
Concept explainers
a.
Find a model of the form
a.
Answer to Problem 105RE
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
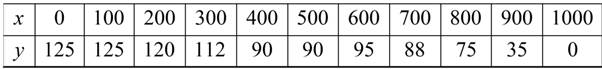
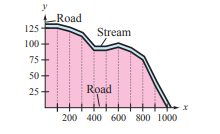
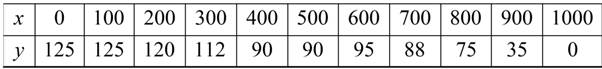
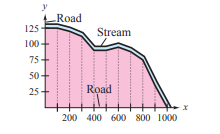
The table shows the measurements (in feet) of a lot bounded by a stream and two straight roads that meet at right angles (see figure)
Use the regression feature of a graphing utility to find a model of the form
Calculation:
Consider the given table.
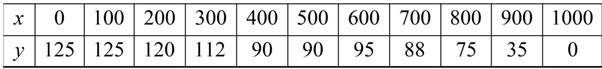
To find the regression model use graphing utility
Press start button and observe the screen,
Now select EDIT and show display,
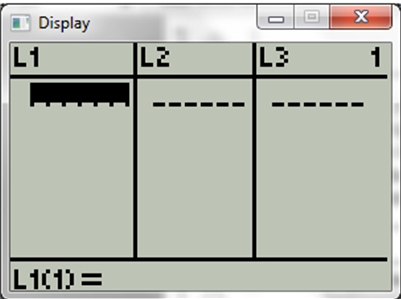
Now feed the data given in table.
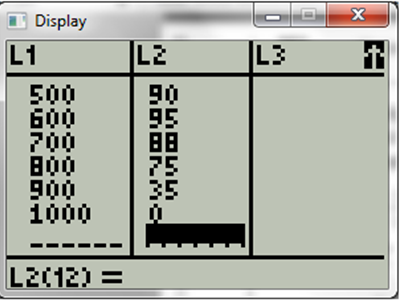
Now press start and calc,
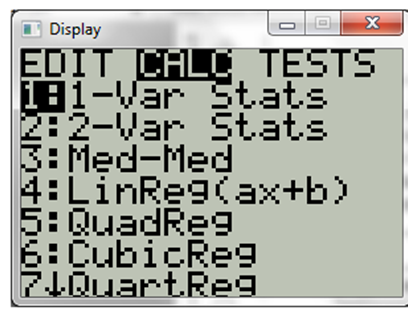
Now choose cubic regression,
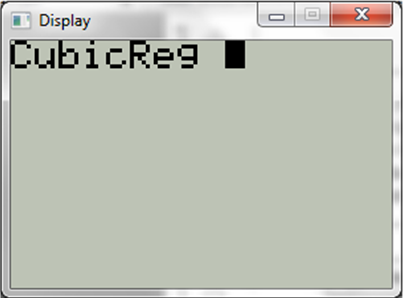
Now press ENTER and display will be,
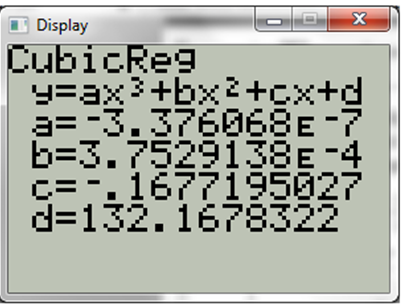
Hence the cubic regression model of the above data,
b.
Use the graphing utility to plot the data.
b.
Answer to Problem 105RE
The graphic model is verified.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The table shows the measurements (in feet) of a lot bounded by a stream and two straight roads that meet at right angles (see figure)
Use the graphing utility to plot the data and graph the model in the same viewing window
Calculation:
Consider the given table.
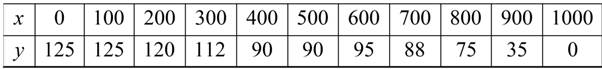
To find the regression model use graphing utility
Press 2nd and Y= and observe the display,
Now press ENTER and show display,
Now press WINDOW to choose proper scale.
