
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 65P
SSM WWW Two 2.00 kg balls are attached to the ends of a thin rod of length 50.0 cm and negligible mass. The rod is free to rotate in a vertical plane without friction about a horizontal axis through its center. With the rod initially horizontal (Fig. 11-57), a 50.0 g wad of wet putty drops onto one of the balls, hitting it with a speed of 3.00 m/s and then sticking to it. (a) What is the angular speed of the system just after the putty wad hits? (b) What is the ratio of the kinetic energy of the system after the collision to that of the putty wad just before? (c) Through what angle will the system rotate before it momentarily stops?
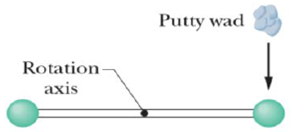
Figure 11-57 Problem 65.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls
The position of a coffee cup on a table as referenced by the corner of the room in which it sits is r=0.5mi +1.5mj +2.0mk . How far is the cup from the corner? What is the unit vector pointing from the corner to the cup?
No chatgpt pls
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 11 - Figure 11-23 shows three particles of the same...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-24 shows two particles A and B at xyz...Ch. 11 - What happens to the initially stationary yo-yo in...Ch. 11 - The position vector r of a particle relative to a...Ch. 11 - In Fig. 11-26, three forces of the same magnitude...Ch. 11 - The angular momenta t of a particle in four...Ch. 11 - A rhinoceros beetle rides the rim of a horizontal...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-27 shows an overhead view of a...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-38 gives the angular momentum magnitude...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-29 shows a particle moving at constant...
Ch. 11 - A cannonball and a marble roll smoothly from rest...Ch. 11 - Prob. 12QCh. 11 - A car travels at 80 km/h on a level road in the...Ch. 11 - An automobile traveling at 80.0 km/h has tires of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 3PCh. 11 - A uniform solid sphere rolls down an incline. a...Ch. 11 - ILW A 1000 kg car has four 10 kg wheels. When the...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-30 gives the speed v versus time t for a...Ch. 11 - ILW In Fig. 11-31, a solid cylinder of radius 10cm...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-32 shows the potential energy Ux of a...Ch. 11 - GO In Fig. 11-33, a solid ball rolls smoothly from...Ch. 11 - A hollow sphere of radius 0.15 m, with rotational...Ch. 11 - In Fig. 11-34, a constant horizontal force Fapp of...Ch. 11 - GO In Fig. 11-35, a solid brass ball of mass 0.280...Ch. 11 - GO Nonuniform ball. In Fig. 11-36, a ball of mass...Ch. 11 - In Fig. 11-37, a small, solid, uniform ball is to...Ch. 11 - GO A bowler throws a bowling ball of radius R = 11...Ch. 11 - GO Nonuniform cylindrical object. In Fig. 11-39, a...Ch. 11 - SSM A yo-yo has a rotational inertia of 950 gcm2...Ch. 11 - Prob. 18PCh. 11 - In unit-vector notation, what is the net torque...Ch. 11 - A plum is located at coordinates 2.0 m, 0, 4.0 m....Ch. 11 - In unit-vector notation, what is the torque about...Ch. 11 - A particle moves through an xyz coordinate system...Ch. 11 - Force F=(2.0N)i(3.0N)k acts on a pebble with...Ch. 11 - In unit-vector notation, what is the torque about...Ch. 11 - SSM Force F=(8.0N)i+(6.0N)j acts on a particle...Ch. 11 - At the instant of Fig. 11-40, a 2.0 kg particle P...Ch. 11 - SSM At one instant, force F=4.0N acts on a 0.25 kg...Ch. 11 - A 2.0 kg particle-like object moves in a plant...Ch. 11 - ILW In the instant of Fig, 11-41, two particles...Ch. 11 - At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg...Ch. 11 - In Fig. 11-42, a 0.400 kg ball is shot directly...Ch. 11 - A particle is acted on by two torques about the...Ch. 11 - SSM WWW ILW At time t = 0, a 3.0 kg particle with...Ch. 11 - A particle is to move in an xy plane, clockwise...Ch. 11 - At time t, the vector r=4.0t2i(2.0t+6.0t2)j gives...Ch. 11 - Prob. 36PCh. 11 - GO In Fig. 11-44, three particles of mass m = 23 g...Ch. 11 - A sanding disk with rotational inertia 1.2 103...Ch. 11 - SSM The angular momentum of a flywheel having a...Ch. 11 - A disk with a rotational inertia of 7.00 kgm2...Ch. 11 - GO Figure 11-45 shows a rigid structure consisting...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-46 gives the torque that acts on an...Ch. 11 - Prob. 43PCh. 11 - A Texas cockroach of mass 0.17 kg runs...Ch. 11 - SSM WWW A man stands on a platform that is...Ch. 11 - The rotational inertia of a collapsing spinning...Ch. 11 - SSM A track is mounted on a large wheel that is...Ch. 11 - A Texas cockroach walks from the center of a...Ch. 11 - Two disks are mounted like a merry-go-round on...Ch. 11 - The rotor of an electric motor has rotational...Ch. 11 - SSM ILW A wheel is rotating freely at angular...Ch. 11 - GO A cockroach of mass m lies on the rim of a...Ch. 11 - GO In Fig. 11-50 an overhead view, a uniform thin...Ch. 11 - GO Figure 11-51 shows an overhead view of a ring...Ch. 11 - A horizontal vinyl record of mass 0.10 kg and...Ch. 11 - In a long jump, an athlete leaves the ground with...Ch. 11 - A uniform disk of mass 10m and radius 3.0r can...Ch. 11 - A horizontal platform in the shape of a circular...Ch. 11 - Figure 11-52 is an overhead view of a thin uniform...Ch. 11 - In Fig. 11-53, a 1.0 g bullet is tired into a 0.50...Ch. 11 - The uniform rod length 0.60 m, mass 1.0 kg in Fig....Ch. 11 - GO During a jump to his partner, an aerialist is...Ch. 11 - GO In Fig. 11-56, a 30 kg child stands on the edge...Ch. 11 - A ballerina begins a tour jet Fig. 11-19a with...Ch. 11 - SSM WWW Two 2.00 kg balls are attached to the ends...Ch. 11 - Prob. 66PCh. 11 - Prob. 67PCh. 11 - Prob. 68PCh. 11 - A certain gyroscope consists of a uniform disk...Ch. 11 - A uniform solid ball rolls smoothly along a floor,...Ch. 11 - SSM In Fig. 11-60, a constant horizontal force...Ch. 11 - A thin-walled pipe rolls along the floor. What is...Ch. 11 - Prob. 73PCh. 11 - Prob. 74PCh. 11 - Prob. 75PCh. 11 - A uniform block of granite in the shape of a book...Ch. 11 - SSM Two particles, each of mass 2.90 104 kg and...Ch. 11 - A wheel of radius 0.250 m, moving initially al...Ch. 11 - Wheels A and B in Fig. 11-61 are connected by a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 80PCh. 11 - SSM A uniform wheel of mass 10.0 kg and radius...Ch. 11 - A uniform rod rotates in a horizontal plane about...Ch. 11 - A solid sphere of weight 36.0 N rolls up an...Ch. 11 - Suppose that the yo-yo in Problem 17, instead of...Ch. 11 - A girl of mass M stands on the rim of a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 86P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. HF 5.0 µF 3.5 µF №8.0 μLE 1.5 µF Ι 0.75 μF 15 μFarrow_forwardthe answer is not 0.39 or 0.386arrow_forwardFind the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. 2.01 0.30 µF 2.5 µF 10 μF × HFarrow_forward
- I do not understand the process to answer the second part of question b. Please help me understand how to get there!arrow_forwardRank the six combinations of electric charges on the basis of the electric force acting on 91. Define forces pointing to the right as positive and forces pointing to the left as negative. Rank in increasing order by placing the most negative on the left and the most positive on the right. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) [most negative 91 = +1nC 92 = +1nC 91 = -1nC 93 = +1nC 92- +1nC 93 = +1nC -1nC 92- -1nC 93- -1nC 91= +1nC 92 = +1nC 93=-1nC 91 +1nC 92=-1nC 93=-1nC 91 = +1nC 2 = −1nC 93 = +1nC The correct ranking cannot be determined. Reset Help most positivearrow_forwardPart A Find the x-component of the electric field at the origin, point O. Express your answer in newtons per coulomb to three significant figures, keeping in mind that an x component that points to the right is positive. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Eoz = Η ΑΣΦ ? N/C Submit Part B Now, assume that charge q2 is negative; q2 = -6 nC, as shown in (Figure 2). What is the x-component of the net electric field at the origin, point O? Express your answer in newtons per coulomb to three significant figures, keeping in mind that an x component that points to the right is positive. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Eoz= Η ΑΣΦ ? N/Carrow_forward
- 1. A charge of -25 μC is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical volume of radius 11.5 cm. Determine the electric field due to this charge at a distance of (a) 2 cm, (b) 4.6 cm, and (c) 25 cm from the center of the sphere. (a) = = (b) E = (c)Ẻ = = NC NC NCarrow_forward1. A long silver rod of radius 3.5 cm has a charge of -3.9 ис on its surface. Here ŕ is a unit vector ст directed perpendicularly away from the axis of the rod as shown in the figure. (a) Find the electric field at a point 5 cm from the center of the rod (an outside point). E = N C (b) Find the electric field at a point 1.8 cm from the center of the rod (an inside point) E=0 Think & Prepare N C 1. Is there a symmetry in the charge distribution? What kind of symmetry? 2. The problem gives the charge per unit length 1. How do you figure out the surface charge density σ from a?arrow_forward1. Determine the electric flux through each surface whose cross-section is shown below. 55 S₂ -29 S5 SA S3 + 9 Enter your answer in terms of q and ε Φ (a) s₁ (b) s₂ = -29 (C) Φ զ Ερ (d) SA = (e) $5 (f) Sa $6 = II ✓ -29 S6 +39arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardthe cable may break and cause severe injury. cable is more likely to break as compared to the [1] ds, inclined at angles of 30° and 50° to the vertical rings by way of a scaled diagram. [4] I 30° T₁ 3cm 3.8T2 cm 200 N 50° at it is headed due North and its airspeed indicat 240 km/h. If there is a wind of 100 km/h from We e relative to the Earth? [3]arrow_forwardCan you explain this using nodal analysis With the nodes I have present And then show me how many KCL equations I need to write, I’m thinking 2 since we have 2 dependent sourcesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Moment of Inertia; Author: Physics with Professor Matt Anderson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZrGhUTeIlWs;License: Standard Youtube License