
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the
Concept introduction:
The addition reactions are defined as the formation of one product by the combination of two or more products. For example, in halogenation, the addition of a halogen molecule results in the reduction of carbon-carbon double bond to carbon-carbon single bond and formation of
Answer to Problem 12.27E
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is shown below.
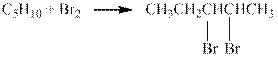
Figure 1
The product
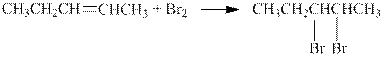
Figure 2
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
Concept introduction:
The addition reactions are defined as the formation of one product by the combination of two or more products. For example, in halogenation, the addition of a halogen molecule results in the reduction of carbon-carbon double bond to carbon-carbon single bond and formation of haloalkane.
Answer to Problem 12.27E
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is shown below.
The product in the given reaction is pentane which can be prepared by the hydrogenation on the
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
Concept introduction:
The Markovnikov’s rule states that the addition of the
Answer to Problem 12.27E
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
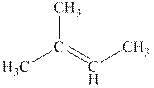
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is shown below.
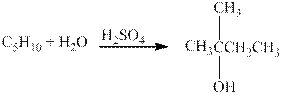
Figure 2
The product in the reaction is
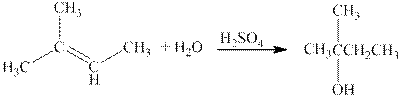
Figure 3
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
Concept introduction:
The Markovnikov’s rule states that the addition of the
Answer to Problem 12.27E
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.

Figure 4
The product in the given reaction is
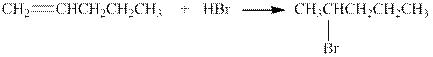
Figure 5
The structural formula for the alkene with molecular formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- What the best source of sulfide to use on a small scale in the lab? Group of answer choices thiourea H2S NaHS Na2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about sulfur is FALSE? Group of answer choices H2S is the product of an oxygen-depleted ecosystem. In the acid mine drainage reaction, FeS2 is a product. One allotrope of sulfur has the formula S20. In the environment, bacterial oxidation can convert S2− to elemental S or SO42−.arrow_forwardOf the following choices, which is the best reason that most materials DON'T spontaneously combust even though our atmosphere is about 21% oxygen? Group of answer choices The reduction of O2 in the gas phase (O2 + e− → O2−) is spontaneous. The reduction of O2 in acid solution (O2 + H+ + e− → HO2(aq)) is spontaneous. O2 is not a reactant in combustion. The O2 bond dissociation energy is 494 kJ/mol, leading to a high activation energy for combustion.arrow_forward
- please answer in the scope of the SCH4U course, I am having a hard time understanding, may you show all steps please and thank you! can you also put the final answers in the table so its understandablearrow_forwardPlan the synthesis of the following compound using the starting material provided and any other reagents needed as long as carbon based reagents have 3 carbons or less. Either the retrosynthesis or the forward synthesis (mechanisms are not required but will be graded if provided) will be accepted if all necessary reagents and intermediates are shown (solvents and temperature requirements are not needed unless specifically involved in the reaction, i.e. DMSO in the Swem oxidation or heat in the KMnO4 oxidation). There may be more than one correct answer, and chemically correct steps will be accepted. Extra points will be given if correct names are provided. The points earned here will be applied to your lowest exam score! H Harrow_forwardDraw the mechanism to make the alcohol 1-hexanol. Please use arrows.arrow_forward
- Answer the followings: 1-What is the difference(s) between DNA and RNA: a- Structure: b- Function: c- Types: 2-What is the meaning of: a- Replication b- Transcription c- Translation 3- Show the base pair connection (hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forwardWhy does the anhydride react with the OH on the benzene rather than the OH on the carboxy group?arrow_forwardAnswer the followings: 1- What is the IP for a amino acid? Give example. 2- What are the types of amino acids? 3- What are the structures of protein? 4- The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N- terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin? 5. MATCH a term from the list below to each definition. Place the letter of the term in the blank to the left of the definition. a. Ligases b. Fibrous proteins c. Conjugated protein d. Hydrolases a. b. C. e. Simple protein f. Globular proteins g. Lyases h. Transferases Proteins that are tough and insoluble in water. Enzymes that catalyze the breaking away of a small molecule such as from a substrate. Enzymes that catalyze the bonding together of two substrates.arrow_forward
- Answer the followings (Four): 1-What is the difference(s) between FOUR: a. Glyceride and phosphoglyceride. b. Wax and fat. c. Soap and fatty acid. d. HDL and LDL cholesterol e. Phospho lipids and sphingosine. 2-What are the types of lipids? 3-What are the main lipid components of membrane structures? 4-How could lipids play important rules as signaling molecules and building units? 5. The Structure variety of Lipids makes them to play significant rules in our body. Conclude briefly on this statement.arrow_forwardHO IV но. = HO но. HO. HO но. зад надо What is the product of the following reaction?arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism to make the alcohol 2-hexanol.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





