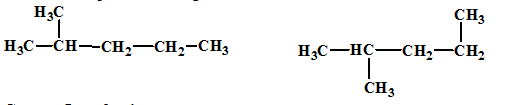
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are two or more compounds which have the same formula but different structures and properties. Constitutional isomers are structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of the constituent atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:
The relationship between the given isomers needs to be established.
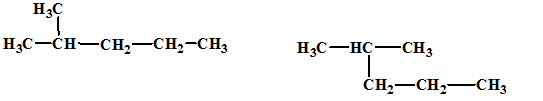
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are two or more compounds which have the same formula but different structures and properties. Constitutional isomers are structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of the constituent atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:
The relationship between the given isomers needs to be established.
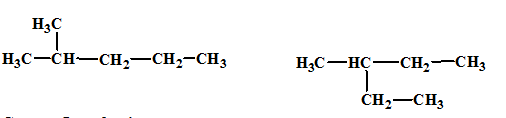
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are two or more compounds which have the same formula but different structures and properties. Constitutional isomers are structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of the constituent atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:
The relationship between the given isomers needs to be established.
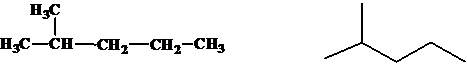
Concept Introduction:
Isomers are two or more compounds which have the same formula but different structures and properties. Constitutional isomers are structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of the constituent atoms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