Now press GRAPH and display will be,
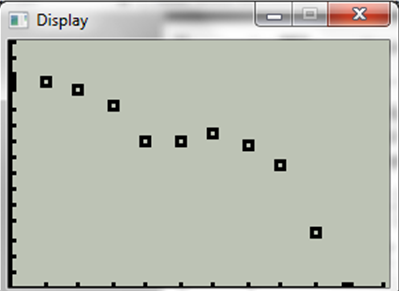
Now plot the regression equation,
Press Y= and choose plot
Now feed the equation,
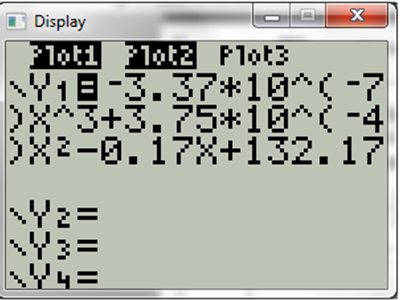
Now press GRAPH and display will be,
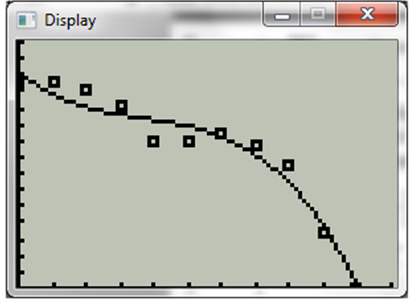
Hence the graphic model is verified.
c.
Find the area of the lot.
c.
Answer to Problem 105RE
Area under the curve is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The table shows the measurements (in feet) of a lot bounded by a stream and two straight roads that meet at right angles (see figure)
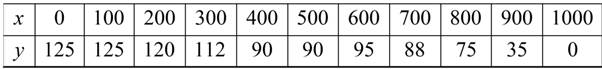
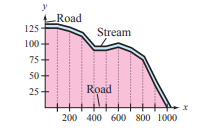
Use the graphing utility to plot the data and graph the model in the same viewing window
Calculation:
Consider the given table.
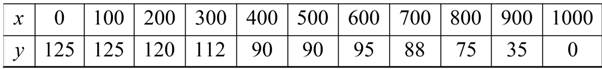
To evaluate the area under the curve,
Define dimension of rectangle,
Therefore,
Now approximation of area is sum of areas of all rectangles.
Now apply properties of submission,
Now calculate the area by taking
Hence area under the curve is
Chapter 12 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits
- Use the following graphs to evaluate the given one-sided limit. Answer exactly. y = f (x): y = g(x): 8 6 ν -8-6-4-2 2- 1-2-2 -4 -6 -8 ° 4 lim (f(x)+g(x)) = x+2+ 8 6 2 ν 0 x x 6 8 -8 -6-4-2 2 6 8 -2 -4 -6 -8arrow_forwardQuestion 1 The points A = (-2, 3, 2) and B = (4, 1, 4) are reflections of one another in a plane S. Find an equation for S.arrow_forwardThe graph below is the function f (x) -D -3-2 4 3 2 Q2 03 Find lim f(x) = x-1- Find lim f(x) = x−1+ Find lim f(x) = x-1 Find f (-1) = 3 4 5arrow_forward
- i circled the correct answer and i did most of the question but i cant figure out how to add both residues to get the correct answer could you please show me how to do itarrow_forwardQuestion 3 Starting at the point (0, −2,0), I walk up the hill z = 4-x² — y². The projection of my path on the xy plane is the line y = 2x-2. (a) At what point on my path is my altitude (the z-value) the greatest? (b) What is the slope m of my path (taking the z-axis to be vertical) when I am at the point (1, 0, 3)? [Hint: Parametrize my path (take x to be t).]arrow_forwardI circled the correct, could you explain using stokearrow_forward
- Use Euler's method to numerically integrate dy dx -2x+12x² - 20x +8.5 from x=0 to x=4 with a step size of 0.5. The initial condition at x=0 is y=1. Recall that the exact solution is given by y = -0.5x+4x³- 10x² + 8.5x+1arrow_forwardFind an equation of the line tangent to the graph of f(x) = (5x-9)(x+4) at (2,6).arrow_forwardFind the point on the graph of the given function at which the slope of the tangent line is the given slope. 2 f(x)=8x²+4x-7; slope of the tangent line = -3arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





