
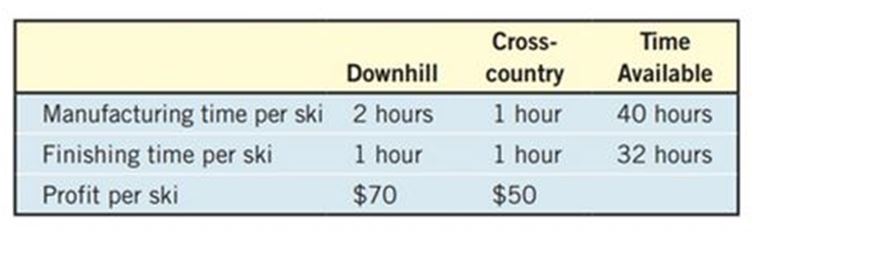
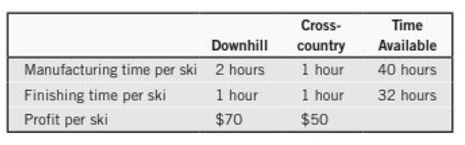
Maximizing Profit A manufacturer of skis produces two types: downhill and cross-country. Use the following table to determine how many of each kind of ski should be produced to achieve a maximum profit. What is the maximum profit? What would the maximum profit be if the time available for manufacturing were increased to 48 hours?
To solve: The given linear programming problem.
Answer to Problem 19AYU
Solution:
1. The maximum profit is 1760, when producing 8 downhill and 24 cross country skis.
2. The maximum profit is 1920, when producing 16 downhill and 16 cross country skis.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Step 1:
Begin by assigning symbols for the two variables.
Number of downhill skis produced.
Number of cross country skis produced.
If is the profit, then
Step 2:
The goal is to maximize subject to certain constraints on and . Because and represents number of skis produced, the only meaningful values of and are non-negative.
Therefore, .
Time available for manufacturing and finishing also given. From that, we get
Therefore, the linear programming problem may be stated as
Subject to
Step 3:
The graph of the constraints is illustrated in the figure below.
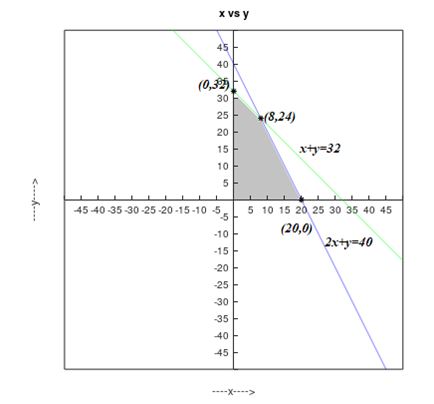
The below table lists the corner points and the corresponding values of objective function.
| Corner points are | Value of objective function |
| 1400 | |
| 1600 | |
| 1760 |
From the table,
1. The maximum profit is 1760, when producing 8 downhill and 24 cross country skis.
2. If time available for manufacturing were increased to 48 hrs, the linear programming problem becomes,
Maximize
Subject to
The graph of the constraints is illustrated in the figure below.
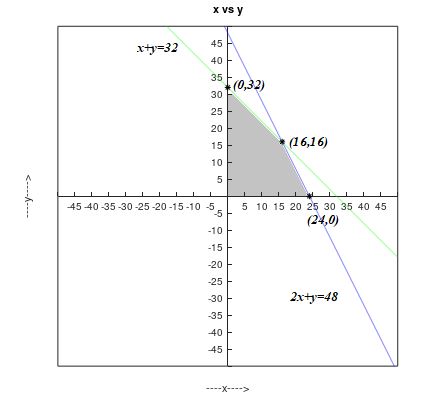
The below table lists the corner points and the corresponding values of objective function.
| Corner points are | Value of objective function |
| 1680 | |
| 1600 | |
| 1920 |
The maximum profit is 1920, when producing 16 downhill and 16 cross country skis.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- please do Q3arrow_forwardUse the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forward
- Find the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forwarda -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forwardUse Green's Theorem to evaluate F. dr, where F = (√+4y, 2x + √√) and C consists of the arc of the curve y = 4x - x² from (0,0) to (4,0) and the line segment from (4,0) to (0,0).arrow_forward
- Evaluate F. dr where F(x, y, z) = (2yz cos(xyz), 2xzcos(xyz), 2xy cos(xyz)) and C is the line π 1 1 segment starting at the point (8, ' and ending at the point (3, 2 3'6arrow_forwardCan you help me find the result of an integral + a 炉[メをメ +炉なarrow_forward2 a Can you help me find the result of an integral a 아 x² dxarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





