
Concept explainers
a.
To calculate the minimum wages.
a.
Answer to Problem 45E
Decade
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Use the graph below, which shows the minimum wages in the United States (in dollars) from
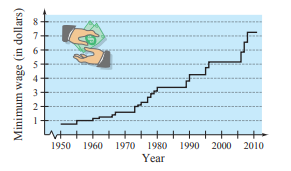
Which decade shows the greatest increase in minimum wage?
Calculation:
The graph shows the minimum wages in the United States (in dollars) from
The greatest increase in minimum wages
The graph show wages in
The graph show wages in
Therefore the increase in minimum wages is,
Hence the decade
b.
To calculate the minimum wages.
b.
Answer to Problem 45E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Use the graph below, which shows the minimum wages in the United States (in dollars) from
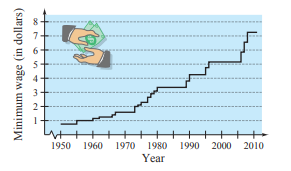
Approximate the percent increases in the minimum wage from 1990 to 1995 and from 1995 to 2011.
Calculation:
The graph shows the minimum wages in
So, % age increase in wages is.
Hence % age increase from
Similarly the minimum wages in
So, % age increase in wages is.
Hence % age increase from
c.
To calculate the minimum wages.
c.
Answer to Problem 45E
The predict wages in
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Use the graph below, which shows the minimum wages in the United States (in dollars) from
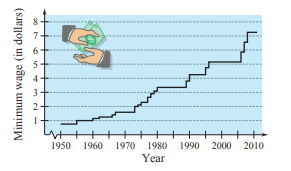
Use the percent increase from 1995 to 2011 to predict the minimum wage in 2016.
Calculation:
From part (b) the %age increase from
So,
Hence predict wages in
d.
To calculate the minimum wages.
d.
Answer to Problem 45E
Prediction is not reasonable
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Use the graph below, which shows the minimum wages in the United States (in dollars) from
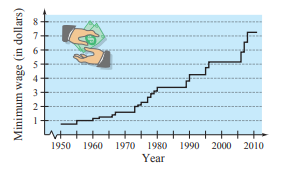
Do you believe that your prediction in part (c) is reasonable? Explain
Calculation:
No the prediction in part C) is not reasonable.
It is too high because %age increase over a seven year period (
Hence prediction is not reasonable.
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- Explain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forwardUse 12.4.2 to determine whether the infinite series on the right side of equation 12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7 converges for every real number x.arrow_forwarduse Cauchy Mean-Value Theorem to derive Corollary 12.6.2, and then derive 12.6.3arrow_forward
- Explain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.1(lim(n->infinite) and sigma of k=0 to n)arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.3 about alternating series. and explain the reason why (sigma k=1 to infinite)(-1)k+1/k = 1/1 - 1/2 + 1/3 - 1/4 + .... converges.arrow_forwardExplain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





