
Figure 11.22 shows a demonstration gyroscope, consisting of a solid disk mounted on a shaft. The disk spins about the shaft on essentially frictionless bearings. The shaft is mounted on a stand so it’s free to pivot both horizontally and vertically. A weight at the far end of the shaft balances the disk, so in the configuration shown there’s no torque on the system. An arrowhead mounted on the disk end of the shaft indicates the direction of the disk’s
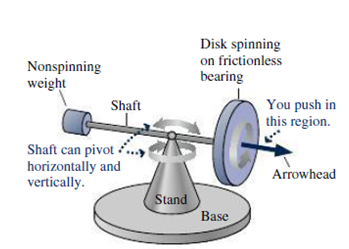 FIGURE 11.22 A gyroscope (Passage Problems 65–68)
FIGURE 11.22 A gyroscope (Passage Problems 65–68)
If you push on the shaft between the arrowhead and the disk, pushing directly upward on the bottom of the shaft, the arrow-head end of the shaft will move
- a. away from you (i.e., into the page).
- b. toward you (i.e., out of the page).
- c. downward.
- d. upward.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essential University Physics Volume 1, Loose Leaf Edition (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- One has to push down a ball with a force of 470 Newtons in order to hold the ball still, completely submerged under the surface of the water. What is the volume of the styrofoam ball in cubic meters? Use 997 kg/m3 as the density of water, 95 kg/m3 for the density of the styrofoam, and g = 9.8 m/s2.arrow_forwardThe cube is placed in a bucket of water and find that it floats, with 33% of its volume submerged below the surface of the water. What is the density of the mystery material? The material is uniformly distributed throughout the solid cube, with the number of kg/m3.arrow_forward2.82 A ball is thrown straight up from the ground with speed Up. At the same instant, a second ball is dropped from rest from a height H, directly above the point where the first ball was thrown upward. There is no air resistance. (a) Find the time at which the two balls collide. (b) Find the value of H in terms of un, and g such that at the instant when the balls collide, the first ball is at the highest point of its motion.arrow_forward
- The small piston has an area A1=0.033 m2 and the large piston has an area A2= 4.0 m2. What force F2 will the large piston provide if the small piston is pushed down with a force of 15 Newtons with an answer in Newtons?arrow_forward2.23 BIO Automobile Airbags. The human body can survive an acceleration trauma incident (sudden stop) if the magnitude of the ac- celeration is less than 250 m/s². If you are in an automobile accident with an initial speed of 105 km/h (65 mi/h) and are stopped by an air- bag that inflates from the dashboard, over what minimum distance must the airbag stop you for you to survive the crash?arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer these problems correctly.Thank you!!arrow_forward
- 2.2. In an experiment, a shearwater (a seabird) was taken from its nest, flown 5150 km away, and released. The bird found its way back to its nest 13.5 days after release. If we place the origin at the nest and extend the +x-axis to the release point, what was the bird's average ve- locity in m/s (a) for the return flight and (b) for the whole episode, from leaving the nest to returning?arrow_forwardUse relevant diagrams where necessary and go through it in detailsarrow_forwardYour blood pressure (usually given in units of "mm of Hg") is a result of the heart muscle pushing on your blood. The left side of the heart creates a pressure of 115 mm Hg by exerting a force directly on the blood over an effective area of 14.5 cm2. What force does it exert to accomplish this? (Give your answer as the number of Newtons and note that you will need to do some unit conversions.)arrow_forward
- What is the absolute (total) pressure experienced by a diver at a depth of 17 meters below the surface of a lake? Assume that atmospheric pressure at the surface of the lake is 101,000 Pascals, g= 9.8 m/s2, and the density of the water in the lake is 997 kg/m3. Give your answer as the number of Pascals.arrow_forwardA particular solid cube has an edge of length 0.59 meters and is made of a material whose density is 3500 kg/m3. What is the mass of the cube? Give your answer as the number of kilograms.arrow_forwardSolve and answer correctly please.Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





