
Concept explainers
Match the vapor pressure diagrams with the solute-solvent combinations and explain your answers.
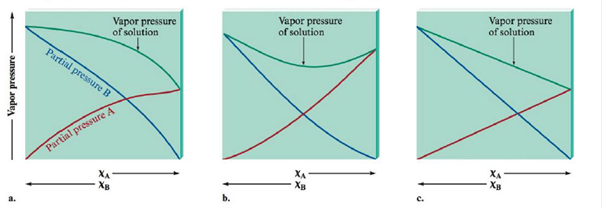
a. 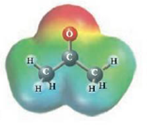 and
and 
b. 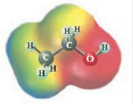 and
and 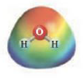
c. 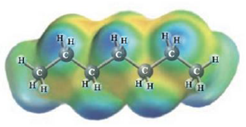 and
and 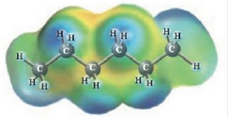
d. 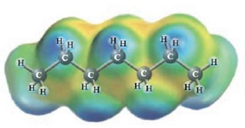 and
and 
(a)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
A Negative deviations from Raoult’s law is the right option for Acetone-Water solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the second diagram match with Acetone and Water
The second diagram illustrates negative variation from Raoult's law. This occurs whilst the solute-solvent connections are stronger than the connections in pure solvent and pure solute.
These two molecules are named Acetone (
(b)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
A Positive deviation from Raoult’s law is the right option for Ethanol-Water solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the first diagram match with
The first diagram shows positive deviation from Raoult's law. This occurs when the solute-solvent connections are weaker than the connections in pure solvent and pure solute.
These two molecules are named Ethanol (
(c)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
No deviation from Raoult’s law is the correct choice for Heptane-Hexane. solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the polarity of Heptane and Hexane
Heptane and Hexane
The third diagram illustrates an perfect solution with no difference from Raoult's law. This occurs what time the solute-solvent interactions are concerning equal to the pure solvent and pure solute interactions.
These two molecules are named Heptane (
(d)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
Heptane and Water results in positive deviations from Raoult’s law (the first diagram).
Explanation of Solution
To find: The Heptane Vs Water.
These two molecules are named Heptane (
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Physical Universe
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. dm Re Explanation Check ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Termarrow_forwardb) Use curved arrows to show the reaction of the radical with hydrogen bromide. Br: Br H .. Answer Bankarrow_forwardIndicate the reaction products when CH3COCH2COOCH2COOC2H5 (ethyl acetoacetoacetate) reacts with 1º OH-/H2O and 2º H3O+arrow_forward
- Indicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forwardPrimary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





